Networking
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
6 likes•1,191 views
The document discusses the OSI reference model and networking concepts. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model from the physical layer to the application layer. It also covers networking topics like LANs, WANs, MANs, internetworking, addressing, modes of service, and connecting networks using devices like repeaters, bridges, routers and gateways.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Osi model with neworking overview

This document provides an overview of networking concepts including the OSI model layers, network types, and networking devices. It describes the responsibilities and issues handled at each OSI layer, from the physical layer transmitting raw bits to the application layer running application-specific protocols. It also covers topics like addressing schemes, modes of service, and how devices like repeaters, bridges, routers, and gateways operate to connect different network types.
Week 2

The document describes the OSI network model, which structures communications functions into a hierarchy of seven layers. Each layer offers services to the higher layers and communicates with corresponding layers in other nodes using agreed protocols. This modular layering reduces network complexity through encapsulation. Data moves down from higher to lower layers at the source, and up from lower to higher layers at the destination.
Osi model in networking

The document summarizes the seven layers of the OSI model from top to bottom. It describes each layer's main responsibilities and concerns. The seven layers are: Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, and Physical. The Physical Layer is responsible for moving data bits across a transmission medium. The Data Link Layer is responsible for moving frames between nodes and handles framing, addressing, error control, and flow control. The Network Layer is responsible for packet delivery from source to destination and handles addressing, routing, and interfacing with data link.
Osi model

Power point presentation on osi model.
A good presentation cover all topics.
For any other type of ppt's or pdf's to be created on demand contact -dhawalm8@gmail.com
mob. no-7023419969
Chapter 2. vantage understanding sensor placement in networks

This document provides an overview of network layering and how it impacts network vantage for sensor placement and data collection. It discusses the OSI 7-layer model and TCP/IP 4-layer model and how sensors can monitor different layers. It describes how vantage is determined at the physical layer through collision domains, at the data link layer through switches, and how routing impacts vantage at the network layer. It also covers the different addressing schemes used at each layer including MAC addresses, IPv4 addresses, and how protocols like ARP are used to map between them.
OSI Model of Networking

A presentation on the OSI model. Describes the need for a layered approach, and discusses the function of each of the layers.
The OSI model and TCP/IP

This document discusses computer networks and networking concepts. It begins by defining what a computer network is and distinguishing between local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It then introduces the OSI model, which describes how systems communicate over a network through seven layers of abstraction. The document discusses each of the seven layers and provides examples. It also categorizes different types of connecting devices like repeaters, bridges, switches, and routers, and notes which OSI layers each operates in.
OSI Reference Model and TCP/IP (Lecture #3 ET3003 Sem1 2014/2015)

This document provides an overview of the OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suite for computer networks. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model from the physical layer to the application layer and their functions. It then explains that while the OSI model was intended as a standard, TCP/IP became dominant in practice. The four layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite are also outlined - the physical and data link layers have no standard protocols, while the network layer uses IP and the transport layer includes TCP and UDP. The application layer combines functions from several OSI layers.
Recommended
Osi model with neworking overview

This document provides an overview of networking concepts including the OSI model layers, network types, and networking devices. It describes the responsibilities and issues handled at each OSI layer, from the physical layer transmitting raw bits to the application layer running application-specific protocols. It also covers topics like addressing schemes, modes of service, and how devices like repeaters, bridges, routers, and gateways operate to connect different network types.
Week 2

The document describes the OSI network model, which structures communications functions into a hierarchy of seven layers. Each layer offers services to the higher layers and communicates with corresponding layers in other nodes using agreed protocols. This modular layering reduces network complexity through encapsulation. Data moves down from higher to lower layers at the source, and up from lower to higher layers at the destination.
Osi model in networking

The document summarizes the seven layers of the OSI model from top to bottom. It describes each layer's main responsibilities and concerns. The seven layers are: Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, and Physical. The Physical Layer is responsible for moving data bits across a transmission medium. The Data Link Layer is responsible for moving frames between nodes and handles framing, addressing, error control, and flow control. The Network Layer is responsible for packet delivery from source to destination and handles addressing, routing, and interfacing with data link.
Osi model

Power point presentation on osi model.
A good presentation cover all topics.
For any other type of ppt's or pdf's to be created on demand contact -dhawalm8@gmail.com
mob. no-7023419969
Chapter 2. vantage understanding sensor placement in networks

