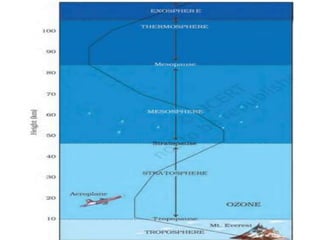
The document summarizes key aspects of air and the atmosphere. It describes the composition of the atmosphere, which is mostly nitrogen and oxygen. It also notes that the atmosphere is divided into five layers - the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere. The first layer, the troposphere, extends from the Earth's surface to around 13 km and contains the air we breathe. Weather occurs within the troposphere, while climate refers to average weather conditions over a longer period of time. The document also discusses air pressure, winds, moisture, clouds, precipitation and the different types of rainfall.