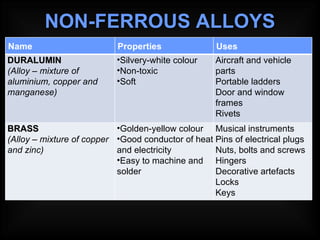
Non-ferrous metals do not contain iron, so they do not rust or attract magnets. Most non-ferrous metals are soft but can be strengthened through alloying with other materials to form non-ferrous alloys. Common non-ferrous metals and alloys include aluminum, copper, lead, tin, zinc, duralumin, brass, bronze, and pewter, each with distinct properties and applications such as in construction, electronics, batteries, and decorative arts.