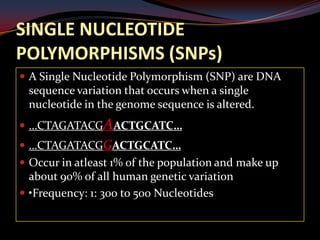
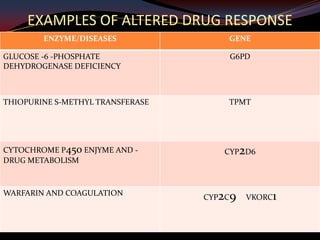
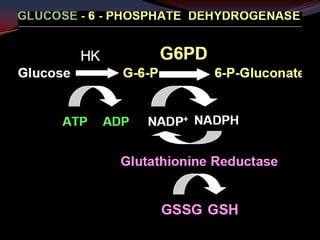
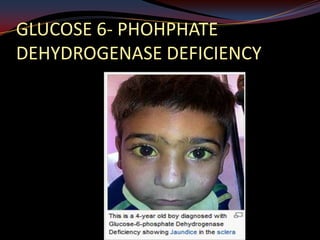
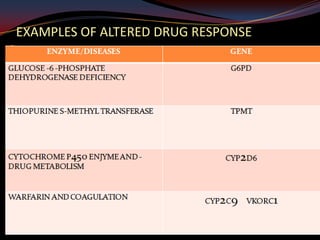
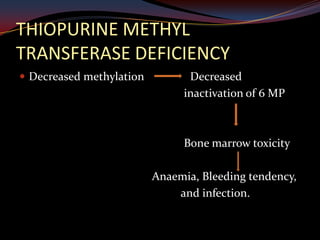
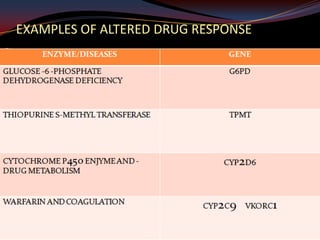
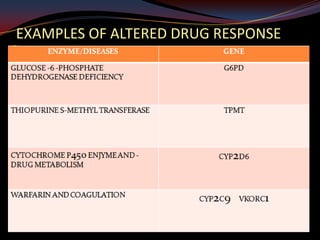
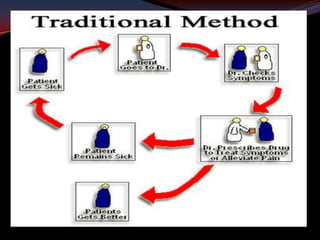
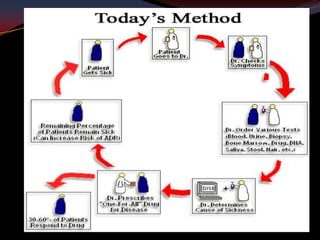
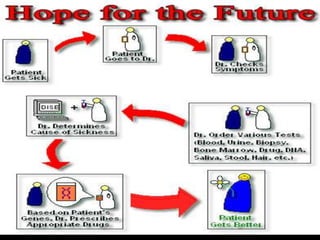
This document provides an overview of pharmacogenomics. It defines pharmacogenomics as the study of how genetic variations influence individual drug responses. It discusses how single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can alter drug metabolism and response. Examples are provided of genes like G6PD, TPMT, CYP2D6 and CYP2C9 that influence drug toxicity and efficacy. Benefits of pharmacogenomics include more powerful and safer drugs through personalized treatment based on an individual's genetic profile. Ethical concerns around privacy, discrimination, and drug availability are also discussed.