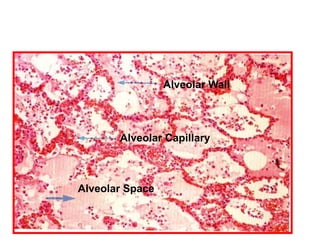
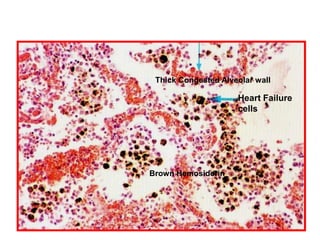
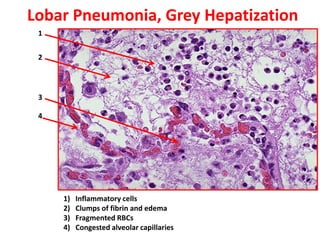
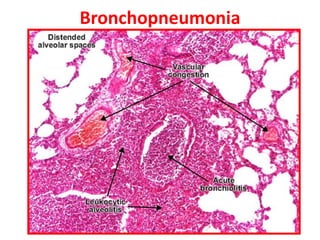
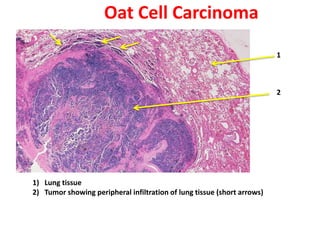
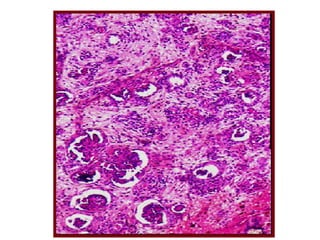
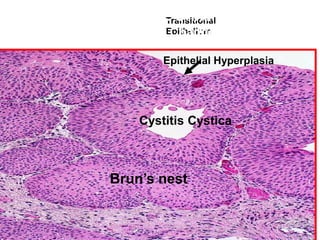
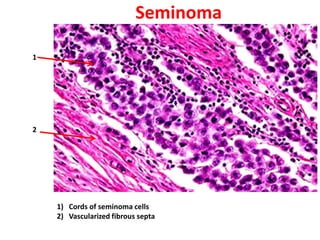
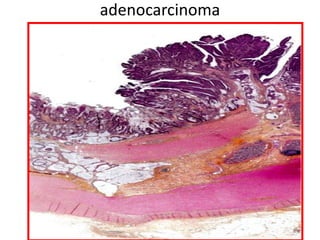
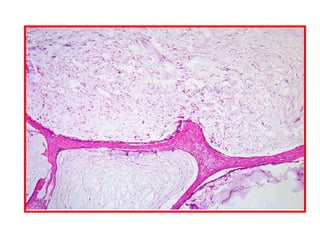
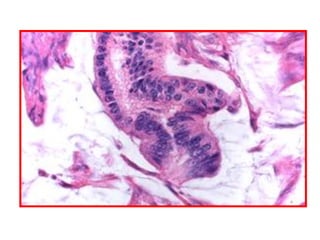
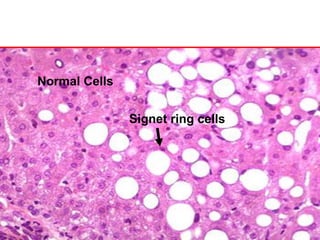
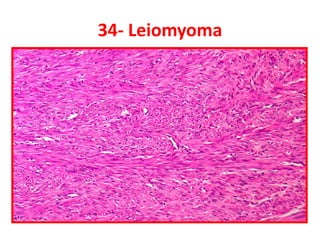
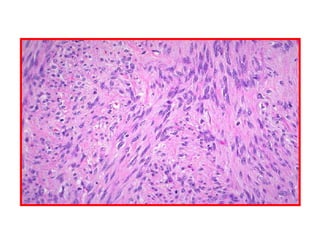
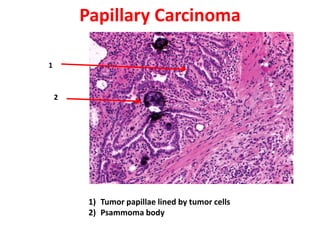
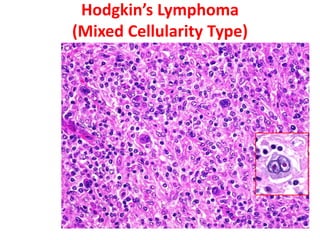
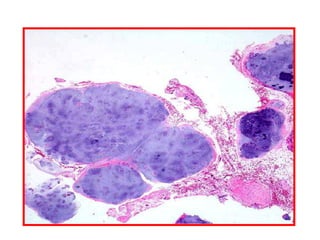
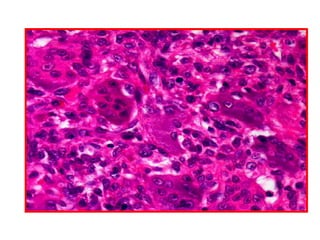
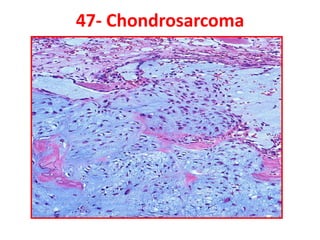
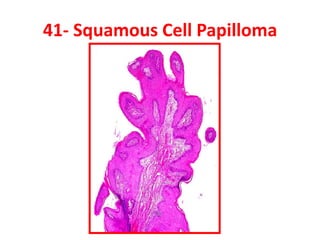
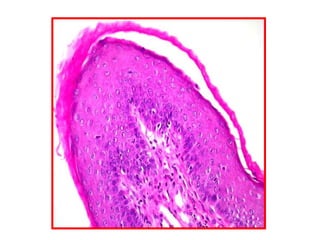
