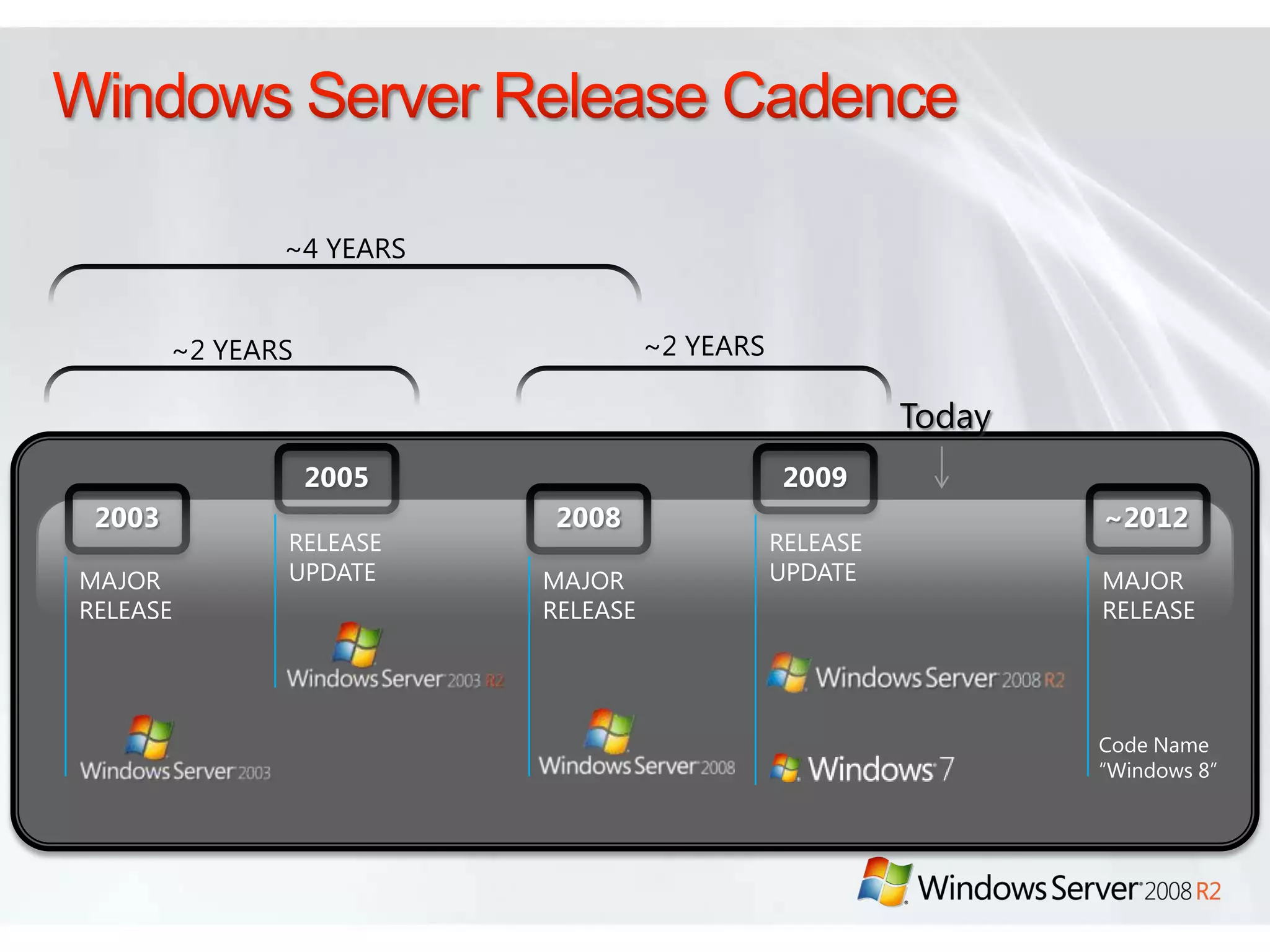
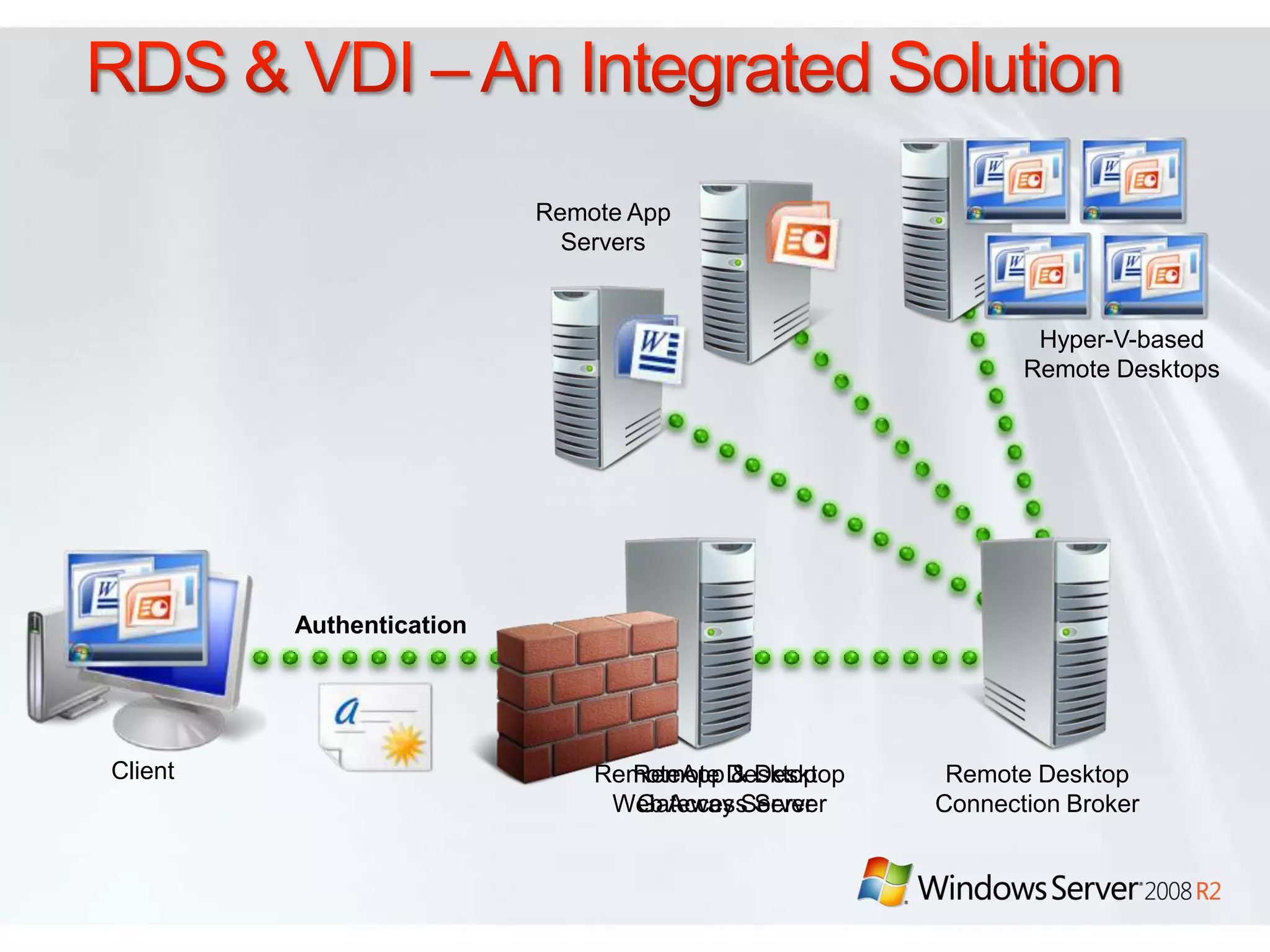
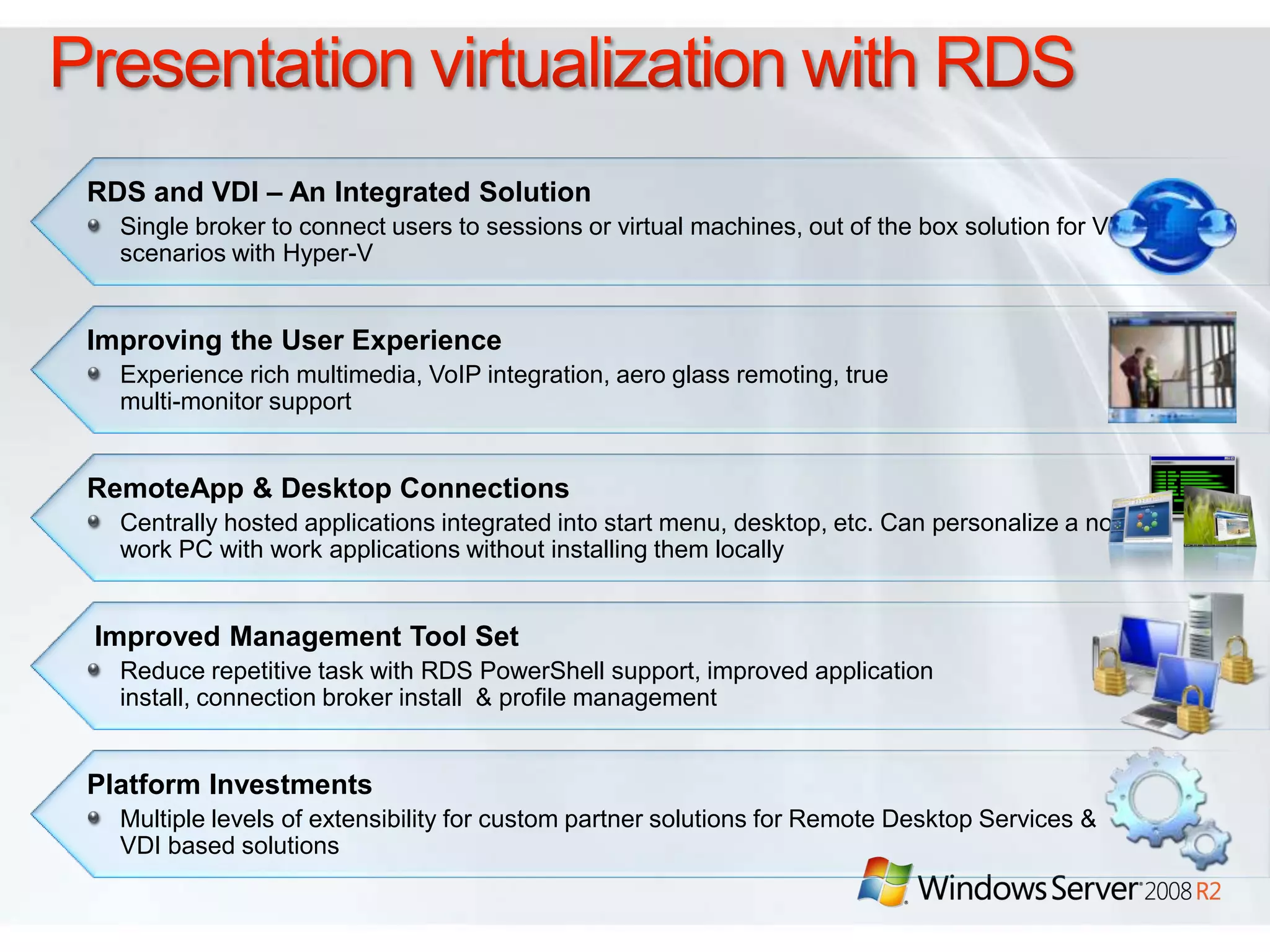
