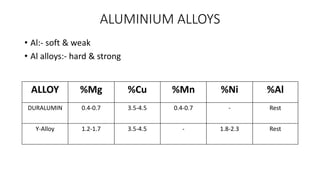
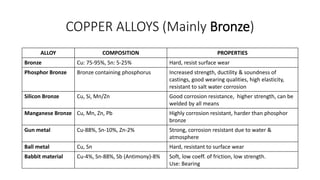
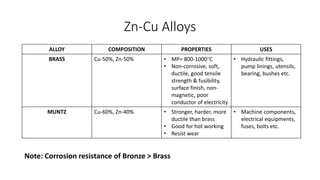
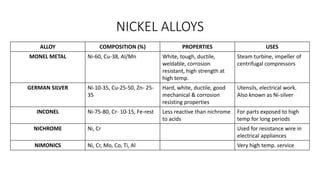
This document discusses non-ferrous metals and alloys, including their properties and uses. It covers aluminum, lead, tin, copper, zinc, and nickel. Key alloys discussed include aluminum alloys like duralumin and y-alloy, tin-based bearing metals, copper alloys like bronze, brass, and babbitt metal, and nickel alloys such as monel metal, german silver, inconel, and nichrome.