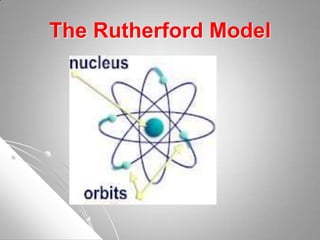
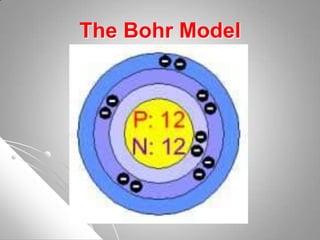
The document traces the development of atomic theory from ancient Greek philosophers to modern scientists. It describes the early atomic models of Democritus, Aristotle, Dalton, Thomson, and Rutherford, and how each built upon the work of previous scientists. Later models such as those proposed by Bohr, Schrodinger, and Heisenberg incorporated the ideas of discrete energy levels and electron clouds rather than fixed orbits, bringing atomic theory closer to its current form.