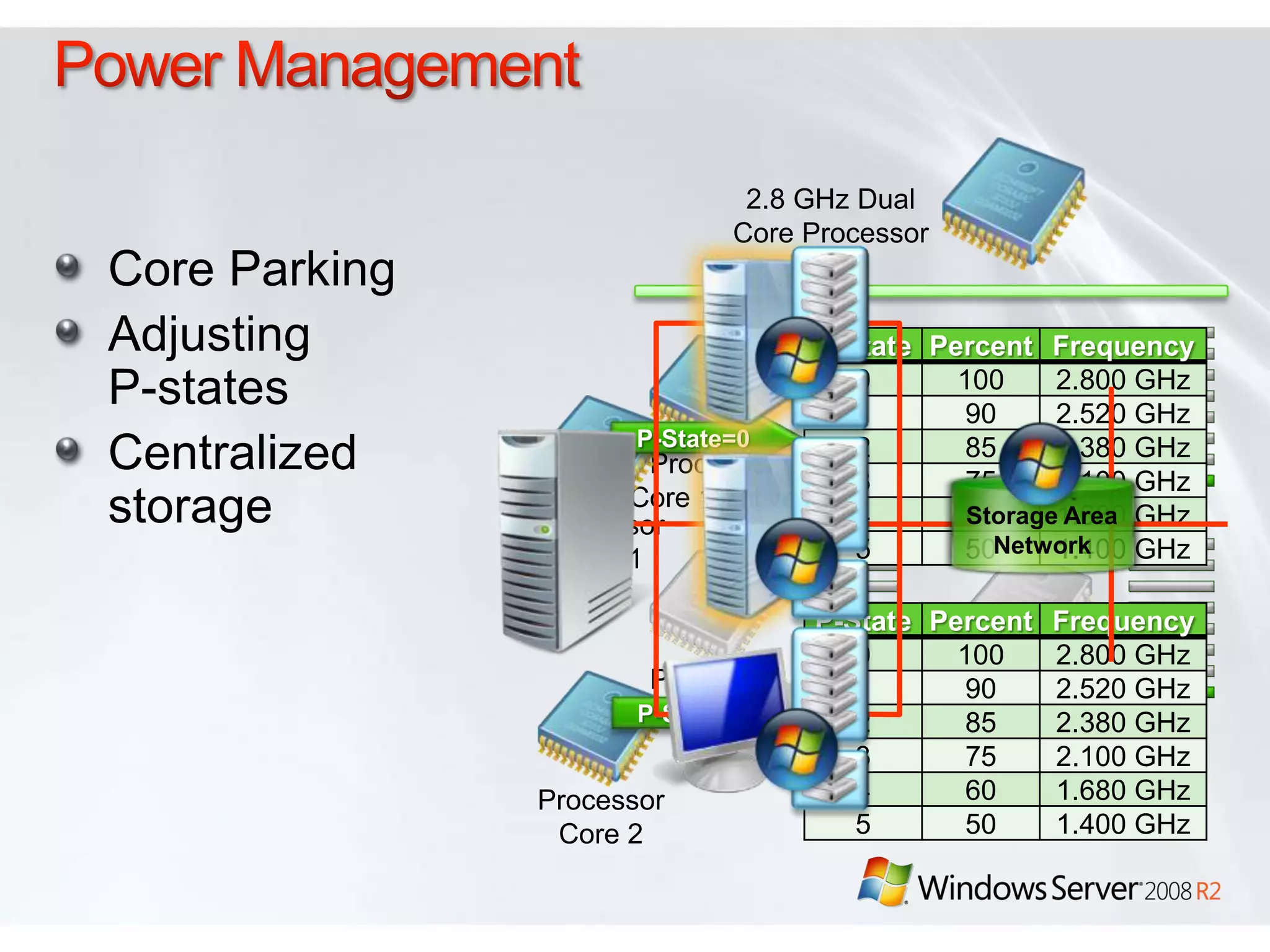
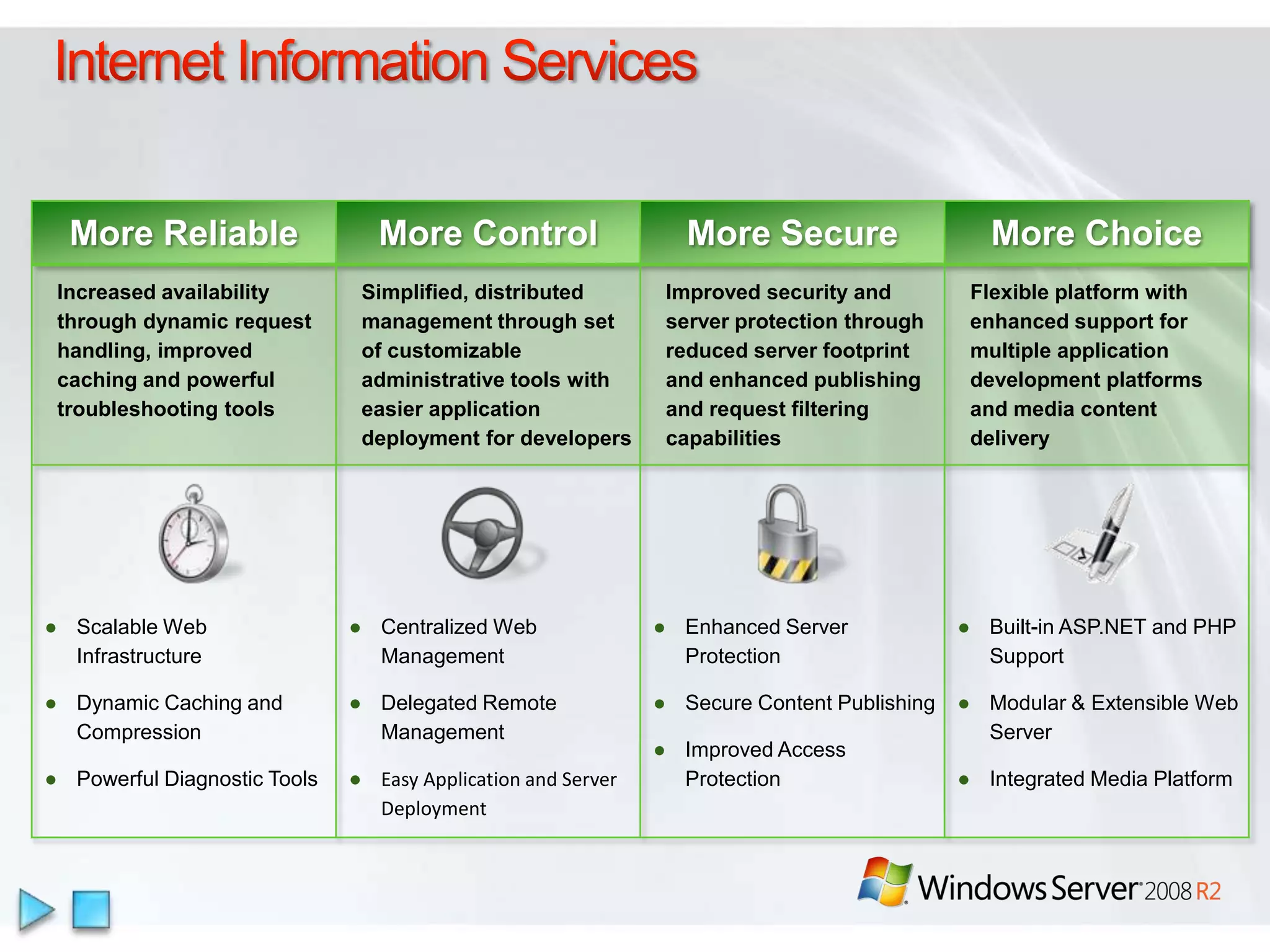
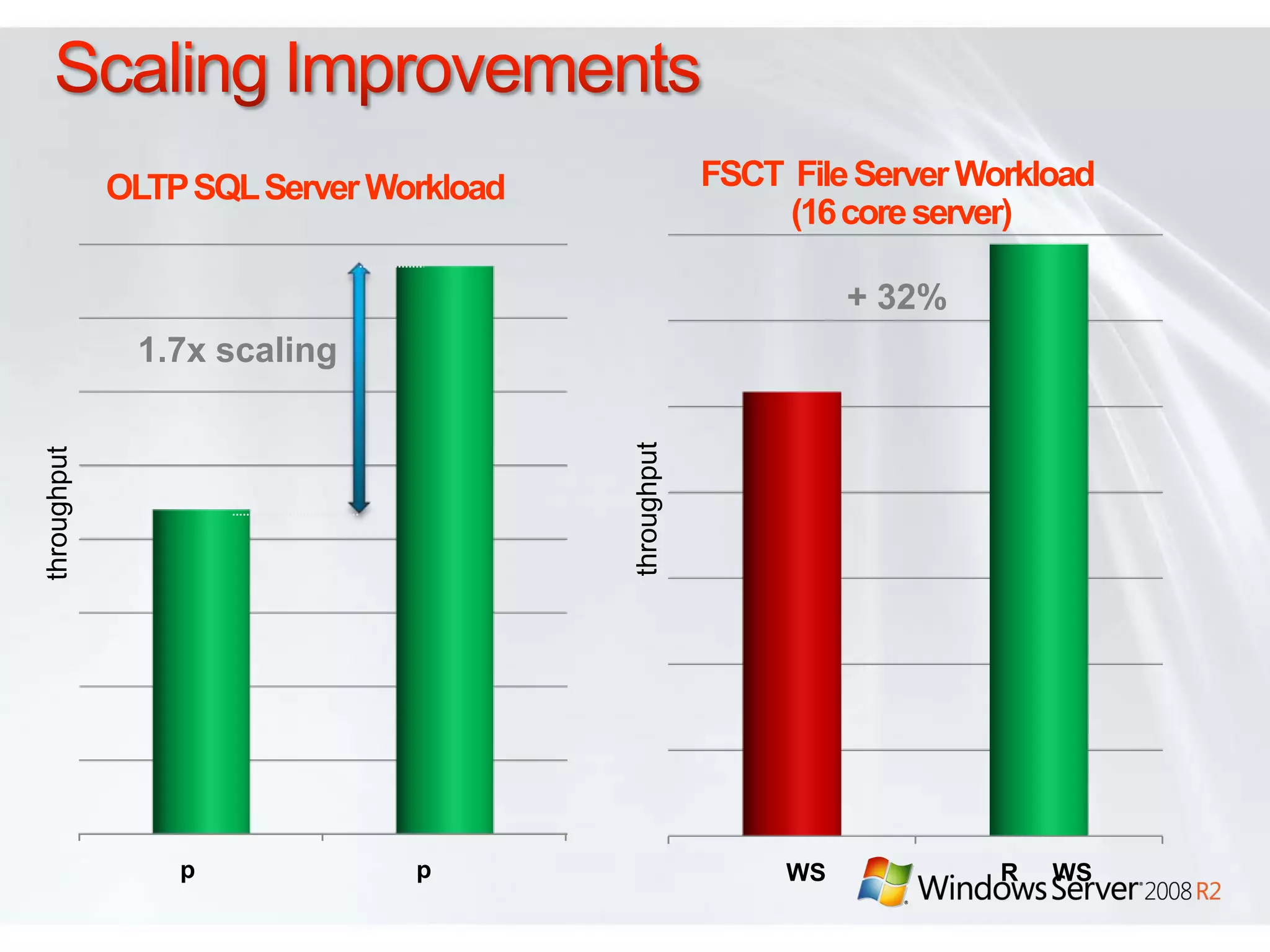
