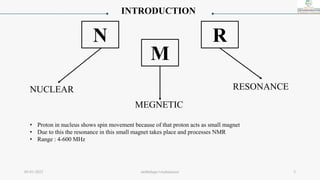
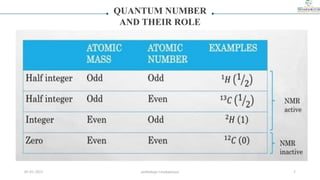
1) The document discusses nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and provides details on the theory, principles, instrumentation, and applications of NMR. It describes how NMR works based on the spin and magnetic properties of atomic nuclei.
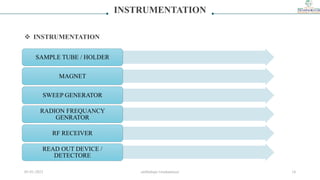
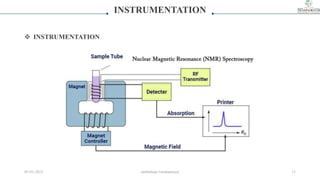
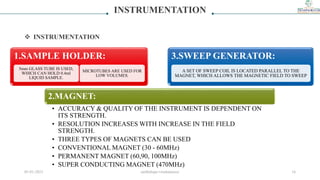
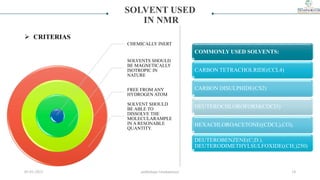
2) The key components of an NMR instrument are described, including the magnet, radiofrequency transmitter and receiver coils, and detector. Common solvents used in NMR experiments are also listed, such as deuterated chloroform and benzene.
3) The concepts of relaxation processes and chemical shifts are explained. Relaxation involves the nuclei returning to equilibrium after excitation by radiofrequency pulses. Chemical shifts refer to small changes in resonant frequencies of different nuclei based on their chemical environment.



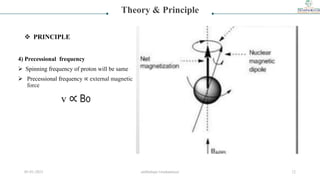
![3) Precessional motion
Proton will be showing precessional motion
due to interaction of spin & gravitational
force of earth [gyroscopic motion ]
Energy of reorientation of magnetic dipole
∆E=hv
Where ,
H= plank’s constant
V= frequency of radiation
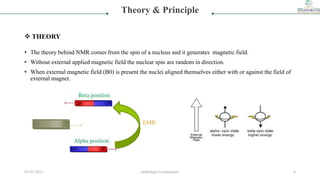
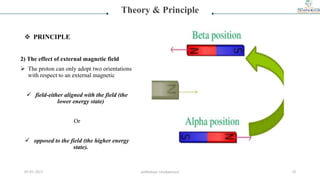
Theory & Principle
PRINCIPLE
05-01-2023 smtbnbspc/vrushantoza/ 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smtbnbswaminaryanpharmacycollegesalvav-230105153830-2df47e7c/85/NMR-SPECTROSCOPY-pptx-11-320.jpg)