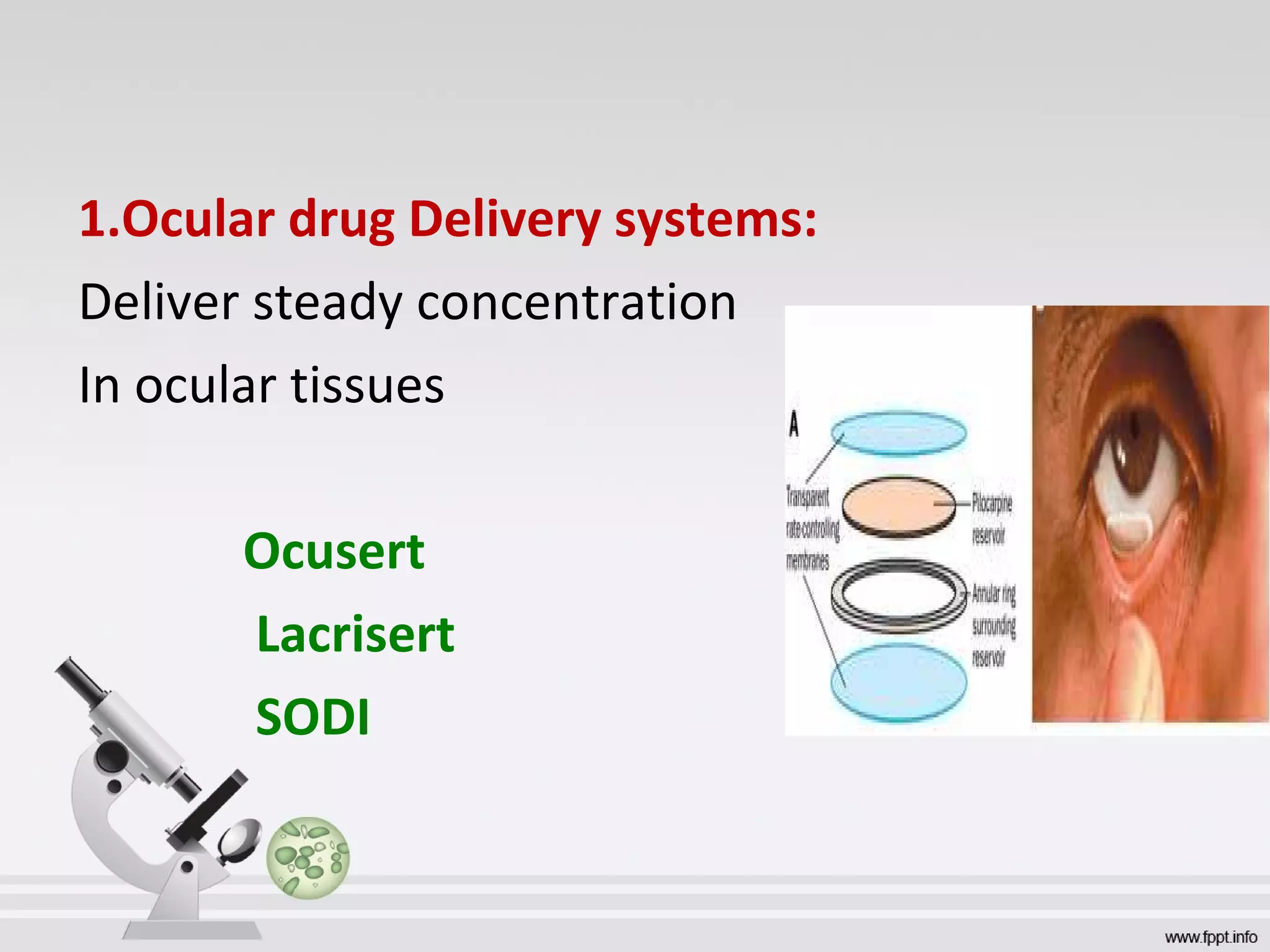
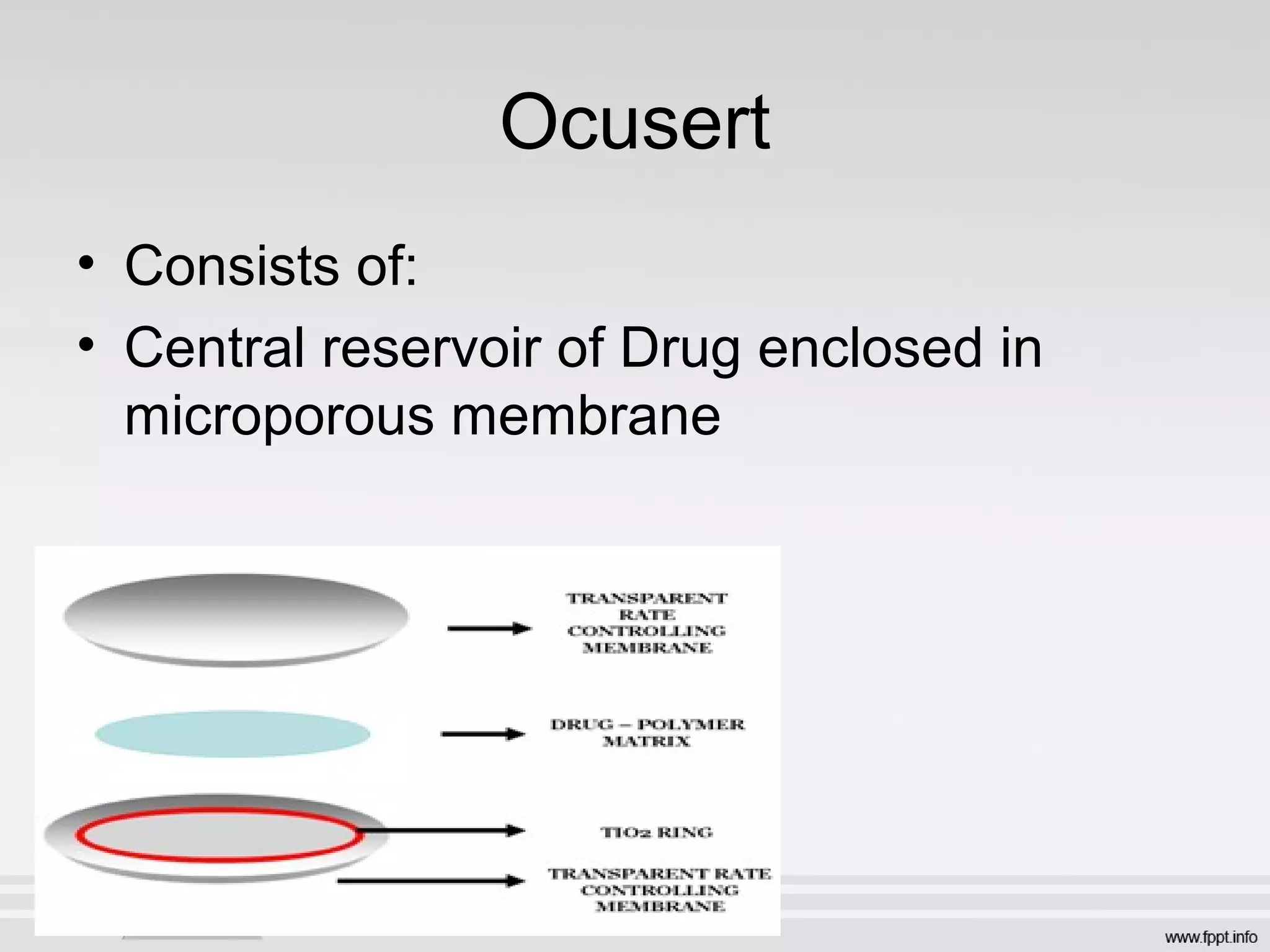
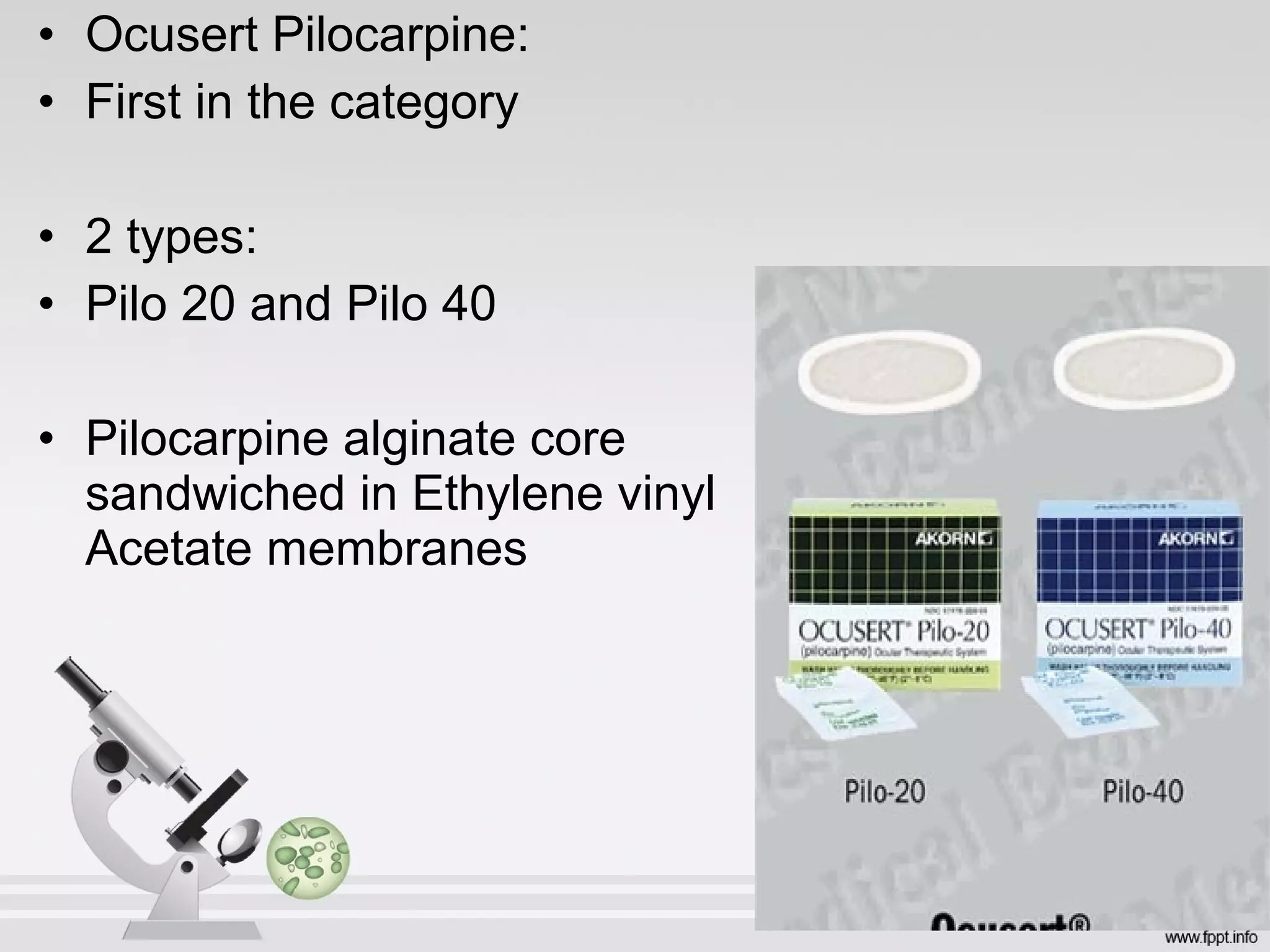
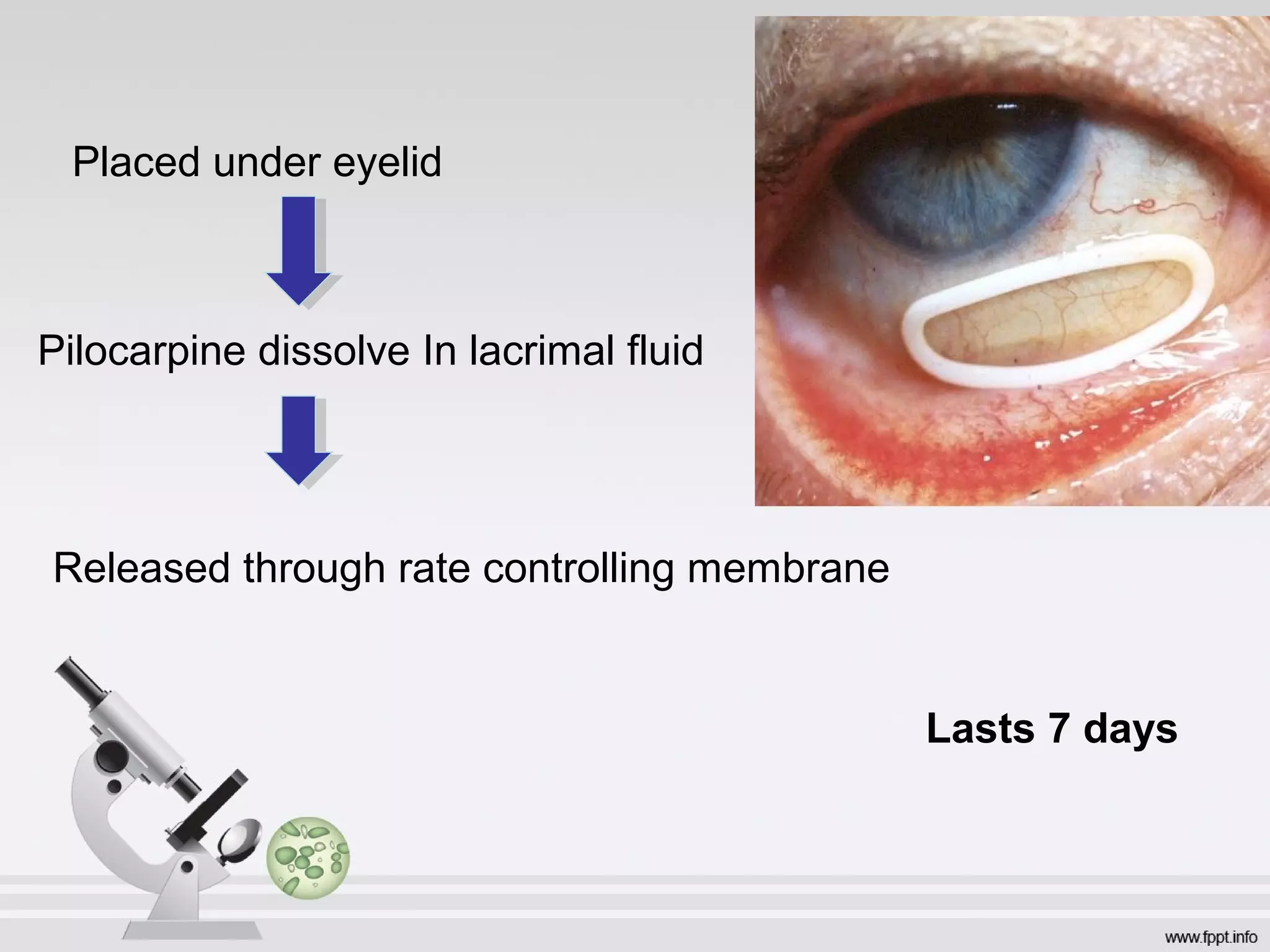
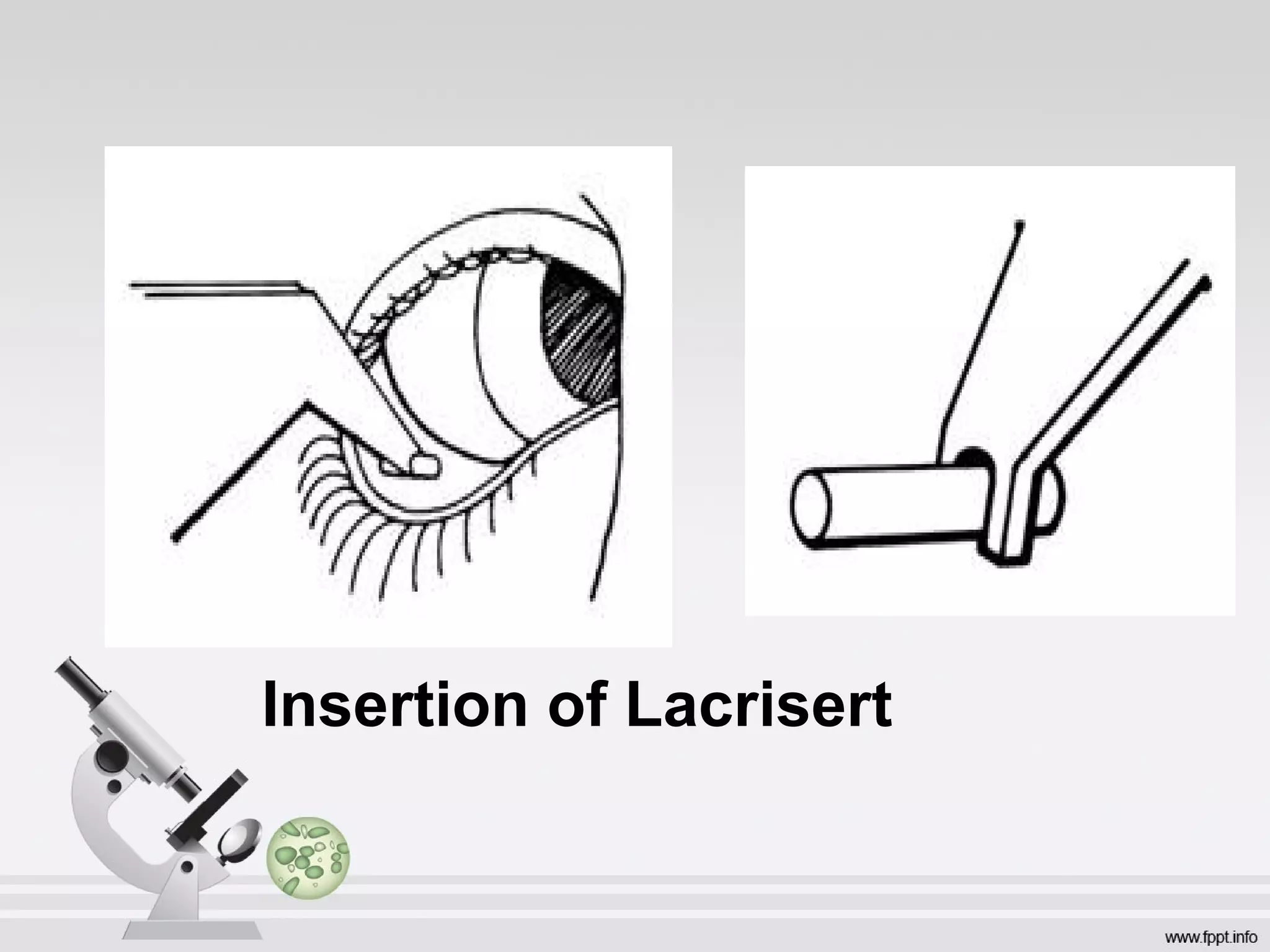
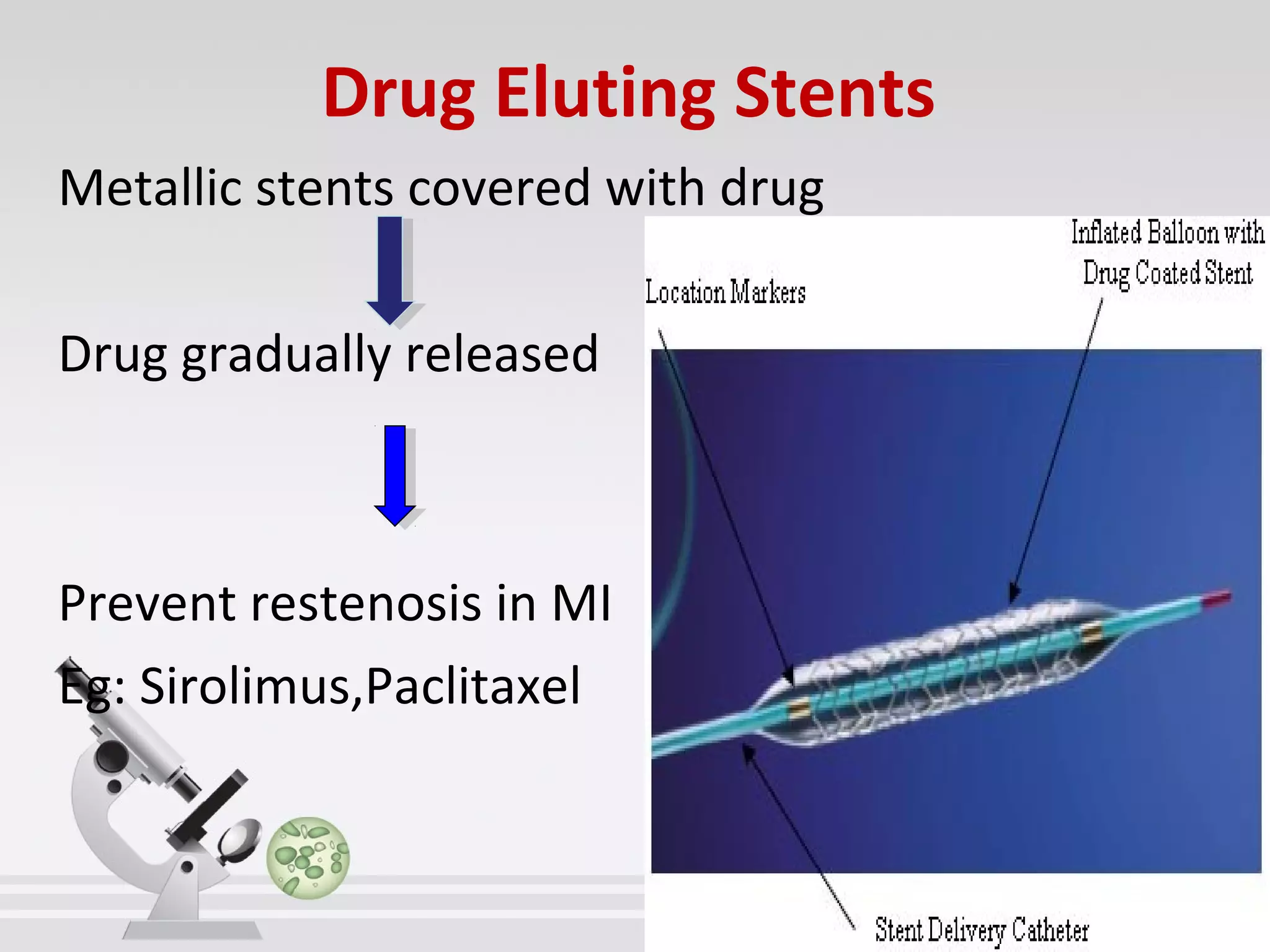
