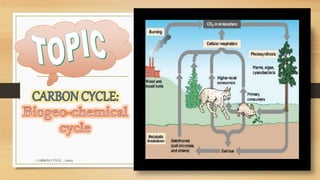
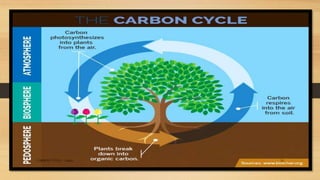
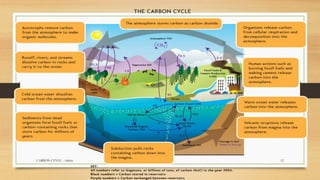
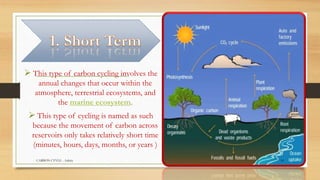
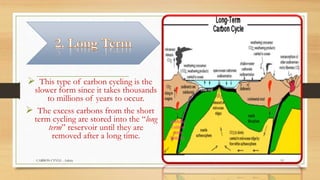
Carbon is essential for life and is continuously cycled through Earth's biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. The carbon cycle involves the exchange of carbon reservoirs between the atmosphere, ocean, biomass and fossil fuels. Photosynthesis absorbs carbon from the atmosphere which enters the biosphere, and respiration and decomposition release it back into the atmosphere. Human activity such as burning fossil fuels has increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, disrupting the natural carbon cycle balance.