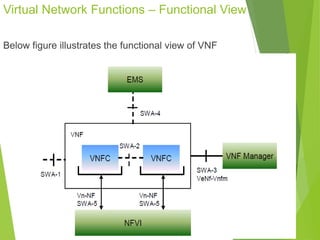
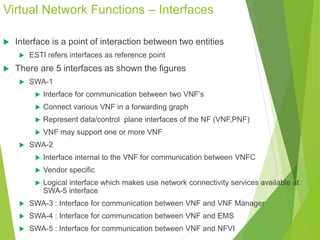
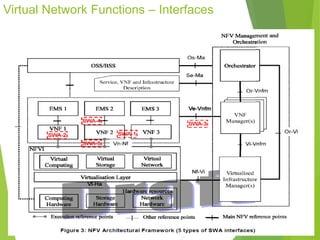
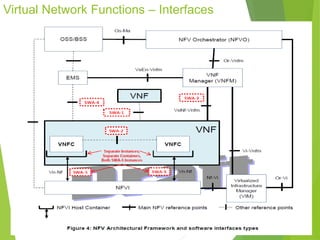
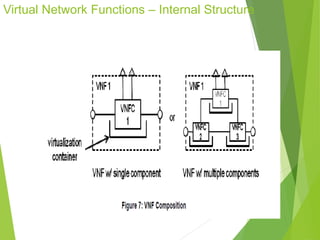
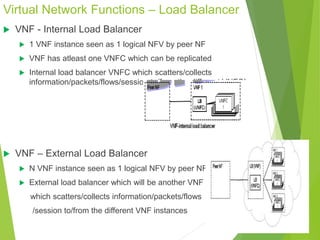
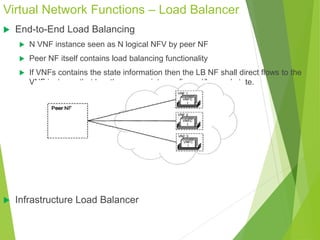
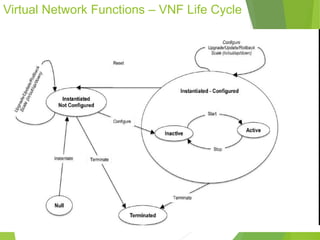
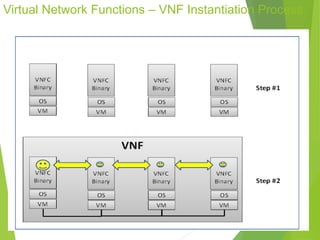
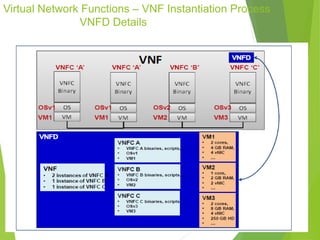
This document discusses network function virtualization (NFV) and virtual network functions (VNFs). It covers the overview of VNF architecture in the NFV framework, including VNF design patterns, properties, lifecycle, and fault management. VNFs are software implementations of network functions that run over NFV infrastructure and are orchestrated by NFV orchestrators and VNF managers. A VNF consists of one or more VNF components that have well-defined interfaces and can be deployed, managed, and upgraded independently. The document describes the various states, interfaces, and descriptors involved in the lifecycle of VNF instantiation, scaling, updating and upgrading.