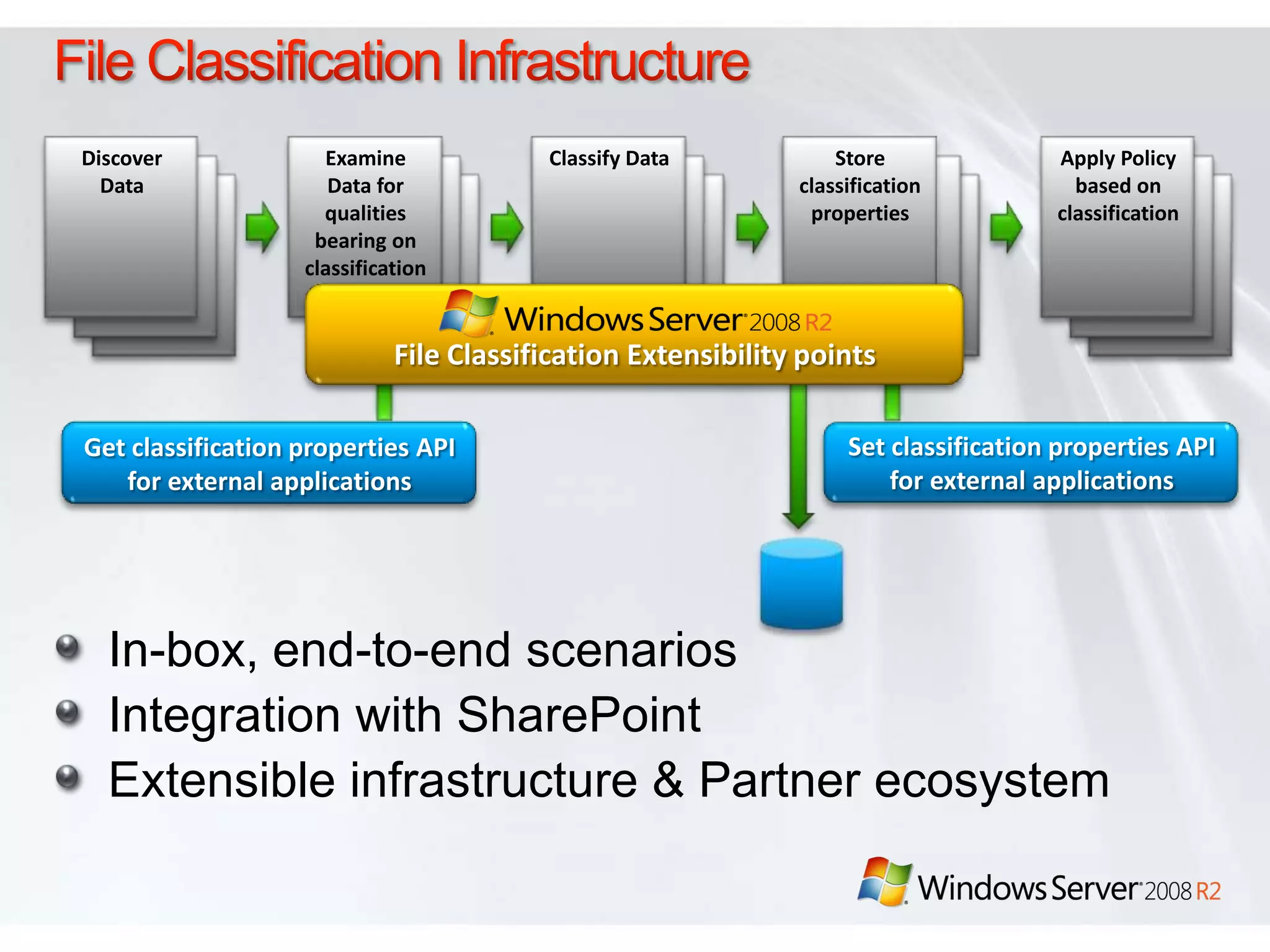
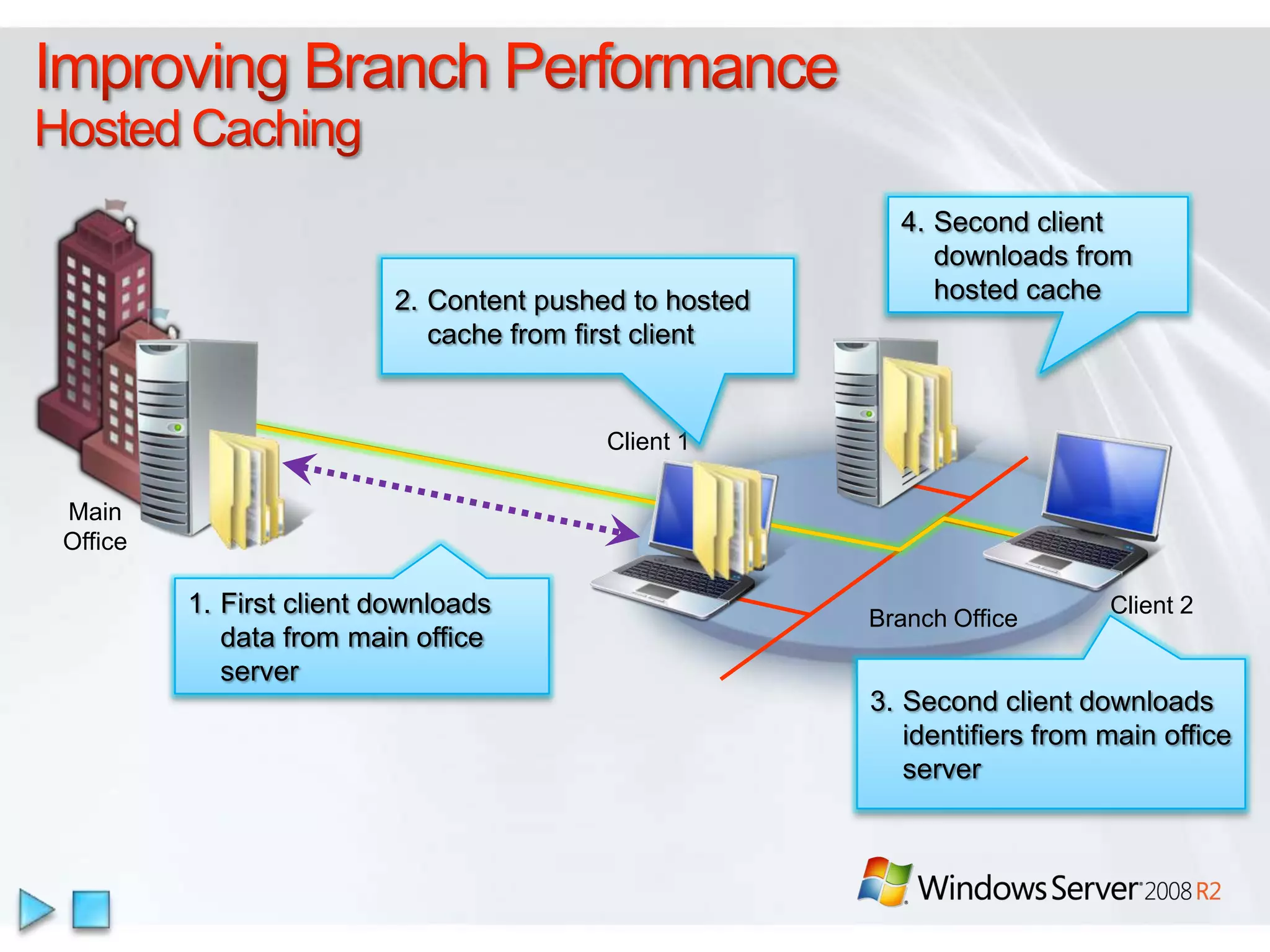
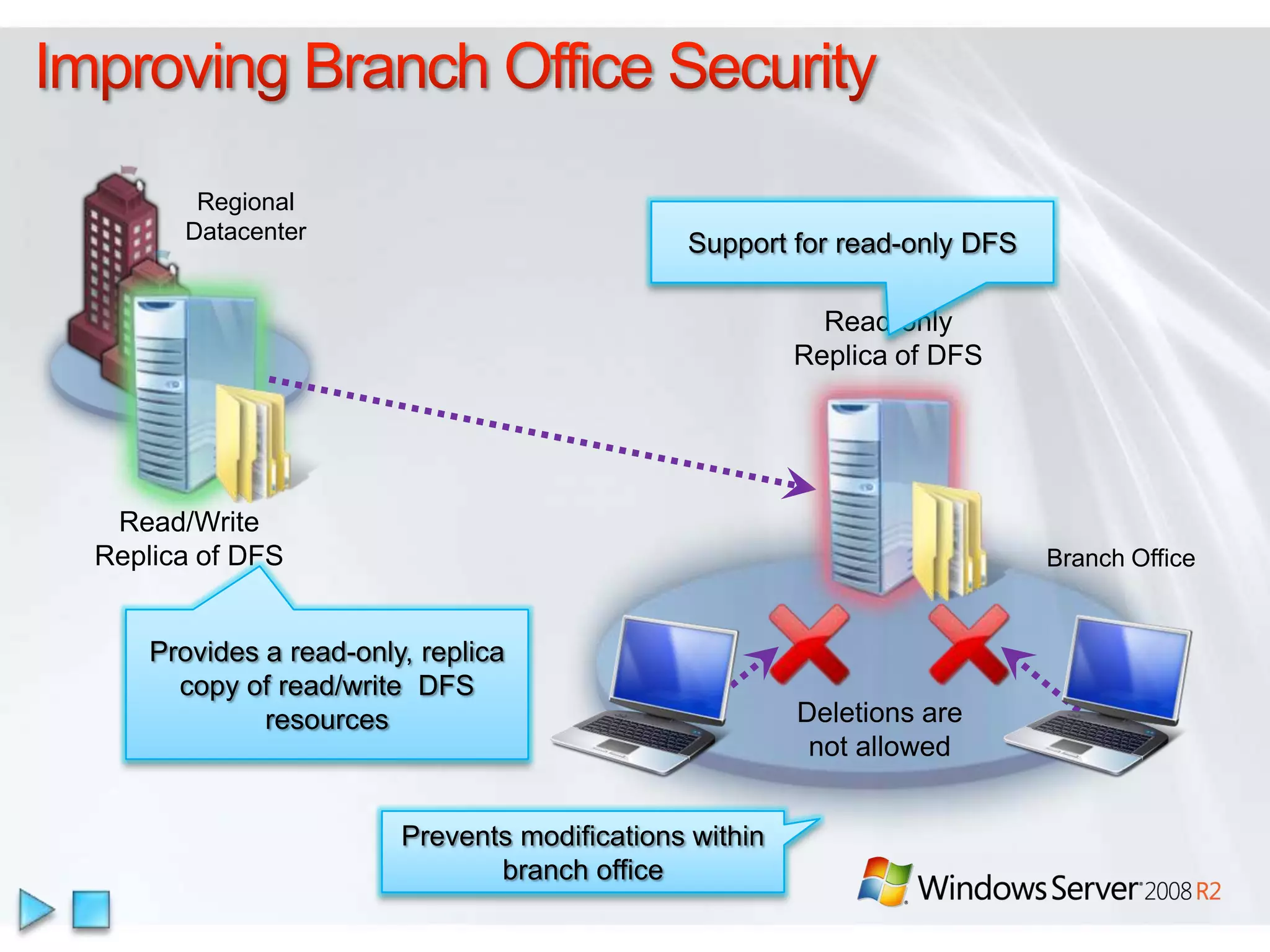