This document provides an overview of network layering and how it impacts network vantage for sensor placement and data collection. It discusses the OSI 7-layer model and TCP/IP 4-layer model and how sensors can monitor different layers. It describes how vantage is determined at the physical layer through collision domains, at the data link layer through switches, and how routing impacts vantage at the network layer. It also covers the different addressing schemes used at each layer including MAC addresses, IPv4 addresses, and how protocols like ARP are used to map between them.
OSI Model of Networking

A presentation on the OSI model. Describes the need for a layered approach, and discusses the function of each of the layers.
The OSI model and TCP/IP

This document discusses computer networks and networking concepts. It begins by defining what a computer network is and distinguishing between local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It then introduces the OSI model, which describes how systems communicate over a network through seven layers of abstraction. The document discusses each of the seven layers and provides examples. It also categorizes different types of connecting devices like repeaters, bridges, switches, and routers, and notes which OSI layers each operates in.
OSI Reference Model and TCP/IP (Lecture #3 ET3003 Sem1 2014/2015)

This document provides an overview of the OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suite for computer networks. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model from the physical layer to the application layer and their functions. It then explains that while the OSI model was intended as a standard, TCP/IP became dominant in practice. The four layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite are also outlined - the physical and data link layers have no standard protocols, while the network layer uses IP and the transport layer includes TCP and UDP. The application layer combines functions from several OSI layers.
OSI 7 Layer Model

The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to their underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard protocols. The model partitions a communication system into abstraction layers. The original version of the model defined seven layers.
OSI Network Reference Model

The document discusses network models and the OSI model. It describes the OSI model as having 7 layers that define standards for computer communication and divide network functions into smaller, manageable parts. Each layer provides services to the layer above it and communicates with the corresponding layer on other devices. The layers include the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layers.
Osi reference model and the tcp

The document compares the OSI reference model and the TCP/IP model. The OSI reference model has 7 layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layer. It was developed by ISO as a standard for network communication. The TCP/IP model has 4 layers - link, internet, transport and application layer. It is the communication protocol used for the internet and defines the rules for communication between computers over the internet. TCP and IP work together, with TCP handling communication between applications and networks, and IP handling communication between computers.
OSI layers

This document discusses reference models for computer networks, including the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It provides details on each of the seven layers of the OSI model, including the layer name and number, example protocols, and key functions. It notes that the OSI model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization while TCP/IP was initially designed by the U.S. Department of Defense. It concludes that it will use the hybrid reference model as the framework.
OSI Model

This document discusses network models and addressing in computer networks. It describes the OSI 7-layer model and its layers from physical to application layer. It also discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and how it maps to the OSI model. Finally, it covers the different types of addressing used in networks, including physical, logical, port, and specific addresses.
Computer Network - OSI model

The document discusses the seven layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, with a focus on the physical and data link layers. It describes the key responsibilities of the physical layer, including representing bits, synchronizing data transmission, defining transmission media and topology. It also outlines the major duties of the data link layer, such as framing data, implementing addressing, and handling errors.
Chapter1ccna

The document provides an overview of networking concepts including:
- The OSI model which divides network communication into 7 layers and describes the function of each layer.
- Ethernet networking standards including half and full duplex modes and different cable types.
- Data encapsulation which involves adding protocol information at each OSI layer as data moves through a network.
- Cisco's three layer model which divides networks into core, distribution, and access layers.
Osi model vs TCP/IP

The document compares the OSI model and the TCP/IP model. The OSI model consists of 7 layers and defines a standardized protocol-independent framework. The TCP/IP model has 4 layers and was developed based on the protocols used for the Internet. Key differences are that OSI has stricter layering while TCP/IP layers are more loosely defined, and TCP/IP focuses on the specific protocols used for Internetworking while OSI aims to be protocol-independent.
OSI and TCPIP Model

The document discusses the OSI reference model and TCP/IP reference model. The OSI model divides network architecture into seven layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layer. The TCP/IP model has four layers - process/application layer, host-to-host layer, internet layer, and network access layer. The TCP/IP model was created by the US Department of Defense to allow networks to survive disruptions like nuclear war.
Reference models in Networks: OSI & TCP/IP

