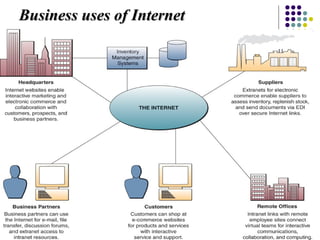
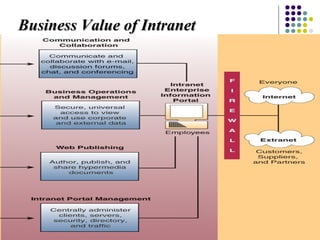
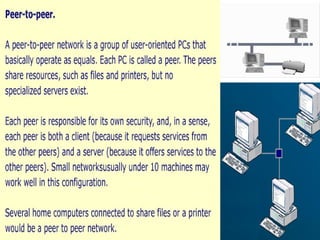
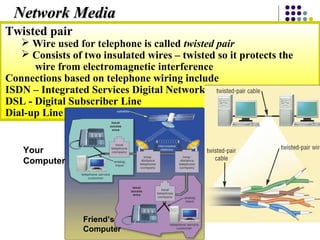
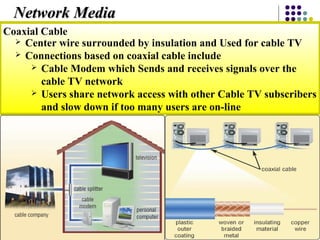
Chapter 6 covers fundamental concepts of telecommunications and networking, detailing the distinctions between the internet, intranets, and extranets. It discusses key trends in the telecommunications industry, the hardware and media used, and the functions of various network types and topologies. The chapter also emphasizes the business importance of networking for data sharing and collaboration.