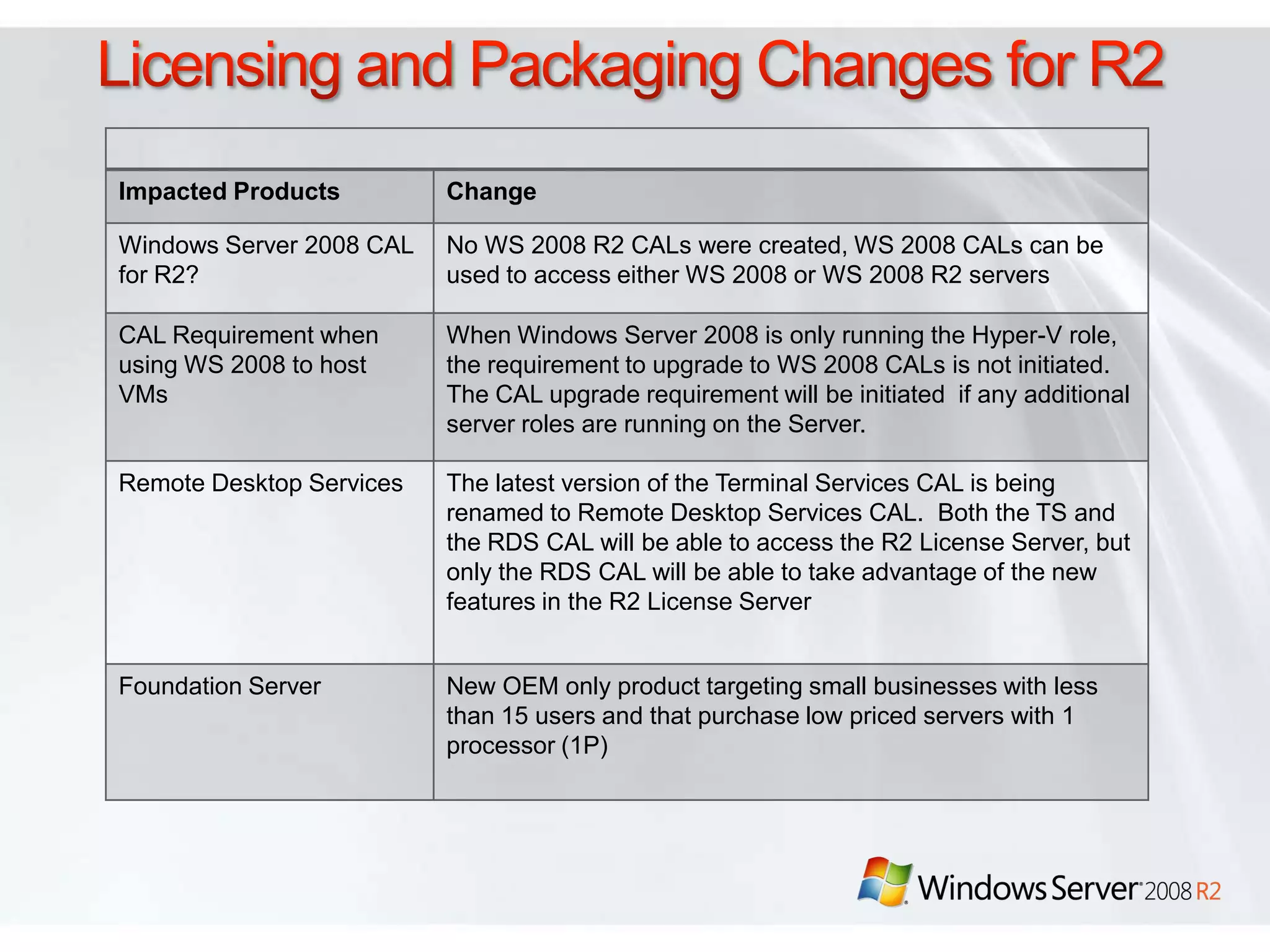
Windows Server 2008 R2 includes several new features and enhancements. It provides improved virtualization capabilities with Hyper-V including live migration and support for up to 64 logical processors. Management is simplified with new consoles like Active Directory Administration Center and PowerShell 2.0. Performance and scalability are increased with support for up to 256 logical processors and reduced memory footprint. New technologies like DirectAccess and BranchCache improve connectivity and performance for remote and branch offices.