The document discusses reference models and the OSI reference model. It provides details on:
- The need for a reference model to standardize network components and layer functions to promote interoperability.
- The OSI reference model, approved in 1984, which divides communication problems into seven layers to aid in network interconnection.
- Each of the seven layers of the OSI model, describing their functions and responsibilities for moving data through the network.
A Technical Seminar on OSI model

The document discusses a technical seminar on the OSI model. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model, including the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layers. It explains the functions of each layer and how they interact to exchange data and deliver messages from source to destination across networks.
Osi model

The document provides information on the OSI reference model and TCP/IP reference model:
1. The OSI model consists of 7 layers that define a standard way for different network components to communicate with each other. Each layer provides services to the layer above it and relies on the layer below.
2. The TCP/IP model has 4 layers - application, transport, internet, and host-to-network. It is a more practical standard used to build the Internet, while the OSI model provides a theoretical framework.
3. Both models separate networking functions into logical layers for modularity and interoperability. However, the TCP/IP model combines some OSI layers and has fewer layers overall.
Osi protocols

This document discusses the OSI protocol suite, which includes numerous standard protocols based on the OSI reference model to facilitate multivendor equipment interoperability. It maps the OSI protocol suite to the seven layers of the OSI reference model, describing standards for the physical, data link, network, and other layers. Key points covered include OSI routing protocols, supported media access protocols, connectionless and connection-oriented network services, and OSI addressing using network service access points.
Network Protocols

Network protocols are sets of rules that govern communications between computers on a network. They configure characteristics like cabling, topology, and bandwidth. The OSI model is an industry standard that defines seven layers of functions for communication between any two points on a network. Each layer has a specific role, with the lowest layers involving physical networking and higher layers dealing with applications and data. Protocols at each layer work together to establish consistent rules for exchanging data and messages between networked devices.
Chap2

This document discusses network models and addressing in computer networks. It describes the OSI 7-layer model and compares it to the TCP/IP protocol suite. Each layer of the OSI model has specific duties, such as physical addressing at the data link layer and logical addressing at the network layer. TCP/IP protocols map to these layers, with IP at the network layer handling logical addressing. There are four levels of addressing in TCP/IP: physical, logical, port, and specific addresses that relate to different layers and allow identification of devices, networks, applications and resources on the network.
OSI model (7 LAYER )

This document discusses layered network models, specifically the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It provides an overview of each layer in both models and their functions. The key points are:
- The OSI model defines 7 layers that break communication into smaller parts to simplify the process and allow different hardware/software to work together.
- The TCP/IP model has 4 layers - application, transport, internet, and network access. It is used widely on the internet.
- Each layer adds header information to data as it moves down the stack. This encapsulation allows communication between layers and across networks.
ZERO-LECTURE.pptx

This document provides information on the course "Data Communication and Computer Networks" including the course code, credits, objectives, description, outcomes and syllabus. The main focus of the course is on local area network organization, implementation, and management. The course introduces computer network design, operations, and topics like the OSI model, error detection, local area networks, routing, and network protocols. Upon completion, students should be able to design, implement and maintain a typical computer network. The syllabus outlines 5 units that cover introductory concepts, data link layer, network layer, transport layer, and application layer. Assessment includes mid-term exams conducted by the college and a university end-term exam.
Lecture 02 networking

The document discusses the OSI reference model, which breaks network communication into 7 layers, with each layer performing a unique task and only interacting with adjacent layers. It also compares the OSI model to the TCP/IP model. The key difference is that TCP/IP combines the functions of the OSI data link and physical layers. The document further explains the Internet Protocol (IP) which specifies packet formatting and addressing for data transmission. It distinguishes between IPv4 and IPv6, noting IPv6 uses a 128-bit addressing scheme and provides improvements over IPv4 such as no NAT.
Osi model

The document discusses network models including the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model and the functions of each layer. It also discusses the four layers of the TCP/IP model and compares the two models, noting they are similar in concept but differ in number of layers and how protocols fit within each model.
Introduction to Computer Networks

Introductory overview of OSI protocol stack and basic protocols. Useful for the first course on computer networks for undergraduates
Internet protocol (ip) ppt

IP specifies the format of packets, also called #datagrams, and the addressing scheme. Most networks combine IP with a higher-level protocol called Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which establishes a virtual connection between a destination and a source.
If you want to purchase the content e-mail me on dulith1989@gmail.com
Call Admission Control (CAC) with Load Balancing Approach for the WLAN Networks