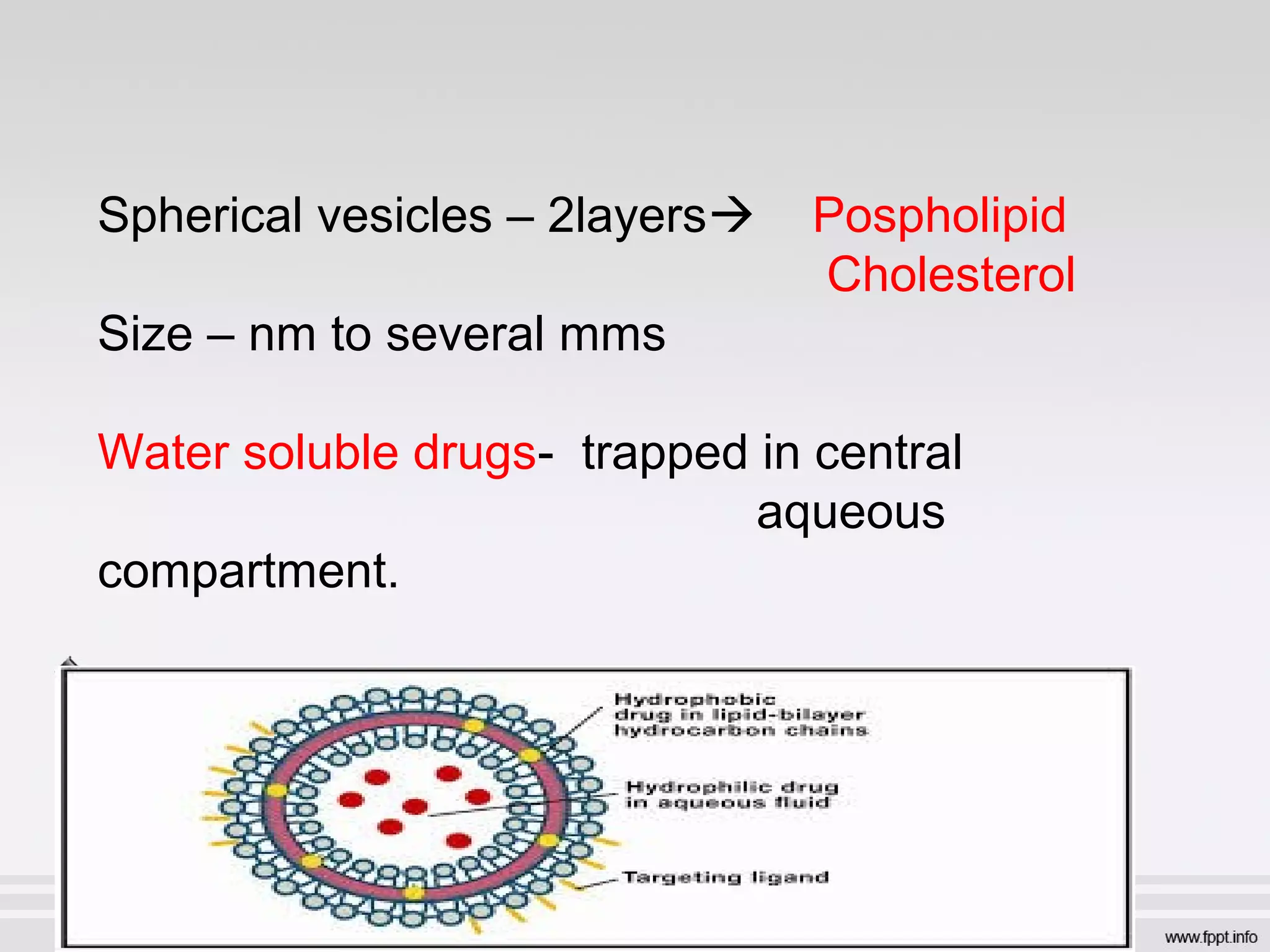
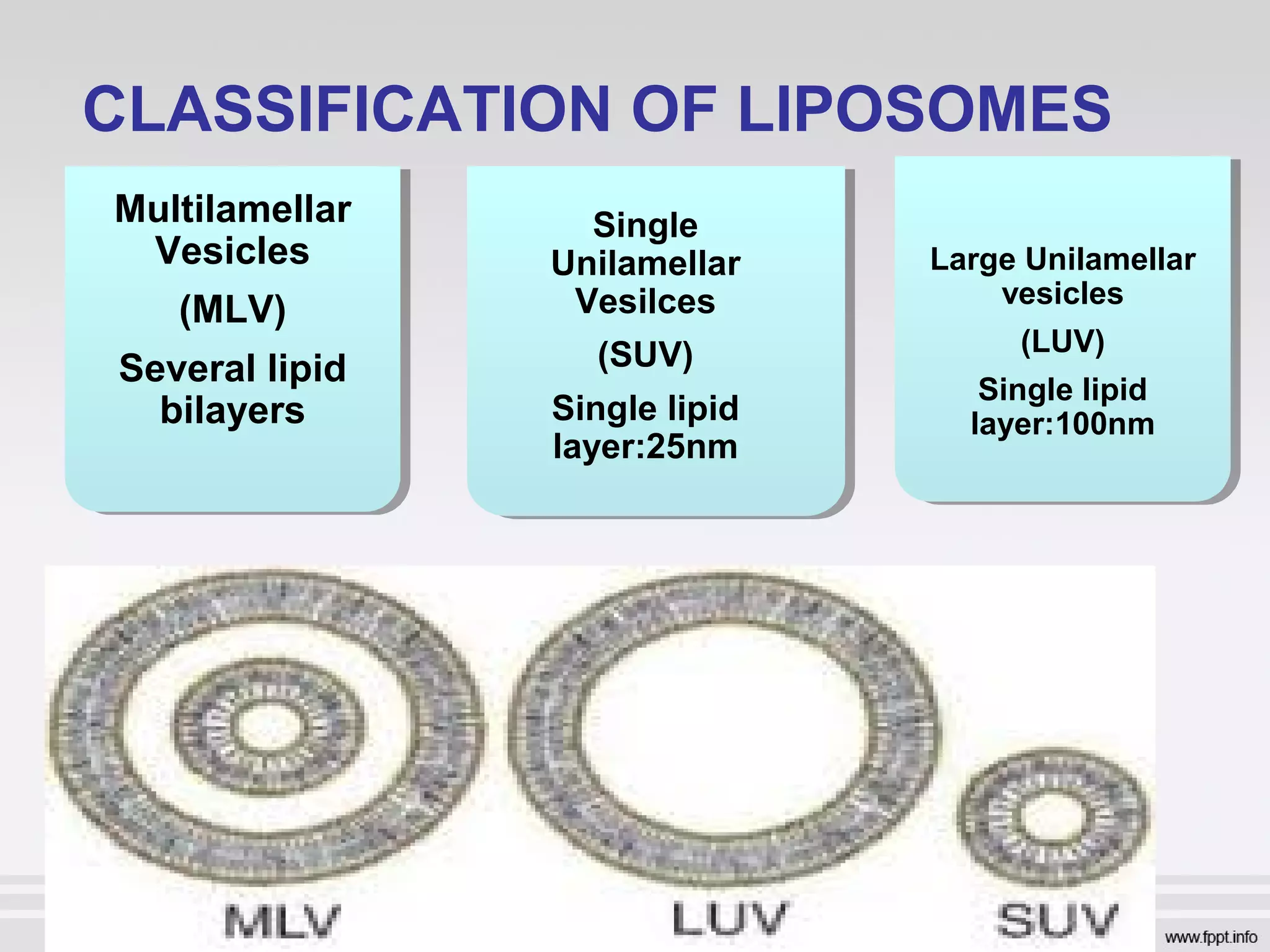
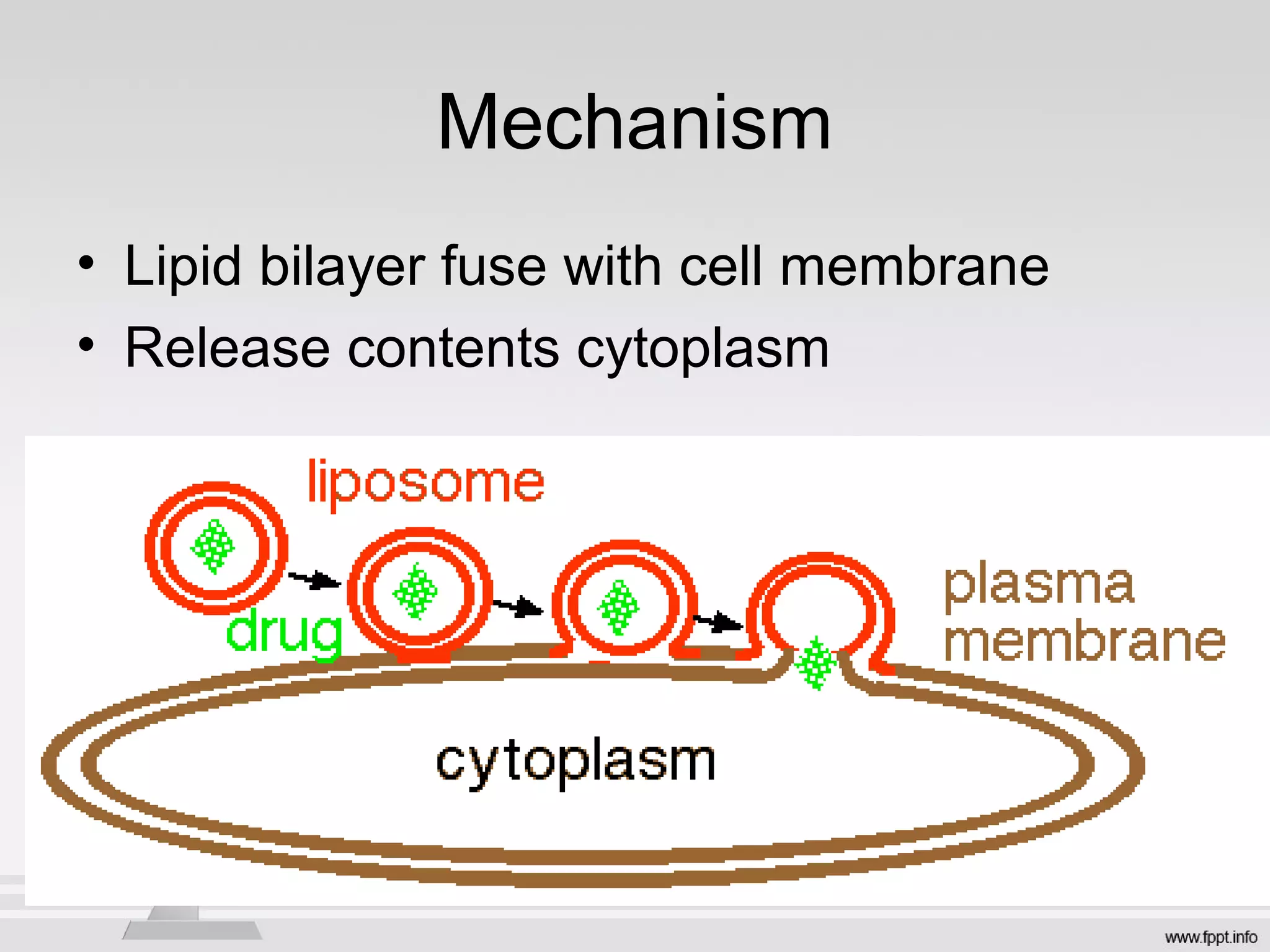
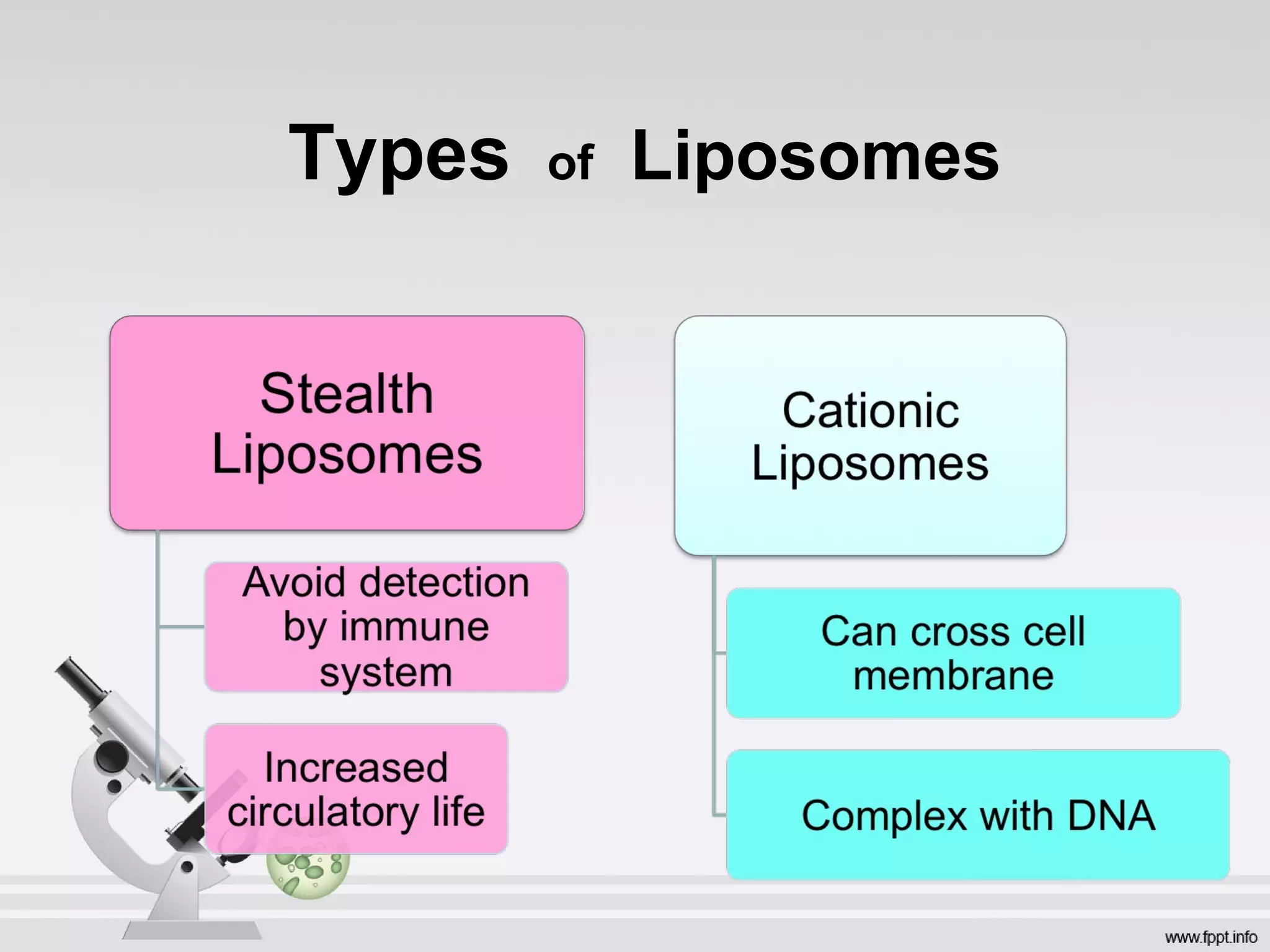
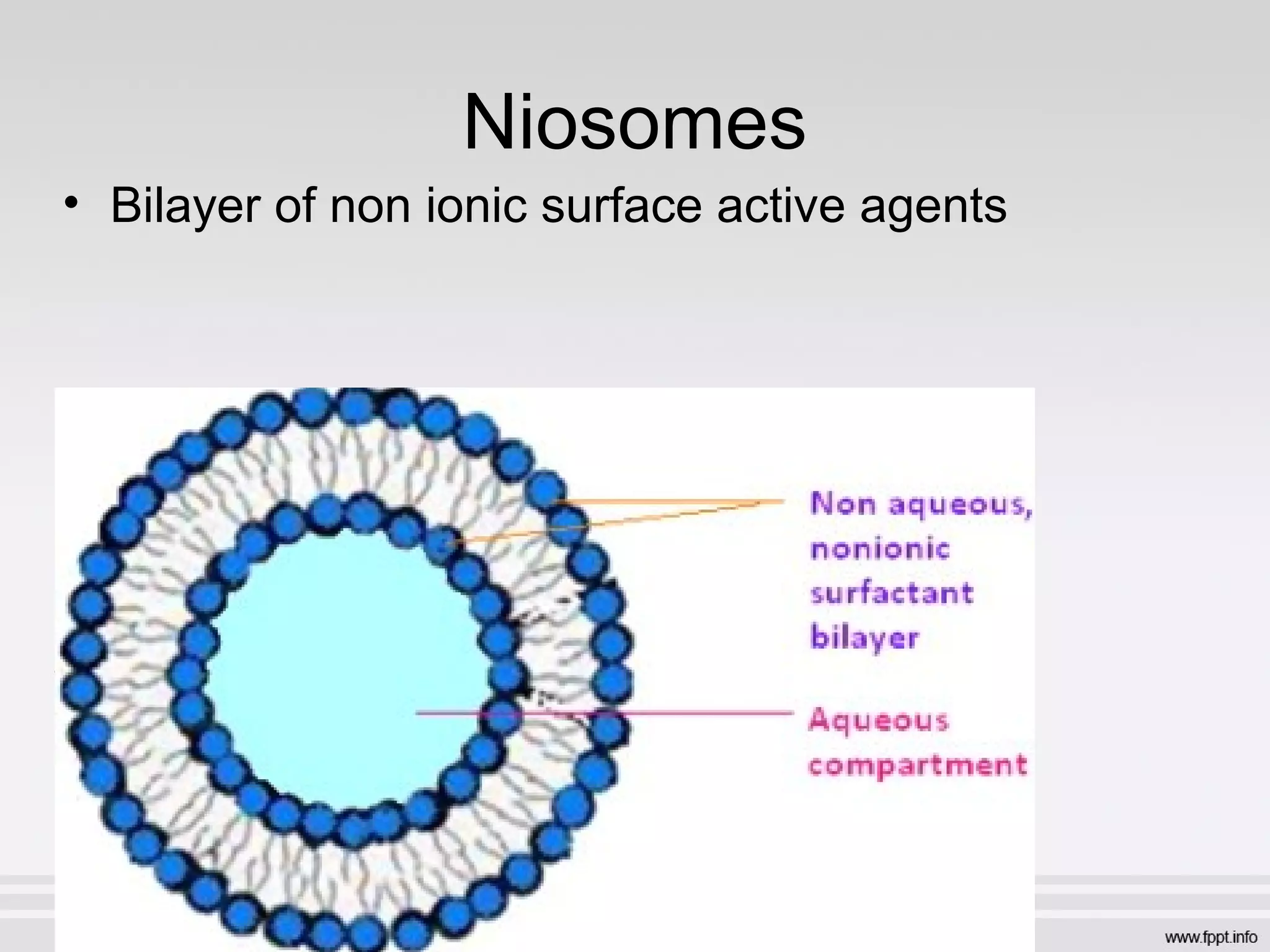
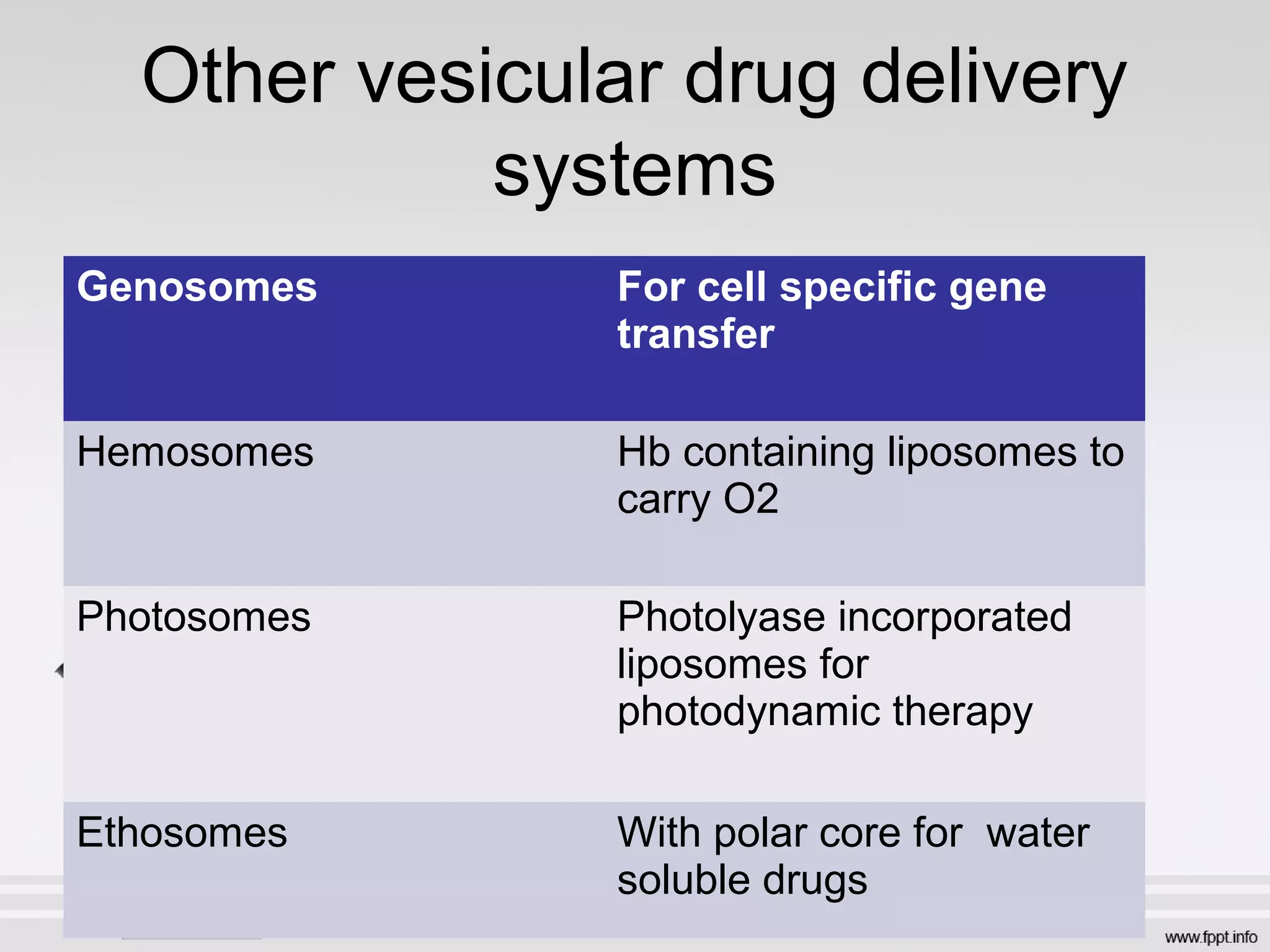
