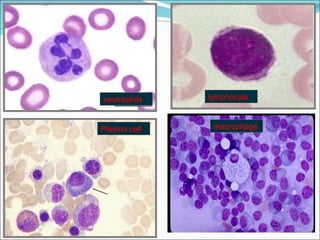
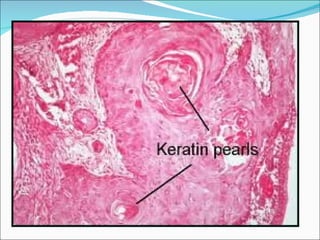
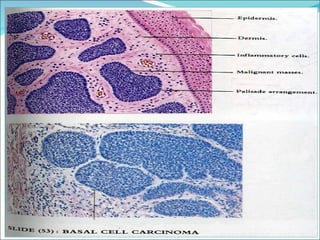
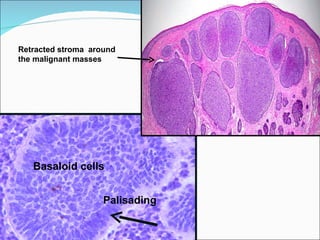
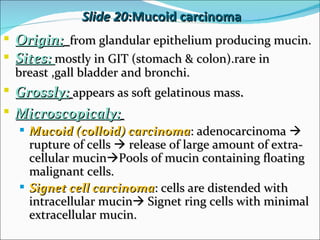
1) The document discusses various types of inflammation, benign and malignant tumors found in different organs of the body. It provides microscopic images and descriptions of slides showing examples like acute appendicitis, chronic skin inflammation, myocardial scarring, etc.
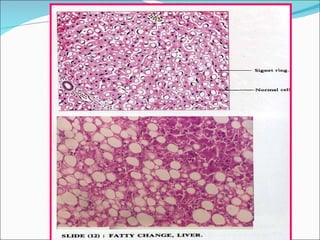
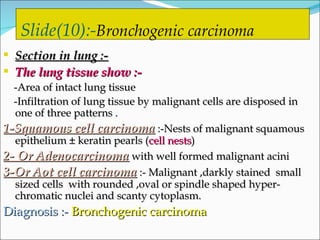
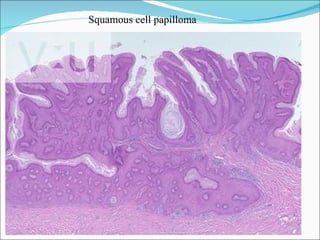
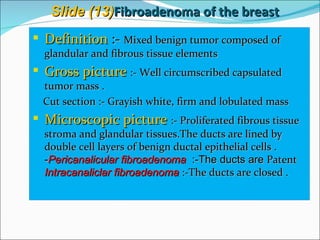
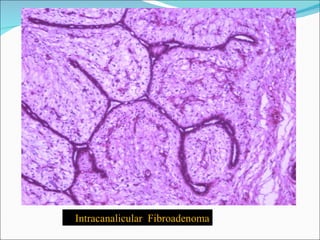
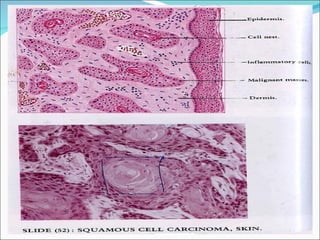
2) Key pathological entities summarized from the slides include acute suppurative appendicitis, chronic skin inflammation, fatty change of the liver, recent thrombus, atherosclerosis, lobar pneumonia, nasal polyp, bronchogenic carcinoma, squamous cell papilloma, fibroadenoma, fibroma, and fibrosarcoma.
3) The document provides detailed summaries of the histological features seen in slides of various common benign and malignant epithelial and mesen