The cell migrations take place between the different network operators, and require the significant information exchange between the operators to handle the migratory users. The new user registration requires the pre-shared information from the user’s equipment, which signifies the user recognition before registering the new user over the network. In this thesis, the proposed model has been aimed at the development of the new call admission control mechanism with the sub-channel assignment. The very basic utilization of the proposed model is to increase the number of the users over the given cell units, which is realized by using the sub-channel assignment to the users of the network. The proposed model is aimed at solving the issue by assigning the dual sub channels over the single communication channel. Also the proposed model is aimed at handling the minimum resource users by incorporating the load balancing approach over the given network segment. The load balancing approach shares the load of the overloaded cell with the cell with lowest resource utilization. The proposed model performance has been evaluated in the various scenarios and over all of the BTS nodes. The proposed model results have been obtained in the form of the resource utilization, network load, transmission delay, consumed bandwidth and data loss. The proposed model has shown the efficiency obtained by using the proposed call admission control (CAC) along with the new load balancing mechanism. The proposed model has shown the robustness of the proposed model in handling the cell overloading factors.
More Related Content
What's hot
OSI 7 Layer Model

The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to their underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard protocols. The model partitions a communication system into abstraction layers. The original version of the model defined seven layers.
OSI Network Reference Model

The document discusses network models and the OSI model. It describes the OSI model as having 7 layers that define standards for computer communication and divide network functions into smaller, manageable parts. Each layer provides services to the layer above it and communicates with the corresponding layer on other devices. The layers include the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layers.
Osi reference model and the tcp

The document compares the OSI reference model and the TCP/IP model. The OSI reference model has 7 layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layer. It was developed by ISO as a standard for network communication. The TCP/IP model has 4 layers - link, internet, transport and application layer. It is the communication protocol used for the internet and defines the rules for communication between computers over the internet. TCP and IP work together, with TCP handling communication between applications and networks, and IP handling communication between computers.
OSI layers

This document discusses reference models for computer networks, including the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It provides details on each of the seven layers of the OSI model, including the layer name and number, example protocols, and key functions. It notes that the OSI model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization while TCP/IP was initially designed by the U.S. Department of Defense. It concludes that it will use the hybrid reference model as the framework.
OSI Model

This document discusses network models and addressing in computer networks. It describes the OSI 7-layer model and its layers from physical to application layer. It also discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and how it maps to the OSI model. Finally, it covers the different types of addressing used in networks, including physical, logical, port, and specific addresses.
Computer Network - OSI model

The document discusses the seven layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, with a focus on the physical and data link layers. It describes the key responsibilities of the physical layer, including representing bits, synchronizing data transmission, defining transmission media and topology. It also outlines the major duties of the data link layer, such as framing data, implementing addressing, and handling errors.
Chapter1ccna

The document provides an overview of networking concepts including:
- The OSI model which divides network communication into 7 layers and describes the function of each layer.
- Ethernet networking standards including half and full duplex modes and different cable types.
- Data encapsulation which involves adding protocol information at each OSI layer as data moves through a network.
- Cisco's three layer model which divides networks into core, distribution, and access layers.
Osi model vs TCP/IP

The document compares the OSI model and the TCP/IP model. The OSI model consists of 7 layers and defines a standardized protocol-independent framework. The TCP/IP model has 4 layers and was developed based on the protocols used for the Internet. Key differences are that OSI has stricter layering while TCP/IP layers are more loosely defined, and TCP/IP focuses on the specific protocols used for Internetworking while OSI aims to be protocol-independent.
OSI and TCPIP Model

The document discusses the OSI reference model and TCP/IP reference model. The OSI model divides network architecture into seven layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layer. The TCP/IP model has four layers - process/application layer, host-to-host layer, internet layer, and network access layer. The TCP/IP model was created by the US Department of Defense to allow networks to survive disruptions like nuclear war.
Reference models in Networks: OSI & TCP/IP

The document discusses reference models and the OSI reference model. It provides details on:
- The need for a reference model to standardize network components and layer functions to promote interoperability.
- The OSI reference model, approved in 1984, which divides communication problems into seven layers to aid in network interconnection.
- Each of the seven layers of the OSI model, describing their functions and responsibilities for moving data through the network.
A Technical Seminar on OSI model

The document discusses a technical seminar on the OSI model. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model, including the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layers. It explains the functions of each layer and how they interact to exchange data and deliver messages from source to destination across networks.
Osi model