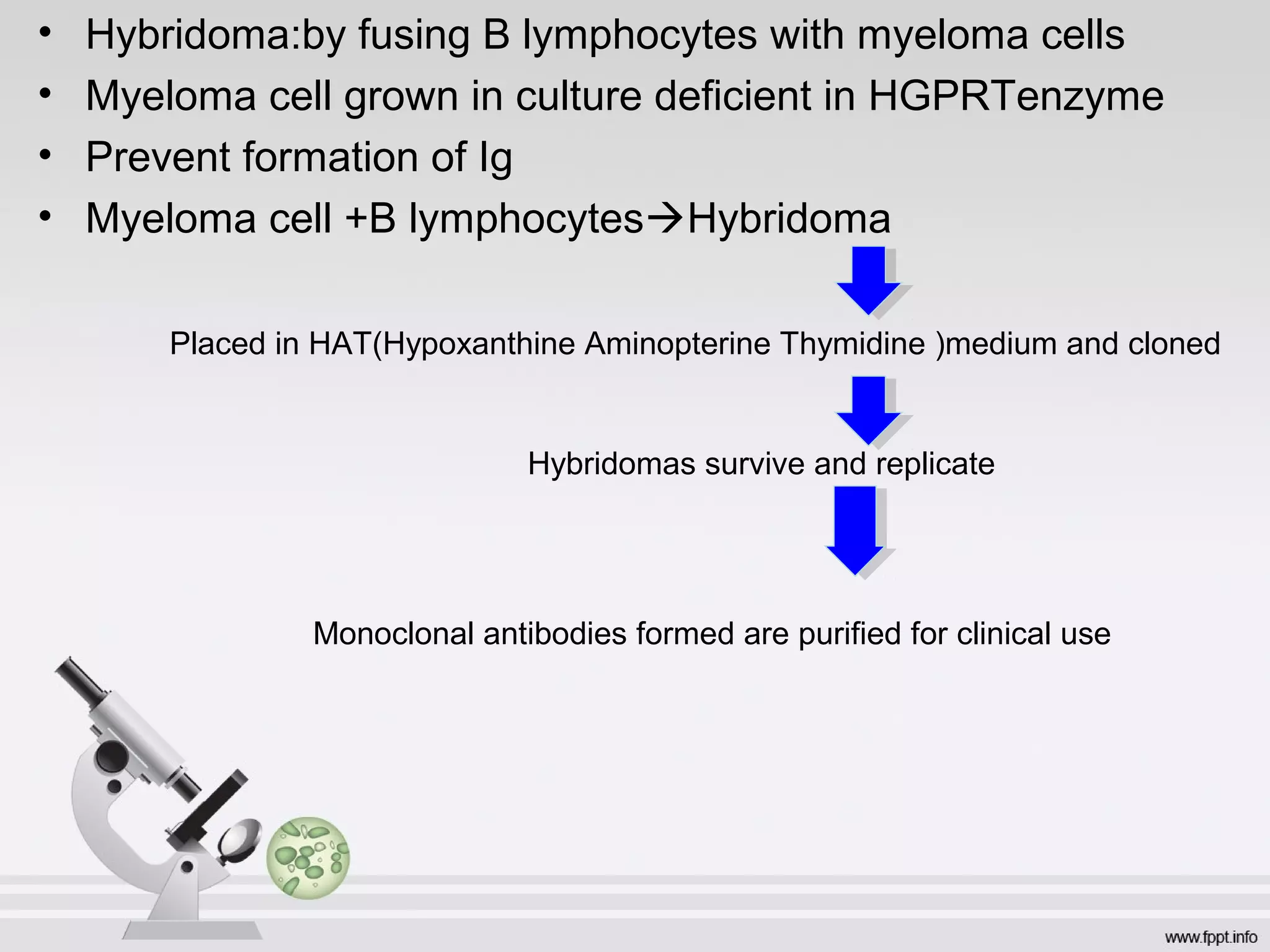
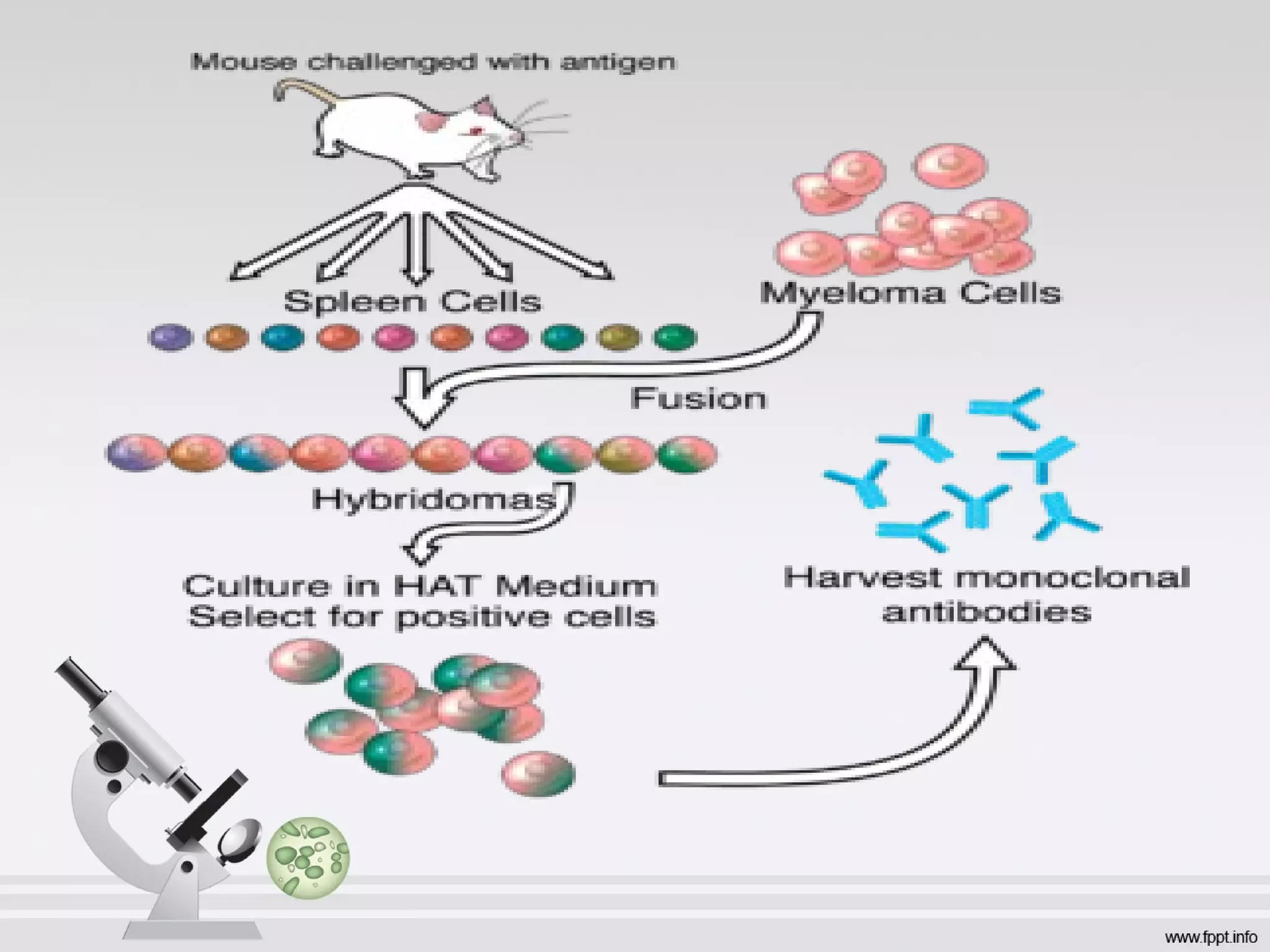
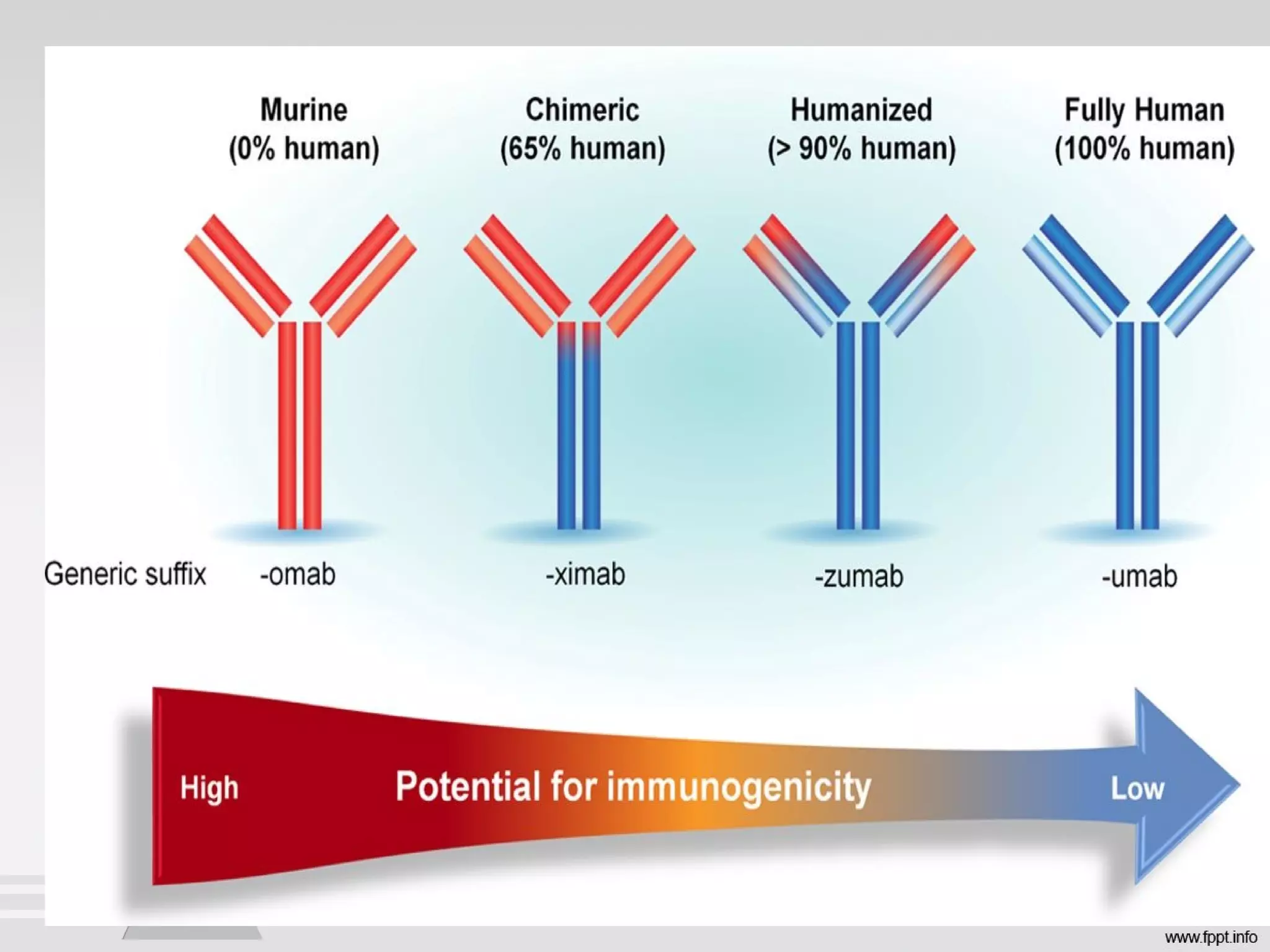
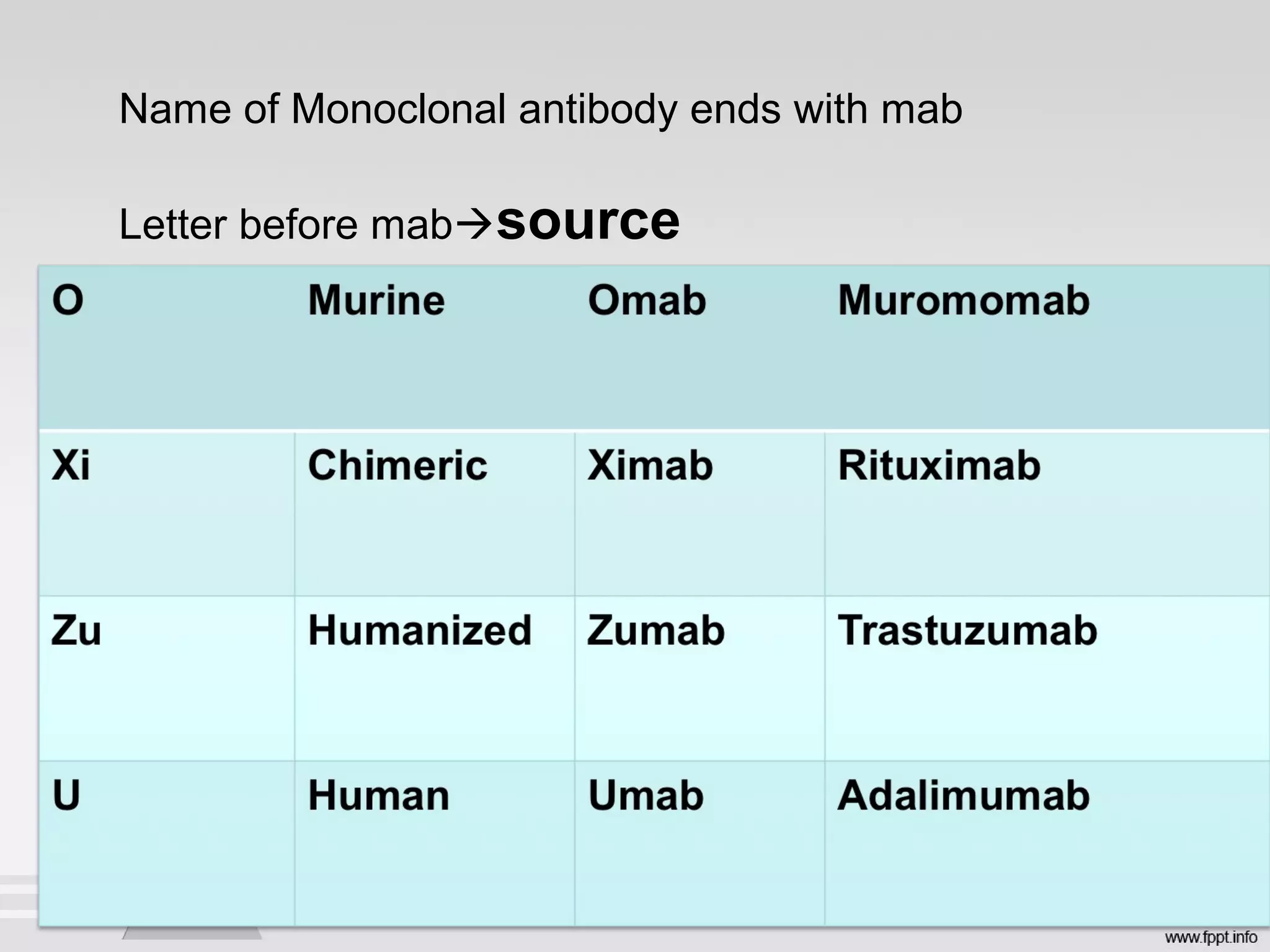
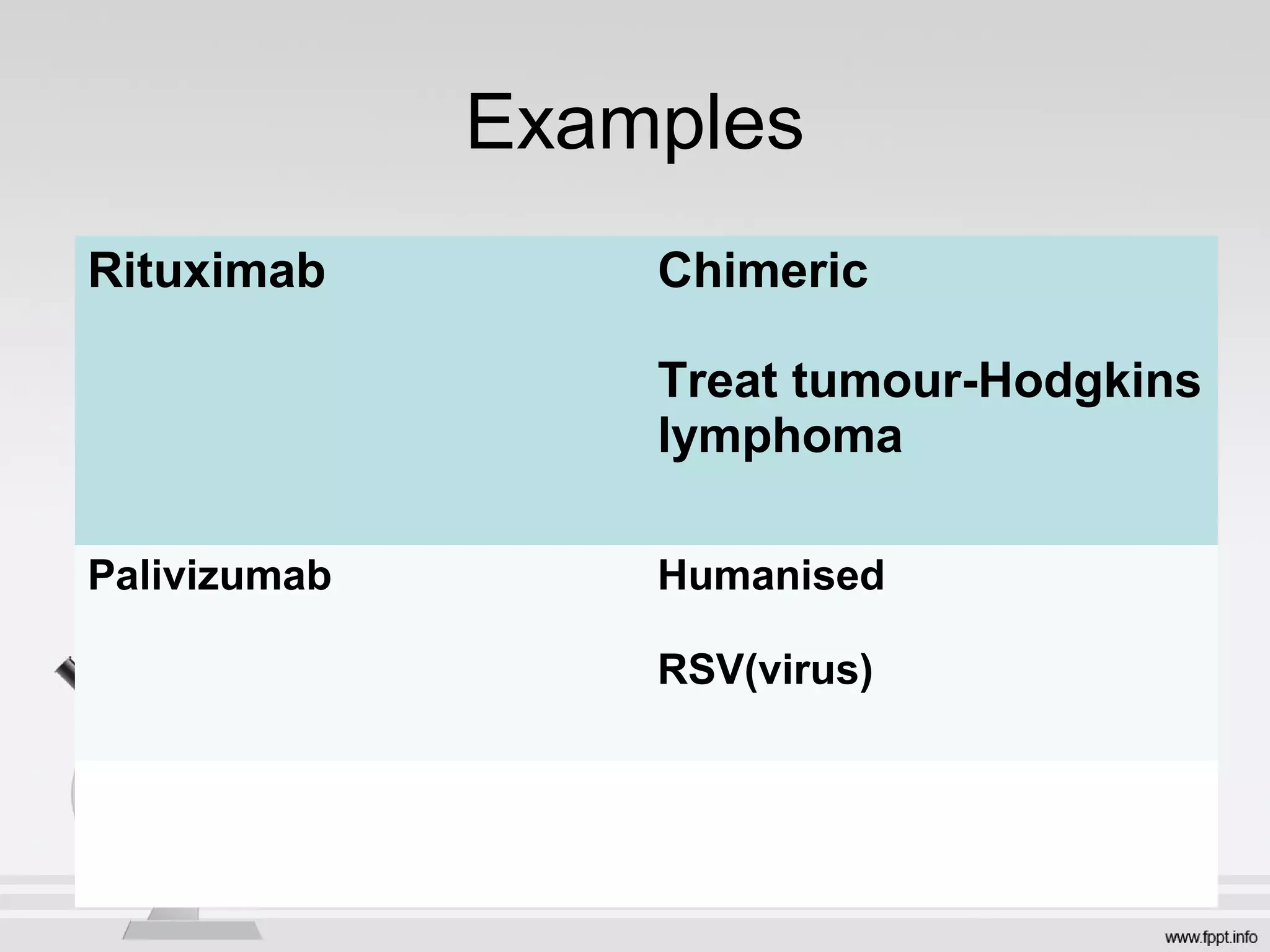
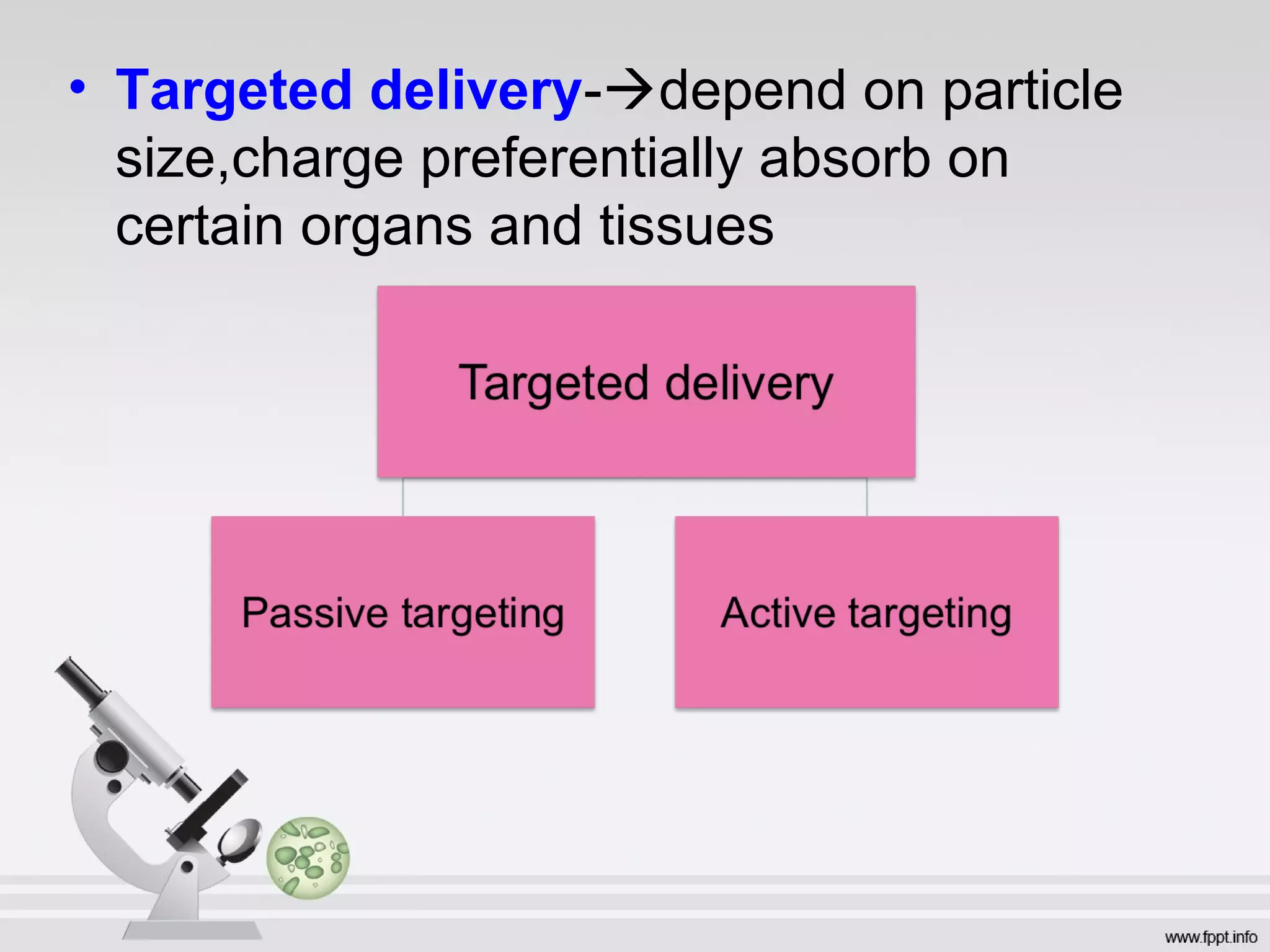