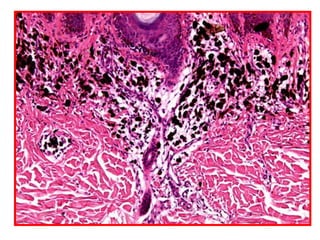
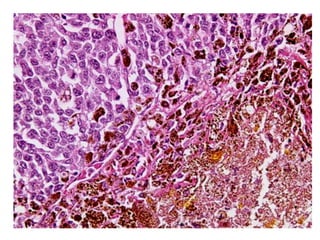
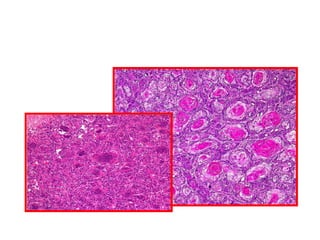
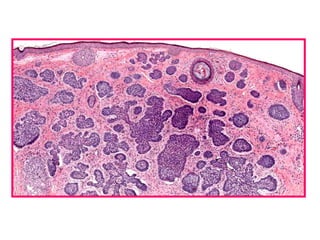
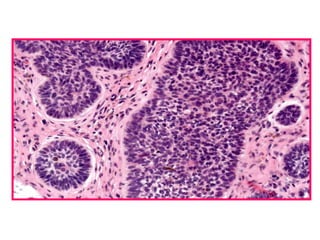
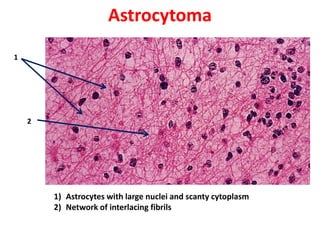
Allergic Nasal Polyp is characterized by:
1) Hyperplastic respiratory epithelium
2) Edematous stroma
3) Dilated congested capillaries
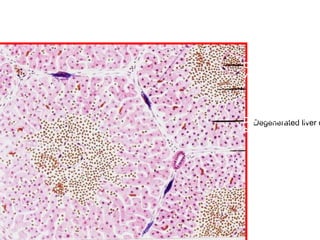
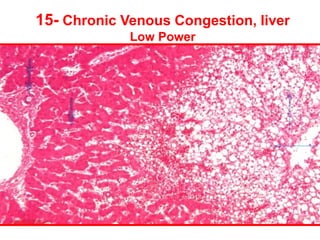
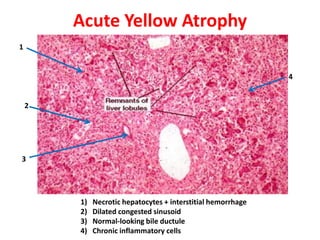
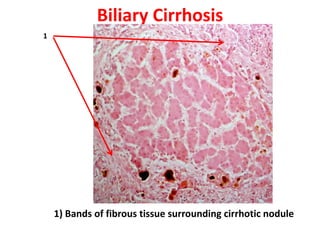
The document contains diagrams and photomicrographs of various pathological conditions affecting multiple organ systems. The sections describe microscopic findings, histological features, and pathological changes seen in conditions such as pneumonia, emphysema, infarction, cancer, glomerulonephritis, bilharziasis, appendicitis, liver diseases, and others.