The document provides information on the OSI reference model and TCP/IP reference model:
1. The OSI model consists of 7 layers that define a standard way for different network components to communicate with each other. Each layer provides services to the layer above it and relies on the layer below.
2. The TCP/IP model has 4 layers - application, transport, internet, and host-to-network. It is a more practical standard used to build the Internet, while the OSI model provides a theoretical framework.
3. Both models separate networking functions into logical layers for modularity and interoperability. However, the TCP/IP model combines some OSI layers and has fewer layers overall.
Osi protocols

This document discusses the OSI protocol suite, which includes numerous standard protocols based on the OSI reference model to facilitate multivendor equipment interoperability. It maps the OSI protocol suite to the seven layers of the OSI reference model, describing standards for the physical, data link, network, and other layers. Key points covered include OSI routing protocols, supported media access protocols, connectionless and connection-oriented network services, and OSI addressing using network service access points.
Network Protocols

Network protocols are sets of rules that govern communications between computers on a network. They configure characteristics like cabling, topology, and bandwidth. The OSI model is an industry standard that defines seven layers of functions for communication between any two points on a network. Each layer has a specific role, with the lowest layers involving physical networking and higher layers dealing with applications and data. Protocols at each layer work together to establish consistent rules for exchanging data and messages between networked devices.
Chap2

This document discusses network models and addressing in computer networks. It describes the OSI 7-layer model and compares it to the TCP/IP protocol suite. Each layer of the OSI model has specific duties, such as physical addressing at the data link layer and logical addressing at the network layer. TCP/IP protocols map to these layers, with IP at the network layer handling logical addressing. There are four levels of addressing in TCP/IP: physical, logical, port, and specific addresses that relate to different layers and allow identification of devices, networks, applications and resources on the network.
OSI model (7 LAYER )

This document discusses layered network models, specifically the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It provides an overview of each layer in both models and their functions. The key points are:
- The OSI model defines 7 layers that break communication into smaller parts to simplify the process and allow different hardware/software to work together.
- The TCP/IP model has 4 layers - application, transport, internet, and network access. It is used widely on the internet.
- Each layer adds header information to data as it moves down the stack. This encapsulation allows communication between layers and across networks.
ZERO-LECTURE.pptx

This document provides information on the course "Data Communication and Computer Networks" including the course code, credits, objectives, description, outcomes and syllabus. The main focus of the course is on local area network organization, implementation, and management. The course introduces computer network design, operations, and topics like the OSI model, error detection, local area networks, routing, and network protocols. Upon completion, students should be able to design, implement and maintain a typical computer network. The syllabus outlines 5 units that cover introductory concepts, data link layer, network layer, transport layer, and application layer. Assessment includes mid-term exams conducted by the college and a university end-term exam.
Lecture 02 networking

The document discusses the OSI reference model, which breaks network communication into 7 layers, with each layer performing a unique task and only interacting with adjacent layers. It also compares the OSI model to the TCP/IP model. The key difference is that TCP/IP combines the functions of the OSI data link and physical layers. The document further explains the Internet Protocol (IP) which specifies packet formatting and addressing for data transmission. It distinguishes between IPv4 and IPv6, noting IPv6 uses a 128-bit addressing scheme and provides improvements over IPv4 such as no NAT.
Osi model

The document discusses network models including the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model and the functions of each layer. It also discusses the four layers of the TCP/IP model and compares the two models, noting they are similar in concept but differ in number of layers and how protocols fit within each model.
Introduction to Computer Networks

Introductory overview of OSI protocol stack and basic protocols. Useful for the first course on computer networks for undergraduates
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked
Internet protocol (ip) ppt

IP specifies the format of packets, also called #datagrams, and the addressing scheme. Most networks combine IP with a higher-level protocol called Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which establishes a virtual connection between a destination and a source.
If you want to purchase the content e-mail me on dulith1989@gmail.com
Call Admission Control (CAC) with Load Balancing Approach for the WLAN Networks