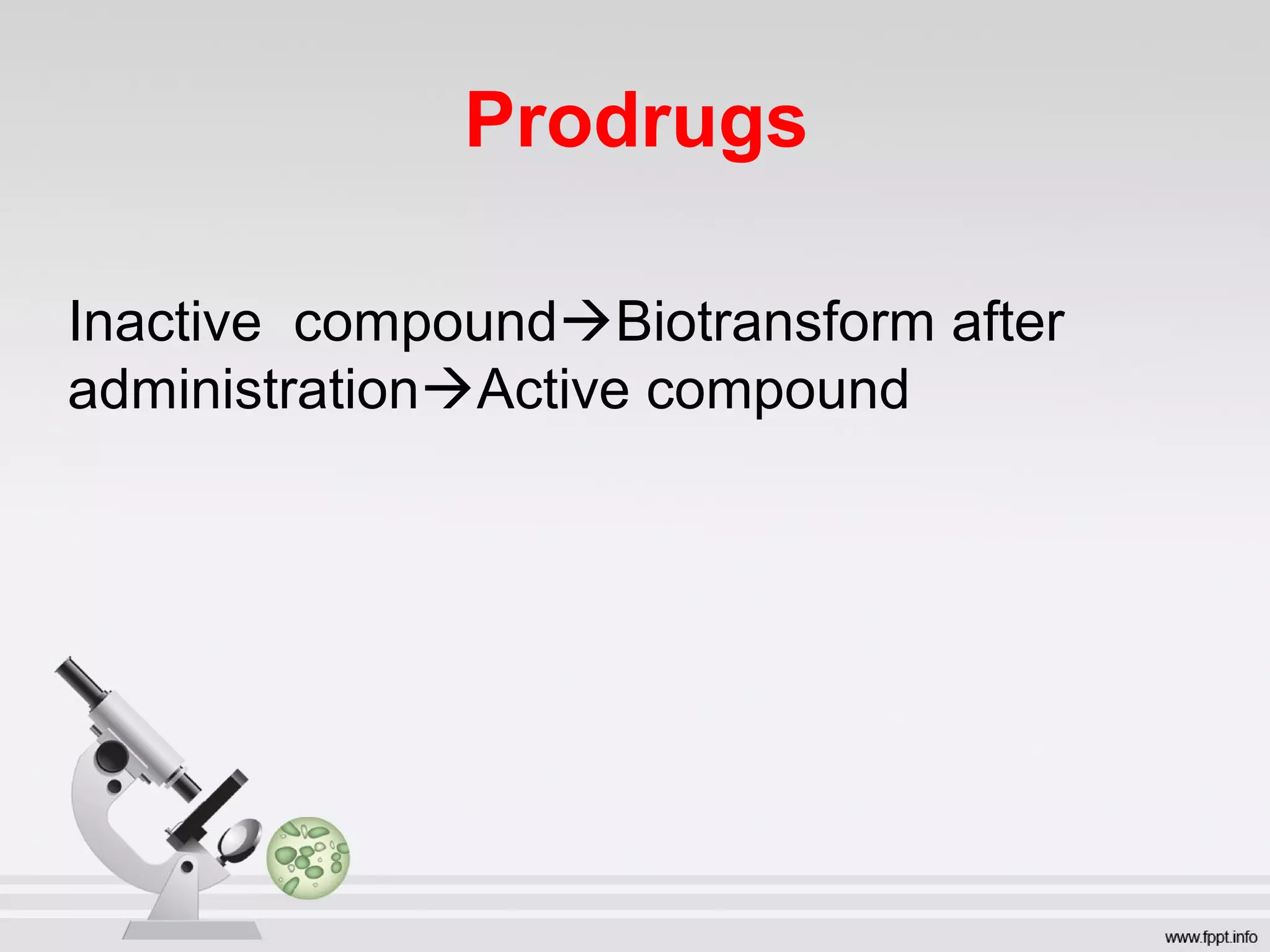
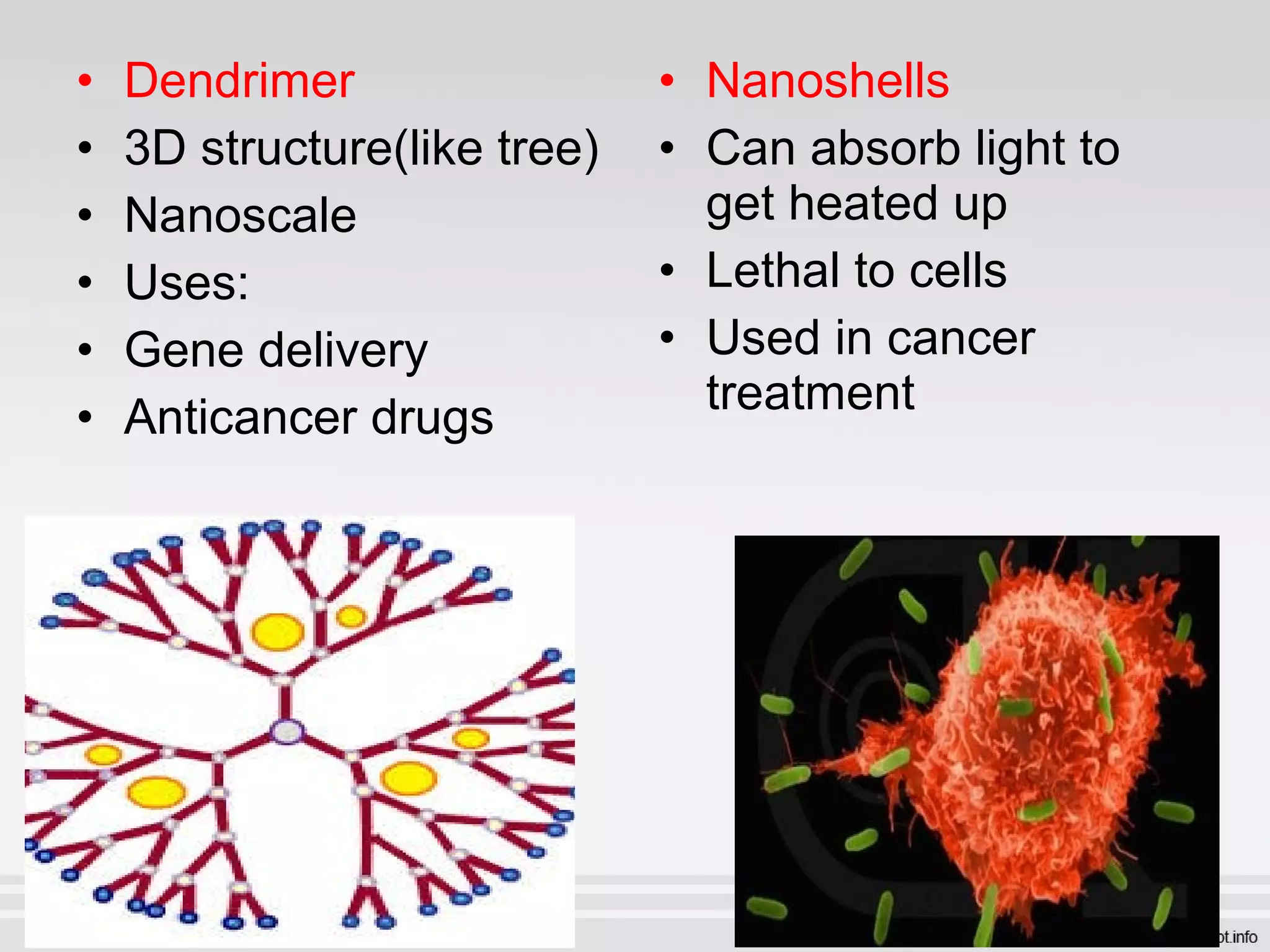
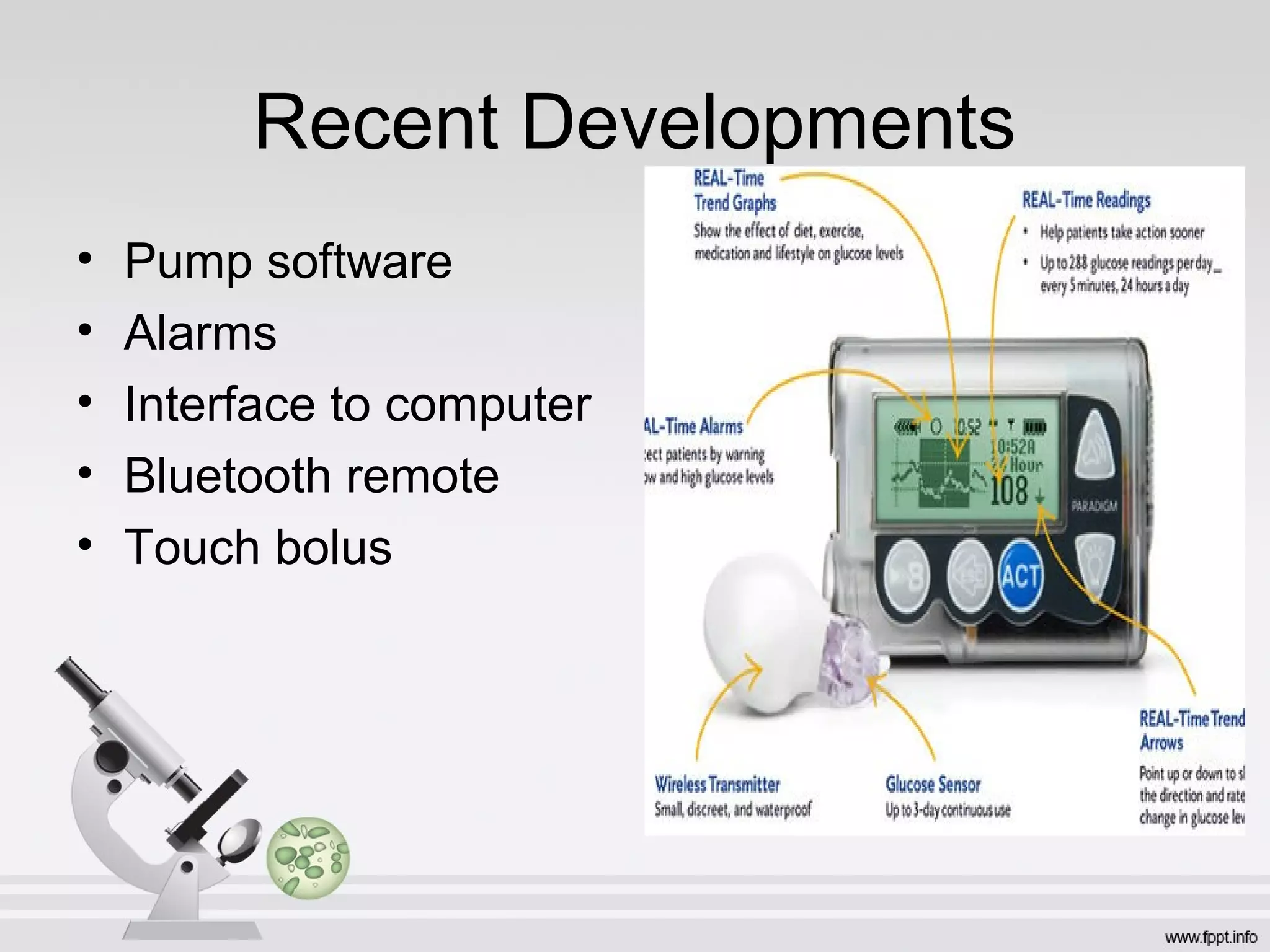
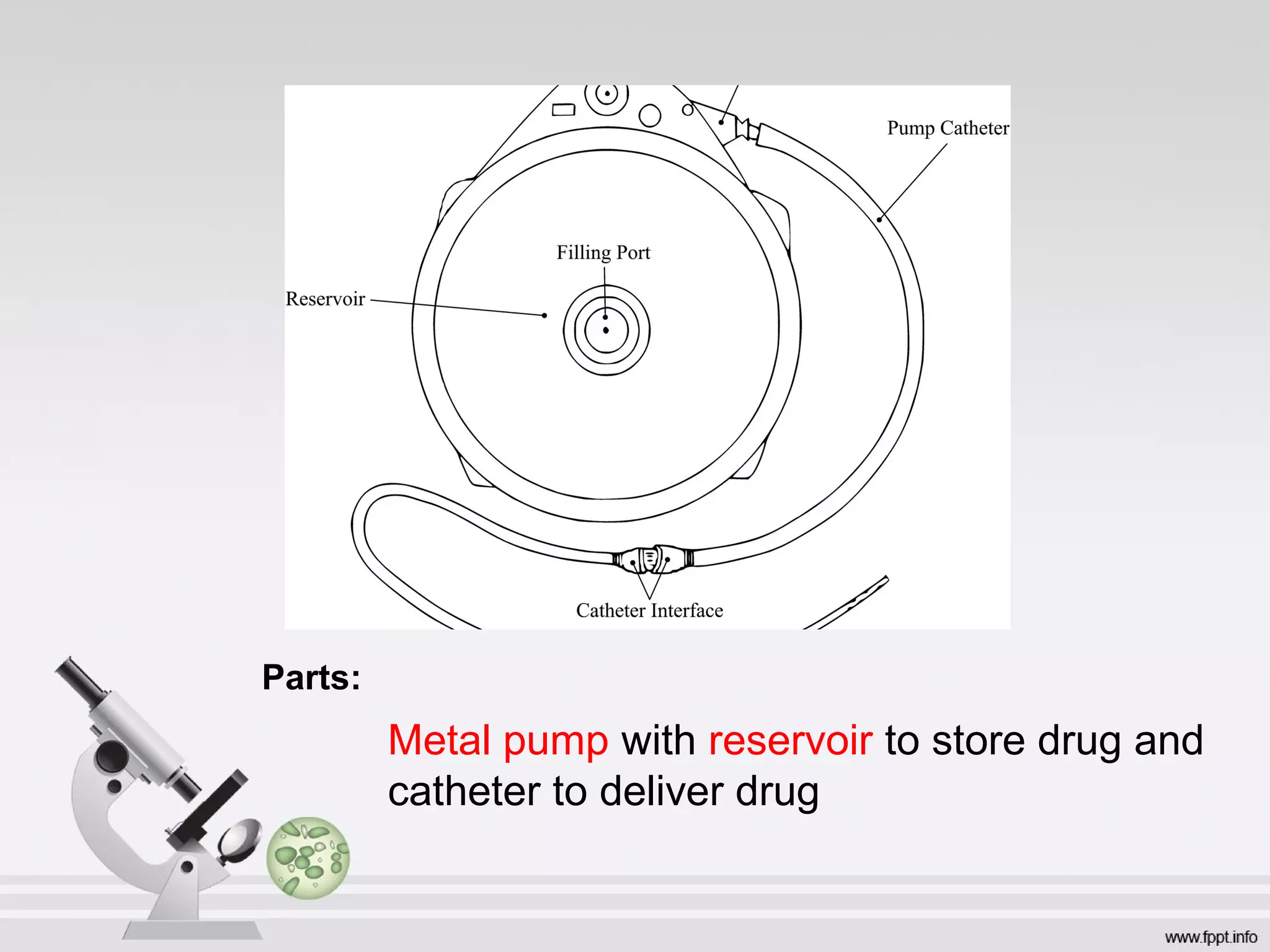
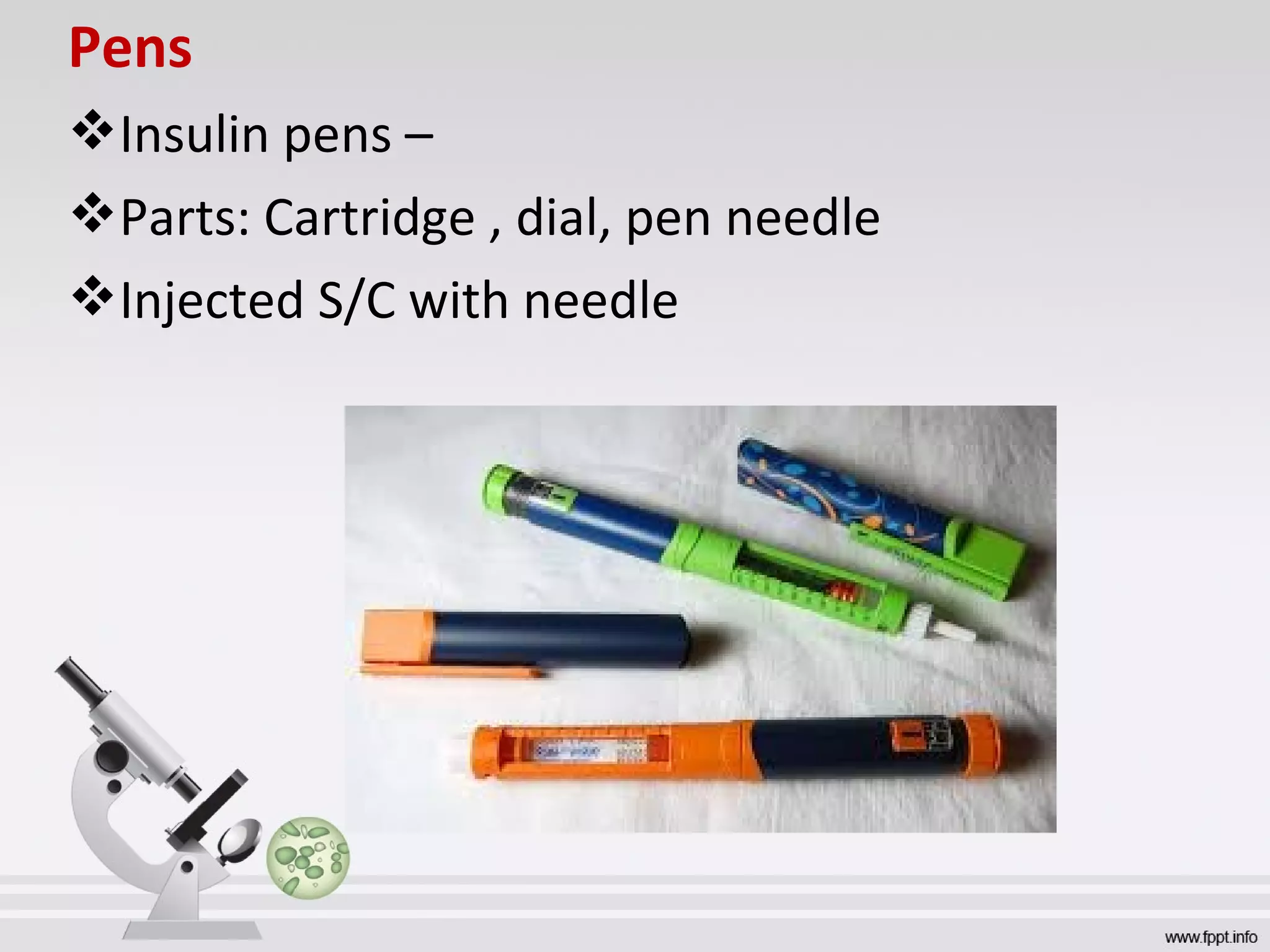
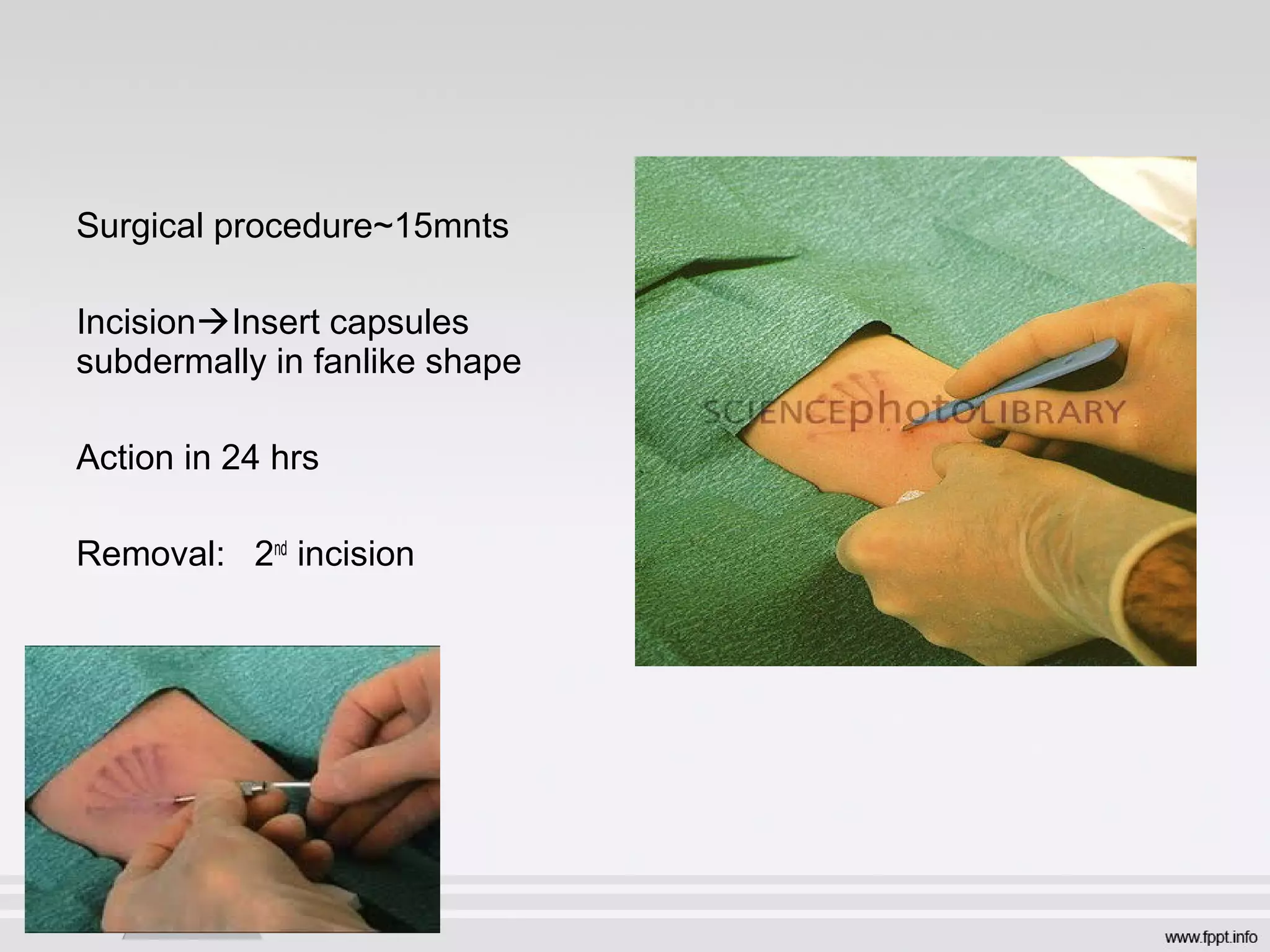
