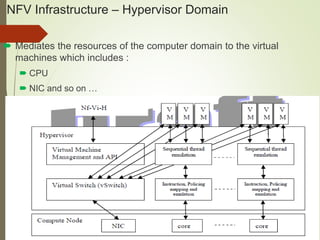
This document provides an overview of network function virtualization (NFV) infrastructure, including:
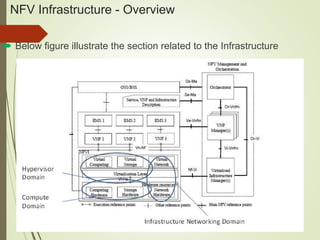
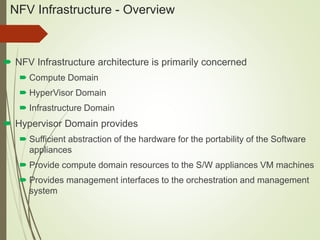
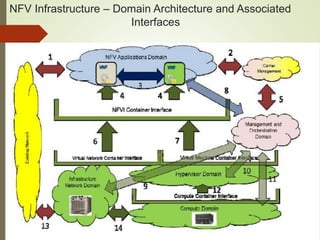
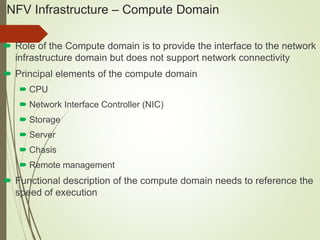
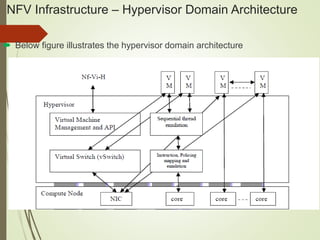
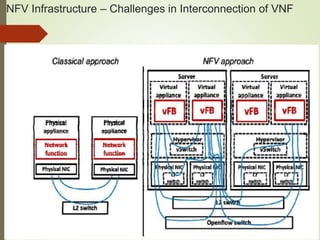
- The NFV infrastructure architecture focuses on the compute, hypervisor, and infrastructure domains. The hypervisor domain provides resources and interfaces for software appliances running as virtual machines.
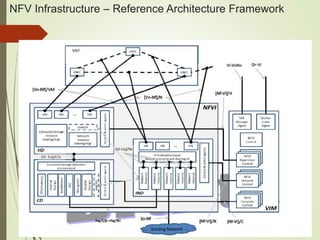
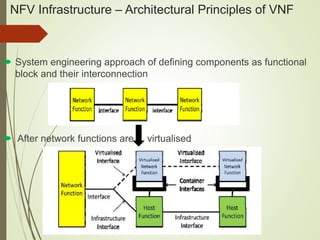
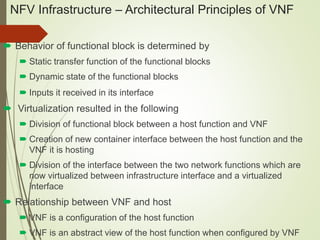
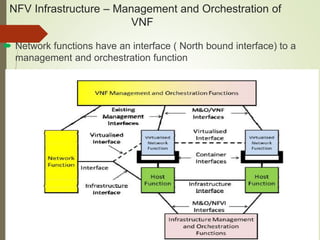
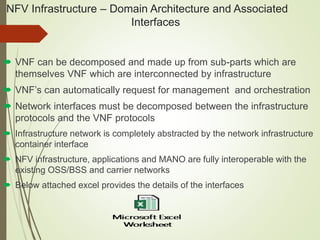
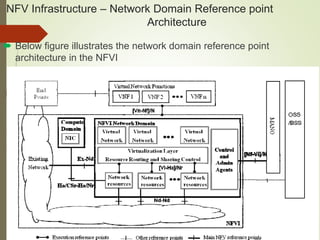
- NFV infrastructure principles include defining functional blocks and their interfaces, and how network functions are divided between host functions and virtual network functions after virtualization.
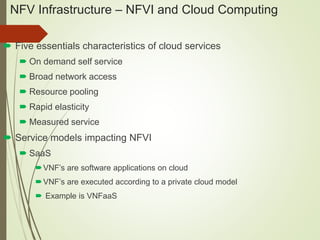
- The document discusses NFV infrastructure in relation to cloud computing models like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS and covers NFV infrastructure domains, interfaces, and challenges related to performance.