The cell migrations take place between the different network operators, and require the significant information exchange between the operators to handle the migratory users. The new user registration requires the pre-shared information from the user’s equipment, which signifies the user recognition before registering the new user over the network. In this thesis, the proposed model has been aimed at the development of the new call admission control mechanism with the sub-channel assignment. The very basic utilization of the proposed model is to increase the number of the users over the given cell units, which is realized by using the sub-channel assignment to the users of the network. The proposed model is aimed at solving the issue by assigning the dual sub channels over the single communication channel. Also the proposed model is aimed at handling the minimum resource users by incorporating the load balancing approach over the given network segment. The load balancing approach shares the load of the overloaded cell with the cell with lowest resource utilization. The proposed model performance has been evaluated in the various scenarios and over all of the BTS nodes. The proposed model results have been obtained in the form of the resource utilization, network load, transmission delay, consumed bandwidth and data loss. The proposed model has shown the efficiency obtained by using the proposed call admission control (CAC) along with the new load balancing mechanism. The proposed model has shown the robustness of the proposed model in handling the cell overloading factors.
Call Admission Control In Mobile Wireless Networks

This is a presentation I did at the pre-Master studies at Ain shams University. It\'s about algorithms and techniques of call admission when a mobile node moves among cell in a wireless network.
Utilizing Call Admission Control To Derive Optimal Pricing Of Multiple Servic...

The document discusses using call admission control to derive optimal pricing for multiple service classes in wireless cellular networks. It presents three methods for admission control: partitioning admission control, threshold-based admission control, and a hybrid partitioning-threshold admission control. The methods are evaluated through numerical analysis to determine the optimal pricing strategy for each service class to maximize total network revenue.
Internet Domain Names

1. The document discusses domain names, IP addresses, and how the Domain Name System (DNS) links domain names to IP addresses.
2. DNS allows users to enter easy-to-remember domain names like "google.com" instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses like "209.85.148.104" when browsing the web.
3. When a user enters a domain name in their browser, the browser uses DNS to find the domain name's corresponding IP address and connect to the proper web server.
IP address and Domain name

IP and Domain Checker, How to Find IP Address Server, How to Trace Someone IP Address:
This pptx shows the IP address, attacks on IP address (i.e. IP Spoofing), Domain name, the difference between domain name and IP address, how to find IP address of the host, and how to convert domain name to IP address
Finance information system

This document provides an overview of financial information systems (FIS). It discusses the traditional and modern roles of financial management in procuring funds and allocating them to maximize profits. The key functions of FIS are procuring funds through long-term and short-term sources, properly allocating funds to long-term and short-term assets to maximize returns, and performing the financial management activities of cash management, investment management, capital budgeting, and financial planning.
OSI layers

This document discusses the seven layers of the OSI network model: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. It describes the purpose and responsibilities of each layer, including how layers communicate with each other on the same or different machines through peer-to-peer protocols. Functions like framing, addressing, error control, routing, and establishing sessions are managed across the layers to enable end-to-end communication between applications.
Financial Information Systems

Financial information systems (FIS) are planned systems that collect, process, store, and disseminate financial data in the form of information. FIS help automate accounting tasks like maintaining accounts and updating ledger books. They allow financial information to be easily generated and accessed through reports. FIS also facilitate audits and forecasting based on previous financial trends. Questions about transactions processed in a FIS include what activity occurred, the source of funding, and which department incurred the cost or revenue.
Financial Information System

This document discusses financial management systems and the types of financing available to businesses. It explains that financial management systems are used to input, analyze, and report financial data to help managers make decisions. The document then covers four main components of financial management systems: cash management, investment management, capital budgeting, and financial planning. It also discusses two major sources of financing for businesses - equity financing such as personal savings, home equity loans, venture capital, and IPOs, and debt financing like loans from banks, commercial lenders, bonds, and government programs.
Ip address

IP addresses are 32-bit numbers that uniquely identify devices on a network. They allow for file transfers and email communication using the Internet Protocol. There are five classes of IP addresses - A, B, C, D, and E - which are divided into ranges to define large, medium, and small networks. Users can determine the IP address of their own device or other computers and websites using commands like ipconfig and ping.
Cellphone based home automation

The document discusses the design of a cell phone-based home control system that allows users to remotely control and monitor appliances like lights, fans, and thermostats from their phone. It covers the system components, including using text messaging for phone communication, selecting a GM28 cellular module and STK300 microcontroller, and programming the system using C language in Visual Studio. The document also addresses authentication and user interaction methods to securely control devices from the phone.
Ip address and subnetting

IP addressing and subnetting allows networks to be logically organized and divided. The key objectives covered include explaining IP address classes, configuring addresses, subnetting networks, and advanced concepts like CIDR, summarization, and VLSM. Transitioning to IPv6 is also discussed as a way to address the depletion of IPv4 addresses and improve security.
Viewers also liked (13)
Call Admission Control (CAC) with Load Balancing Approach for the WLAN Networks

Call Admission Control (CAC) with Load Balancing Approach for the WLAN Networks
Call Admission Control In Mobile Wireless Networks

Call Admission Control In Mobile Wireless Networks
Utilizing Call Admission Control To Derive Optimal Pricing Of Multiple Servic...