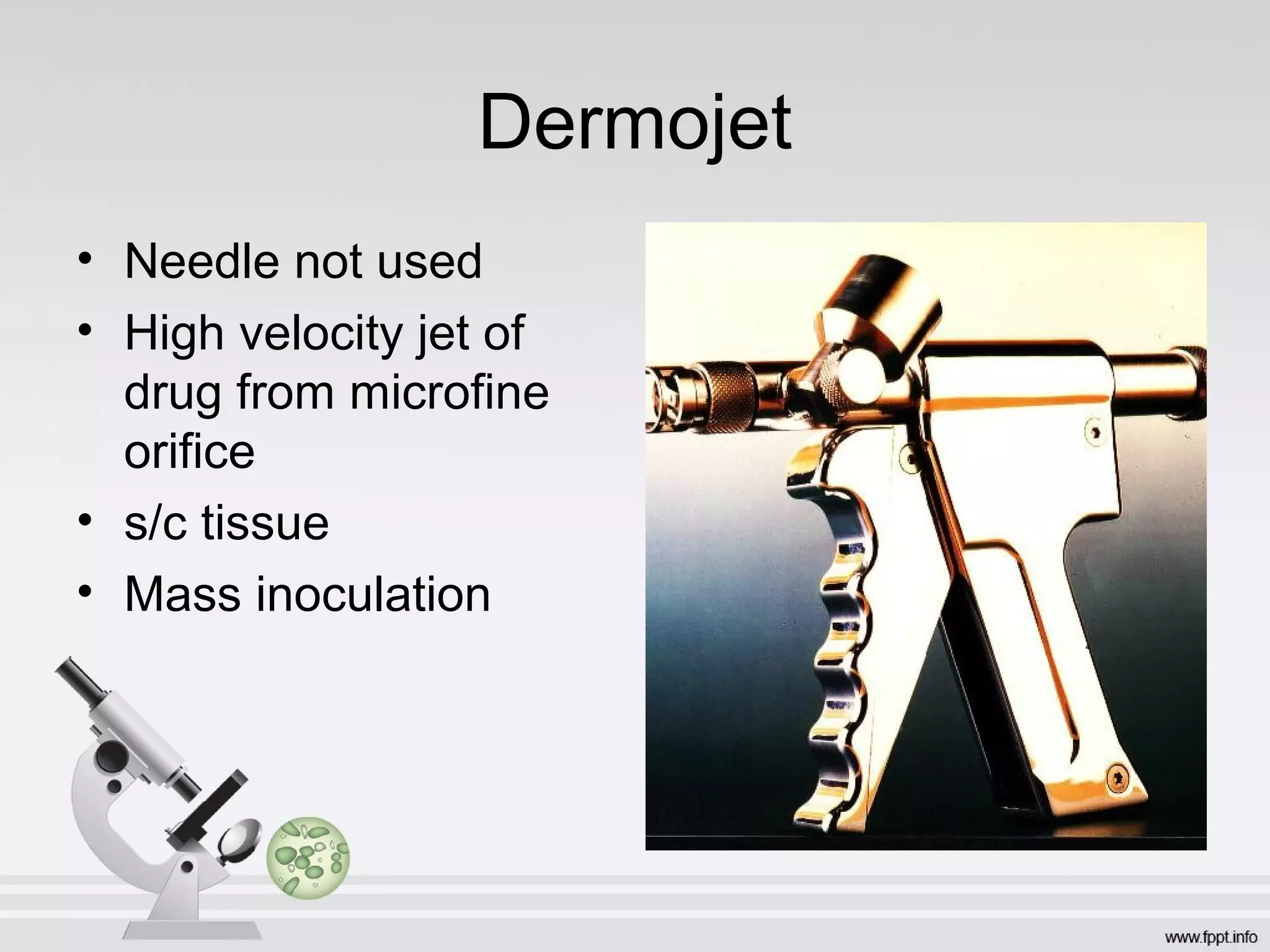
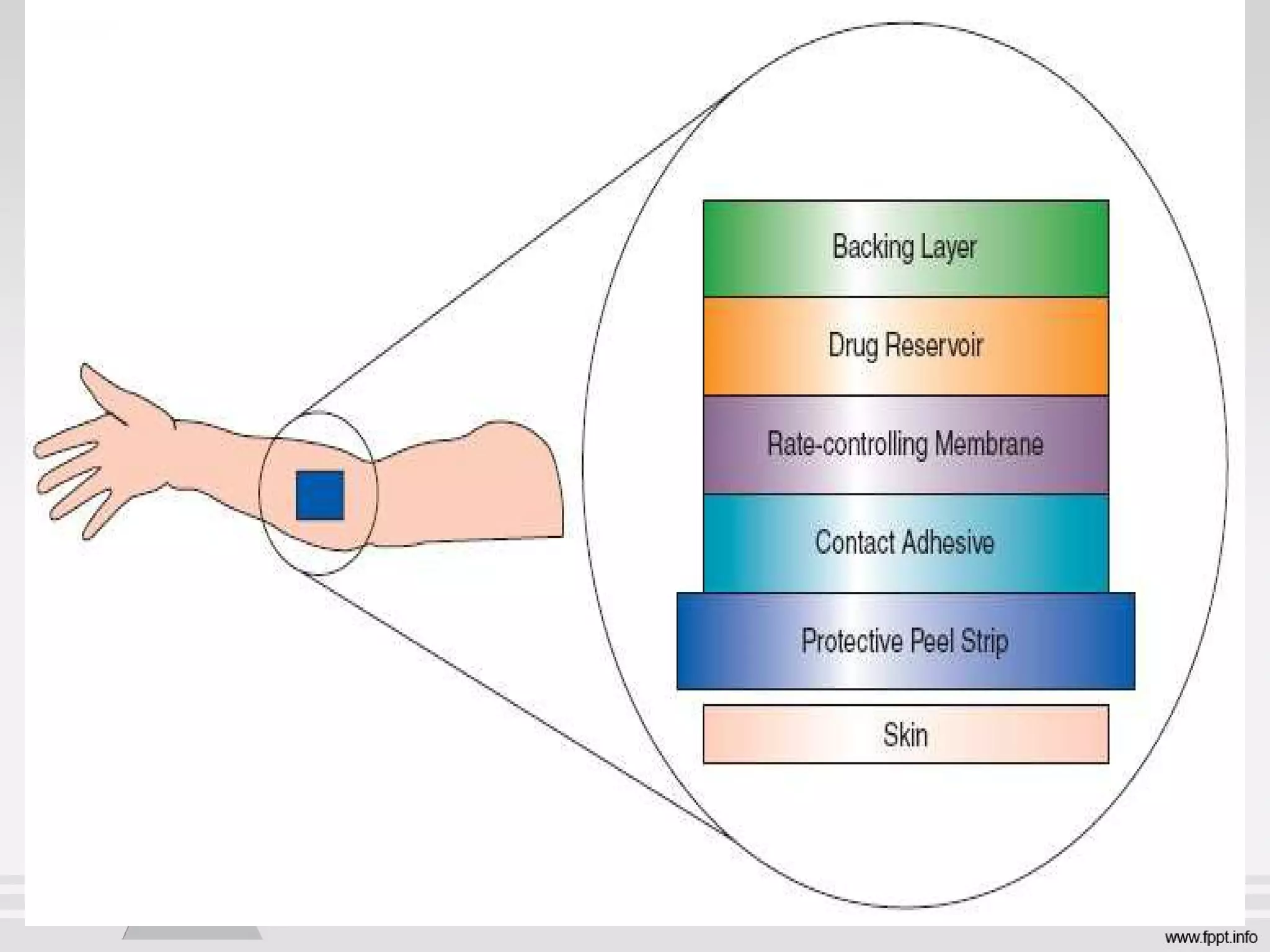
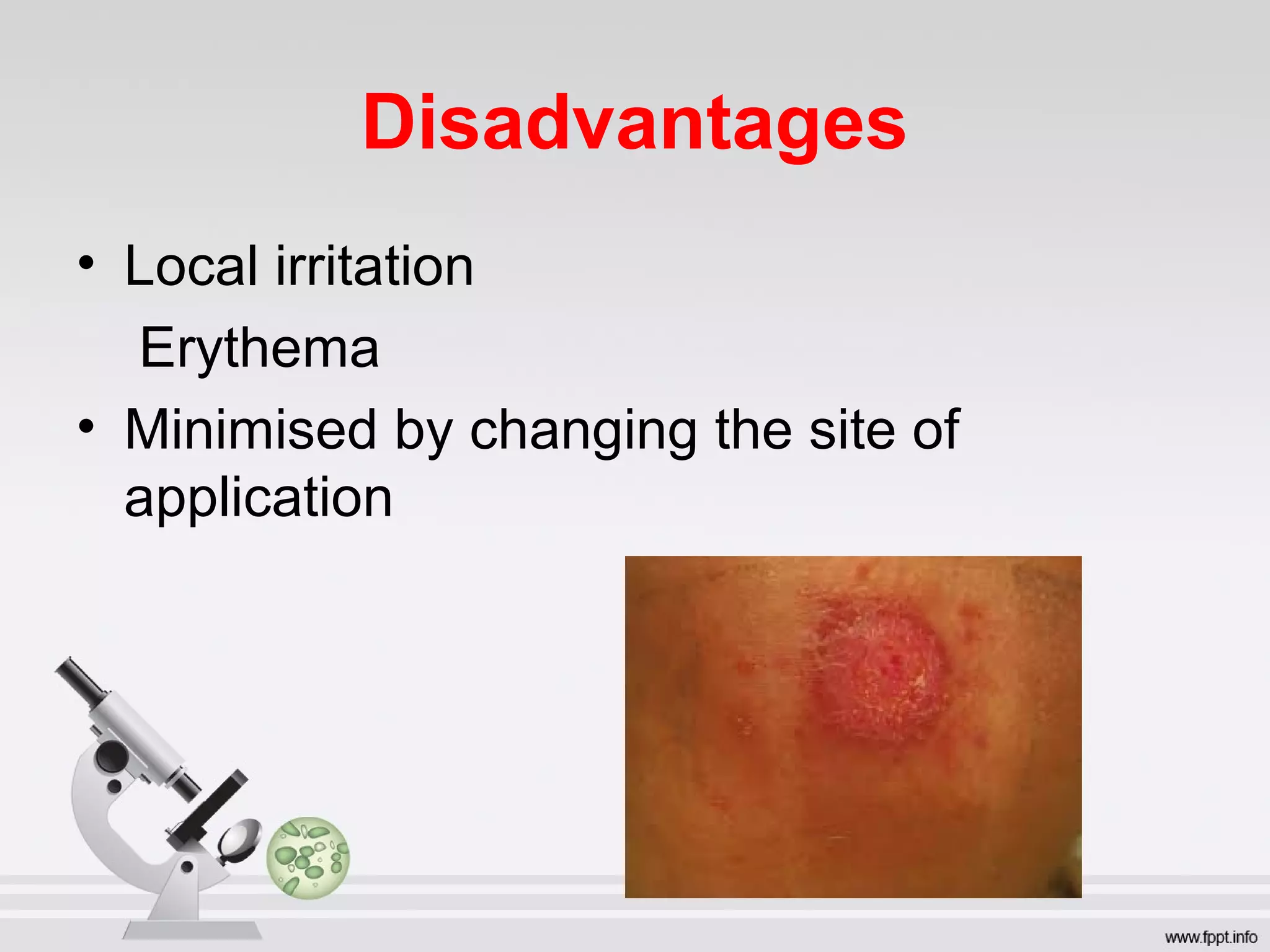
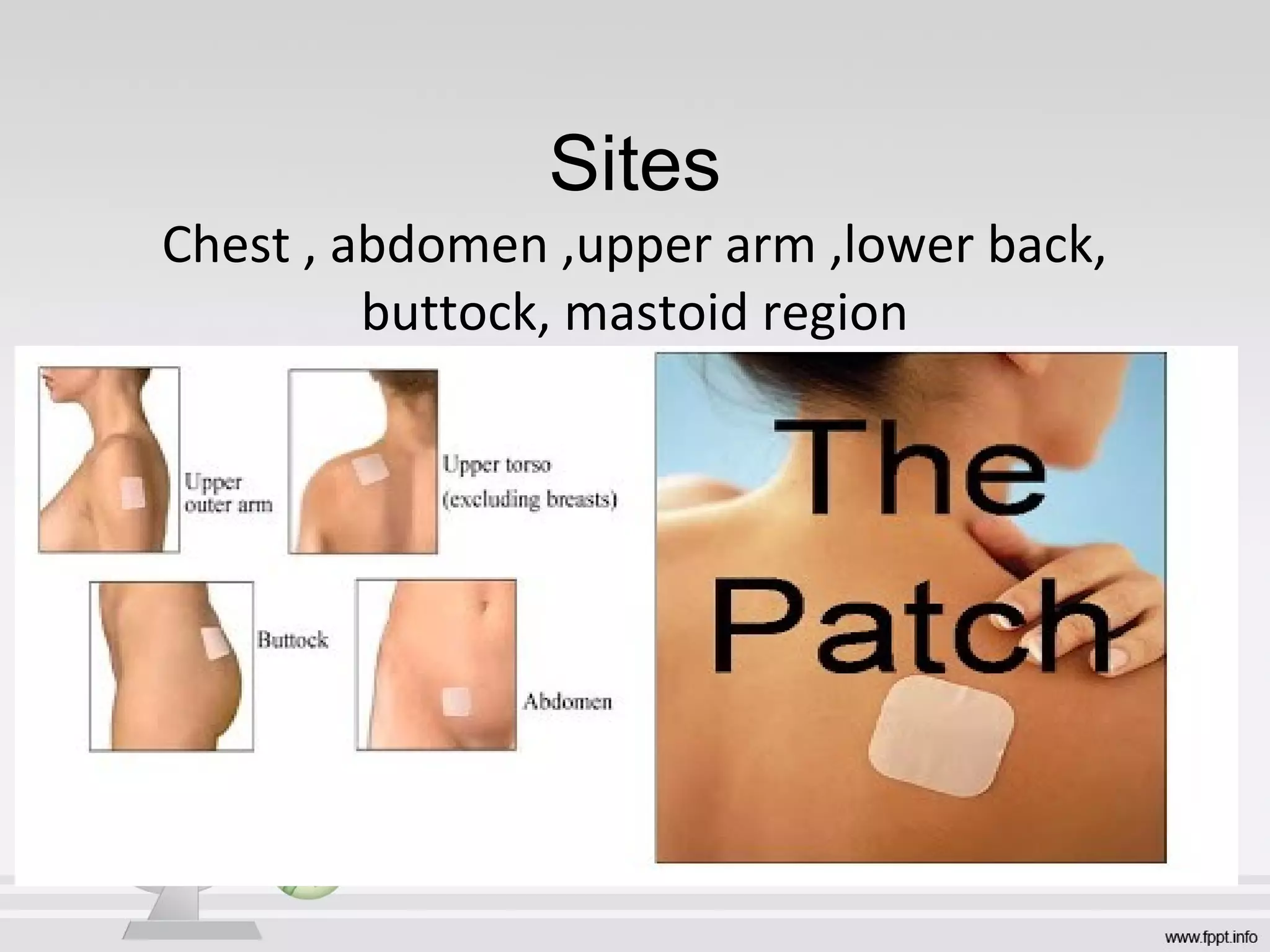
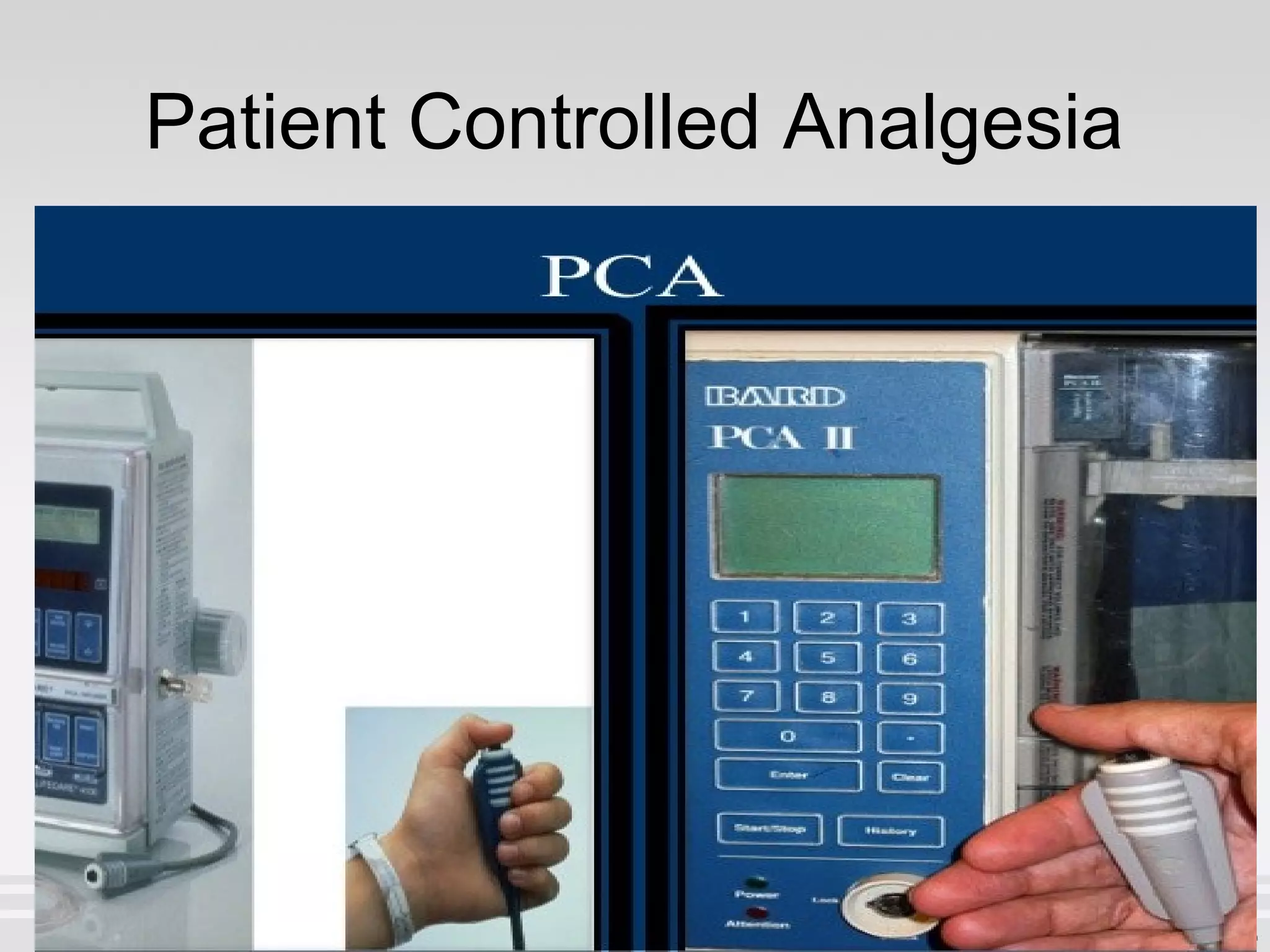
Newer drug delivery systems aim to maintain constant