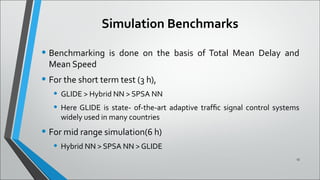
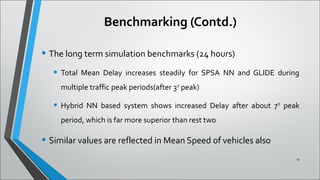
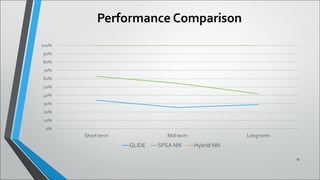
This document describes a neural network system for real-time traffic signal control using a hybrid multi-agent approach. It discusses previous work using neural networks and stochastic approximation for traffic control. The proposed system uses multiple sensors to continuously learn traffic patterns and control signals. Simulation results over 3, 6, and 24 hours showed the hybrid neural network approach had lower mean delays than other methods, especially over longer periods as traffic fluctuated. While this system can automatically control traffic with minimal maintenance, limitations include potential unsuitability for areas with less variable traffic and high implementation costs.






![RealTimeTraffic Signal Control using NN
7
Fig. 1 : Traffic Control Loop[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralnetworkforreal-timetrafficsignalcontrol-150206235042-conversion-gate02/85/Neural-network-for-real-time-traffic-signal-control-7-320.jpg)


![Input to generate signal logic
10Fig. 2 : Chromosome Structure[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralnetworkforreal-timetrafficsignalcontrol-150206235042-conversion-gate02/85/Neural-network-for-real-time-traffic-signal-control-10-320.jpg)





![References
• [1] S. Chiu and S. Chand, ‘Neural Network for real time traffic signal control’,
in Proc. 32nd IEEE Conf. Decision Control, pp. 1987–1902, 2006.
• [2] S. Mikami andY. Kakazu, ‘Genetic reinforcement learning for cooperative
traffic signal control’, in Proc. 1st IEEE Conf. Evol. Comput., vol. 1, pp. 223–
228, 2011.
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralnetworkforreal-timetrafficsignalcontrol-150206235042-conversion-gate02/85/Neural-network-for-real-time-traffic-signal-control-19-320.jpg)