Utilizing Call Admission Control To Derive Optimal Pricing Of Multiple Servic...
Similar to Networking
Osimodelwithneworkingoverview 150618094119-lva1-app6892

This document provides an overview of networking concepts including the OSI model layers, network types, and networking devices. It describes the responsibilities and issues handled at each OSI layer, from the physical layer transmitting raw bits to the application layer running application-specific protocols. It also covers topics like addressing schemes, modes of service, and how devices like repeaters, bridges, routers, and gateways operate to connect different network types.
Osimodelwithneworkingoverview 150618094119-lva1-app6892

This document provides an overview of networking concepts including the OSI model layers, network types, and networking devices. It describes the responsibilities and issues handled at each OSI layer, from the physical layer transmitting raw bits up to the application layer. It also covers topics like network addressing, modes of service, and how devices like repeaters, bridges, routers, and gateways operate to connect different networks.
Computer networking

This document discusses computer networking concepts including the OSI model, TCP/IP model, and common networking devices. It provides an overview of the seven layers of the OSI model and examples of protocols and applications that operate at each layer. Additionally, it describes different types of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN), connecting devices like bridges and routers, and the client-server model.
IMD 251 - Networking

Networking involves connecting electronic devices like computers to share resources and communicate. It allows devices to share internet access, hardware like printers, files and folders, and play multiplayer games. Networks use various topologies like star, bus or mesh to connect devices via physical cables or wireless links, and network protocols allow the connected devices to communicate according to shared rules.
Chapter1ccna

The document provides an overview of networking concepts including:
- The OSI model which divides network communication into 7 layers and describes the function of each layer.
- Ethernet networking standards including half and full duplex modes and different cable types.
- Data encapsulation which involves adding protocol information at each OSI layer as data moves through a network.
- Cisco's three layer model which divides networks into core, distribution, and access layers.
Lecture 1 networking & internetworking

This document provides an overview of networking and internetworking concepts. It defines what a network is and some common network protocols like TCP/IP. It discusses how network speed is measured by bit rate and latency. It then covers local area networks, wide area networks, and the internet. The document explains the purpose of networks for file sharing, communication, and remote program execution. It also discusses network messaging and different network service models like the OSI reference model and TCP/IP model. Finally, it provides a simplified example of how the TCP/IP protocol functions to route a packet from a source to destination across multiple routers.
layering.pdf

This document provides an overview of network models, specifically comparing the OSI reference model and the TCP/IP model. It explains that both models are based on layering with different layers performing distinct functions. The seven layers of the OSI model and four layers of the TCP/IP model are defined along with examples of protocols used in each layer. Key concepts like encapsulation, addresses, broadcasts, and the client-server model are also summarized.
Osi model 7 Layers

OSI layers describes how the data can be send from one parties to another during data communication. it also gives the detailed information of how the data functionally divided into small pieces and reaches the destination.
OSI and TCP/IP reference models in networking

The document describes the OSI reference model and TCP/IP reference model. The OSI model has 7 layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application layer. Each layer has distinct functions and handles different aspects of managing communications. The TCP/IP model also has 4 layers - link, internet, transport and application layer. It was developed for ARPANET and focuses on reliable end-to-end delivery of packets between hosts over diverse network types.
pppppppppppppppppjjjjjjjjjjjpppppppp.pptx

The document discusses network reference models and the OSI and TCP/IP models. It provides details on each layer of the OSI model and its functions. The key points are that reference models divide network communication into simpler components, provide standardization, and prevent changes in one layer from affecting others. The OSI model has 7 layers and separates network functions into upper layers for applications and lower layers for data transmission. The TCP/IP model is based on widely used TCP and IP protocols.
Internet (i mcom)

