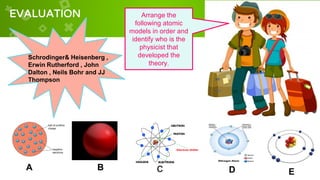
The document describes the development of atomic theory over time through several scientific models. It begins with Democritus' idea in the 5th century BC that all matter is made of indivisible atoms. The document then outlines models by John Dalton, J.J. Thompson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, Erwin Schrodinger and Werner Heisenberg. Each model built on previous work and provided new insights about atoms, such as Dalton's billiard ball model, Thompson's plum pudding model, Rutherford's nuclear model, Bohr's planetary model, and Schrodinger and Heisenberg's quantum mechanical model describing electrons as waves. The document uses these historic theories to teach students