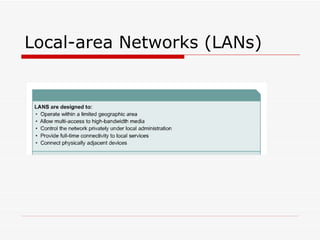
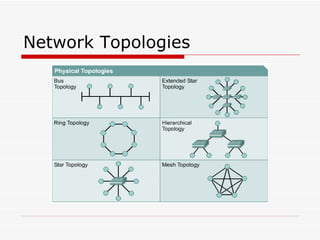
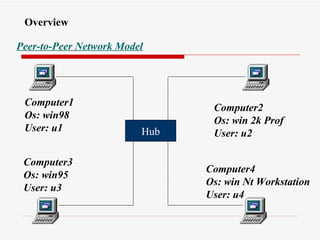
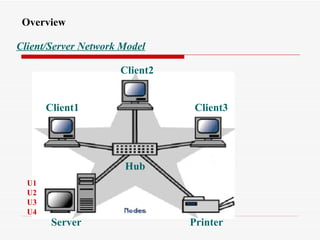
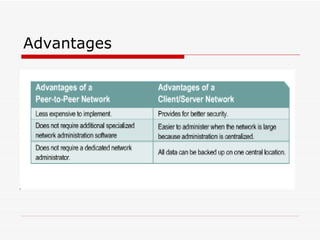
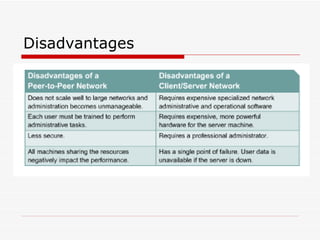
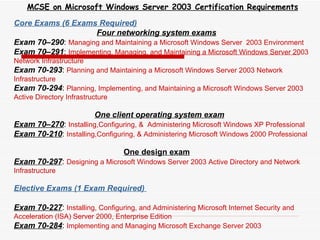
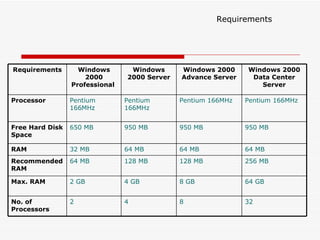
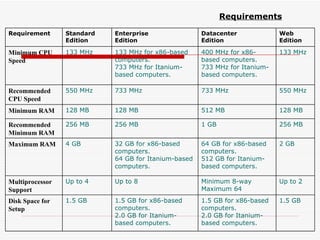
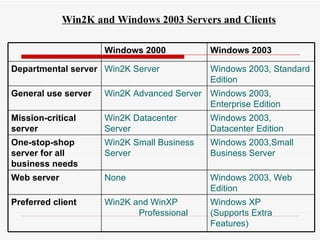
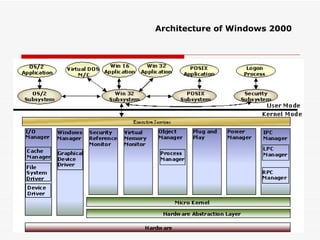
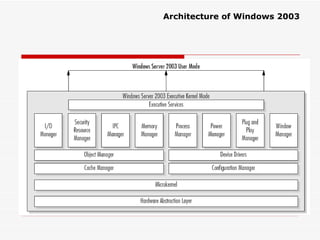
The document provides an overview of networking concepts including network types (LAN, WAN, MAN), common network devices (hub, switch, router, NIC), network topologies (bus, star, ring, mesh), and logical network models (peer-to-peer, client/server). It also discusses Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 server editions, requirements, features, and the boot process.