drug levels in the blood for longer periods of time using various prolonged release preparations and targeted delivery methods. Prolonged release parenteral preparations include portable insulin pumps, implantable intrathecal pumps for chronic pain, and transdermal drug delivery patches. Nanoparticles, liposomes, monoclonal antibodies, and other advanced targeted delivery systems can selectively deliver drugs to specific tissues and organs to improve efficacy and reduce side effects.
















![]
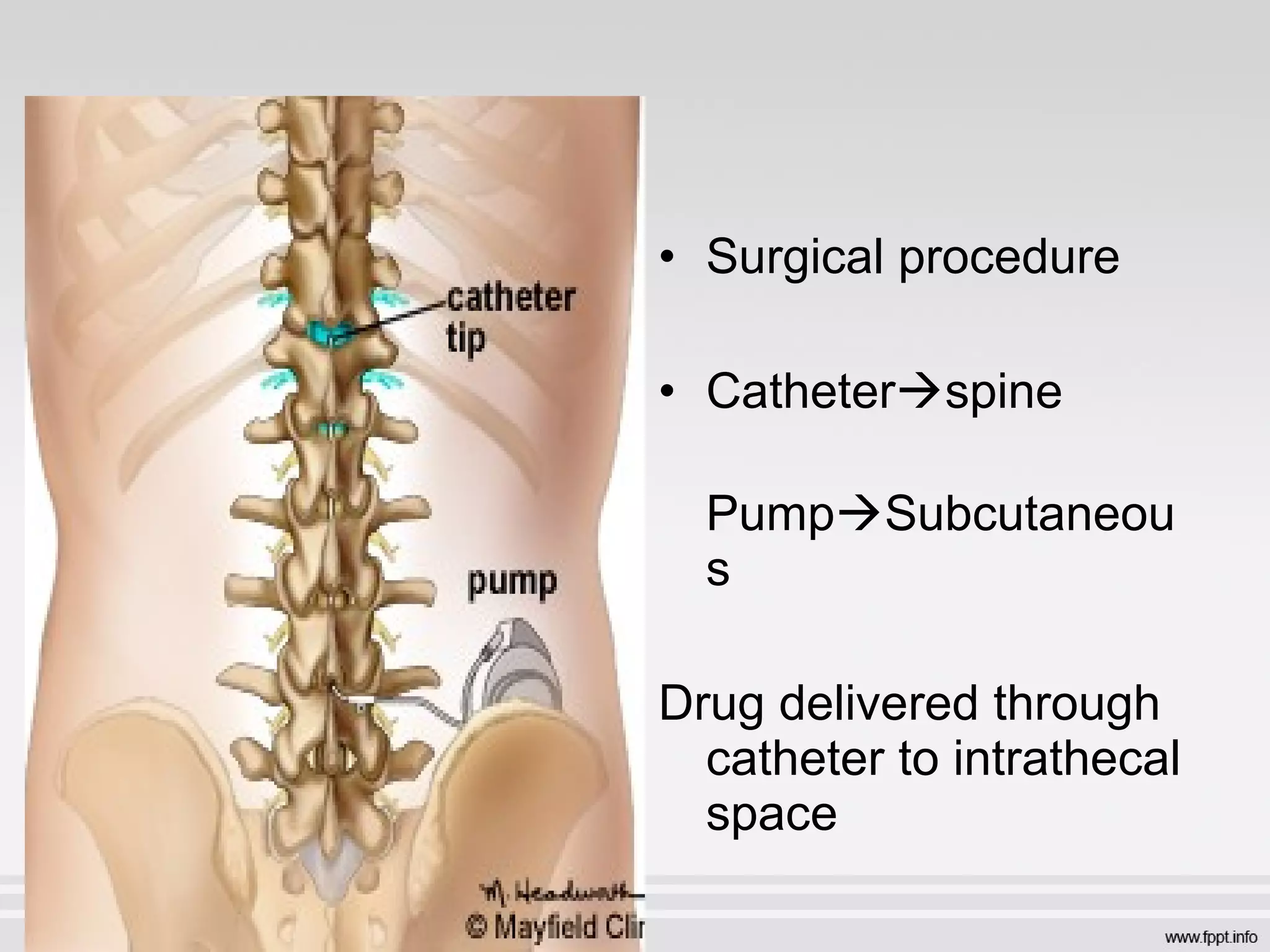
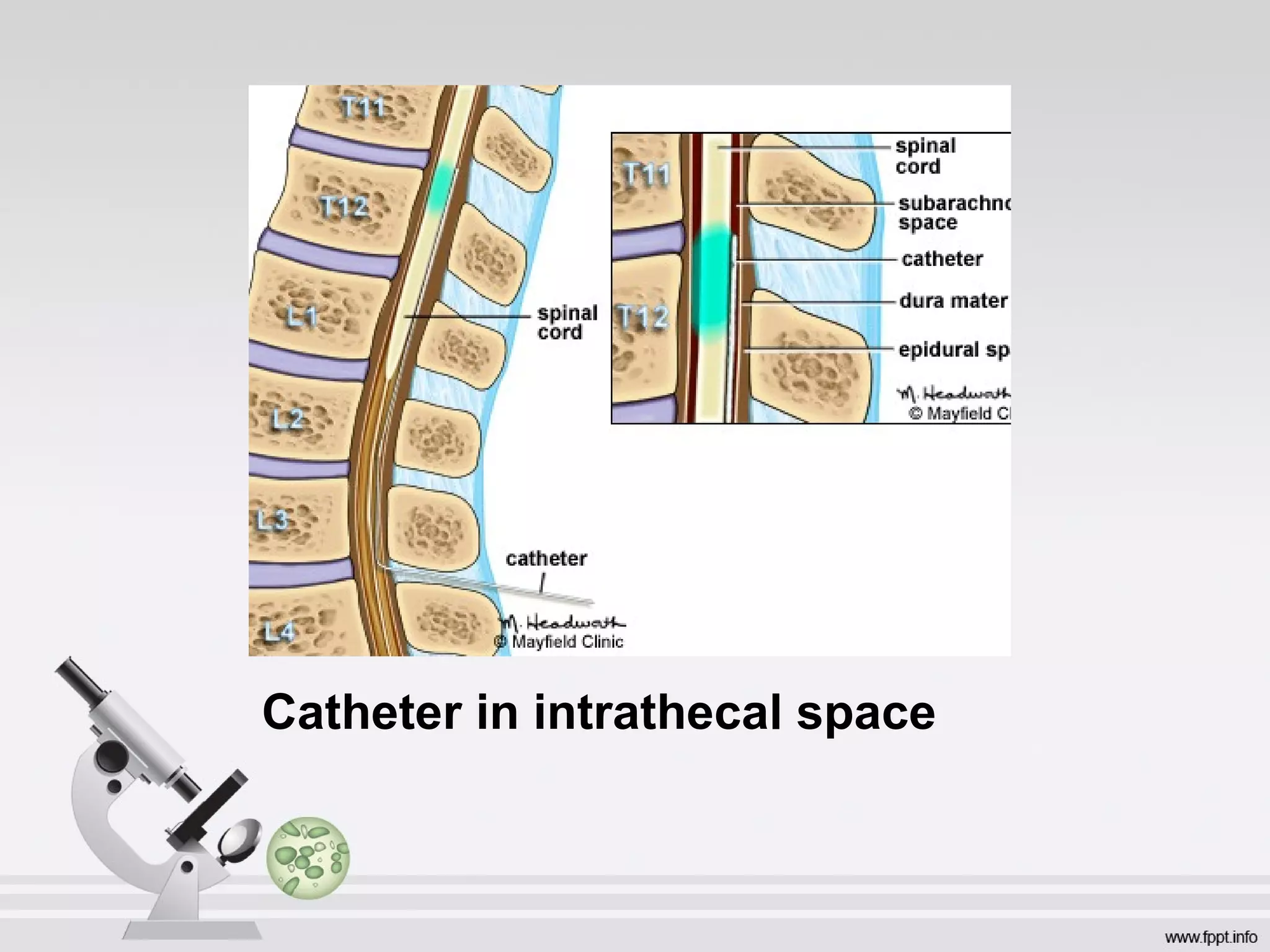
Patient Controlled Epidural Analgesia
PCEA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nddsmy-160122173628/75/Newer-Drug-Delivery-Systems-30-2048.jpg)