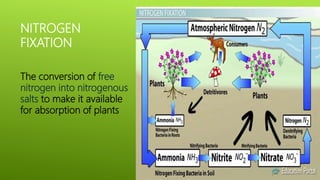
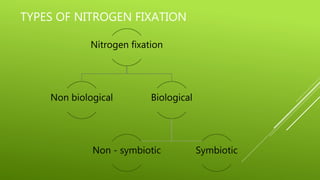
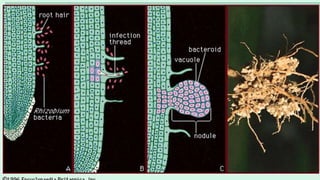
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into nitrogen compounds that can be used by plants. This can occur through non-biological means involving lightning and radiation, or through biological nitrogen fixation. Biological nitrogen fixation is performed by symbiotic and non-symbiotic bacteria and blue-green algae. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation occurs through root nodules formed by legumes via their symbiotic relationship with Rhizobia bacteria, and by some non-leguminous plants with actinomycetes. The bacteria in the nodules produce the nitrogenase enzyme which converts atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia that is used by the plant.