This document discusses different types of computer networks and networking concepts. It begins by defining an internet as a communication system connecting end systems like PCs and workstations. It describes multi-access networks that use a shared medium versus point-to-point networks connecting only two systems. Local area networks (LANs) connect computers within 1 mile using technologies like Ethernet, while wide area networks (WANs) connect locations farther apart using technologies like telephone lines. Metropolitan area networks (MANs) are between LANs and WANs in size. The internet is formed from a network of interconnected networks arranged in tiers. Network protocols establish rules for communication and the OSI model divides networking tasks into layers.
Concept of networking

The document discusses key concepts of networking including the three basic elements required: network hardware, software, and protocols. It describes common network types like LAN, WAN, and MAN and compares peer-to-peer and server-based networks. The OSI reference model and TCP/IP model are explained along with common network devices, cabling, and IP addressing schemes.
Networrrrrrrrkkkk secuiiirtyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy

This document provides an overview of networking concepts including:
- Definitions of a network, LAN, MAN, WAN and their characteristics.
- Explanations of common network topologies like bus, star, ring and their advantages/disadvantages.
- Descriptions of common networking hardware like switches, routers, hubs, bridges and their functions.
- Explanations of protocols like TCP, UDP, IP, DNS and their roles in networking.
- Discussions of other topics like cabling, addressing schemes and standards.
The document serves as a comprehensive introduction to fundamental networking topics at both the conceptual and technical levels.
Chapter 1.2 osi model

The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology.
CN unit 1 part 2 2023.ppt

The document discusses network layering and protocols. It describes how layering decomposes complex network systems into more manageable components and provides a modular design. Protocols define rules for data communication, including syntax, semantics, and timing. Key elements of protocols include service interfaces and peer interfaces. The OSI model is presented as a standard with 7 layers from physical to application. TCP/IP is also summarized as a 4 layer model. Socket programming interfaces are introduced as the main way for applications to connect to networks.
Ccna notes

The document provides information about CCNA certification options and the OSI model. It discusses two options for obtaining the CCNA certification, recommends taking a single exam, and includes a table listing common network device icons. It then covers the seven layers of the OSI model in detail, providing descriptions, examples, and review questions for each layer. Finally, it discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and compares it to the OSI model, listing several example protocols like FTP, TFTP, and HTTP.
Computer networking (nnm)

The document provides an overview of computer networking, including definitions of key terms like computer network and network topology. It discusses why networks are needed, how they work, common network models like OSI and TCP/IP. It also covers topics like IP addressing, different network types (LAN, MAN, WAN), common network devices, applications, and security concerns.
Cisco doc

A computer network connects devices that can communicate using common standards. Devices exchange resources and services by communicating. Networks expand by connecting devices like switches or hubs, which serve as central points for computers to connect to. The OSI model describes network functions in 7 layers, while the TCP/IP model has 4 layers. Encapsulation is the process of adding headers and trailers to data as it passes through layers. Frames, packets, and segments refer to encapsulated data at different layers. Ethernet defines physical and data link standards, using MAC addresses to deliver frames. IP addresses identify devices, while private addresses are non-routable. Switches inspect traffic and make forwarding decisions for each port, unlike hubs which broadcast to all
CN Module 1 ppt final 20.08.2020.ppt

This document provides an introduction to computer networks and network topologies. It discusses the basics of computer networks including definitions, examples, advantages and applications. It also describes different network topologies like bus, star, ring and mesh and analyzes their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, it introduces two common reference models for networking - OSI model and TCP/IP model, explaining their layers and differences between the two approaches.
1658897215230.pdf

The document provides an overview of computer networking concepts. It begins by defining what a computer network is and listing different types of networks, including PAN, LAN, WAN, MAN, SAN, and VPN. It then explains the OSI 7-layer model and TCP/IP model, describing each layer. Finally, it compares the OSI and TCP/IP models, noting differences in how layers are combined in each model. The document serves as an introduction to fundamental networking topics for someone learning about computer networks.
Similar to Networking (20)
Osimodelwithneworkingoverview 150618094119-lva1-app6892

Osimodelwithneworkingoverview 150618094119-lva1-app6892
Osimodelwithneworkingoverview 150618094119-lva1-app6892

Osimodelwithneworkingoverview 150618094119-lva1-app6892
Recently uploaded
AI 101: An Introduction to the Basics and Impact of Artificial Intelligence

Imagine a world where machines not only perform tasks but also learn, adapt, and make decisions. This is the promise of Artificial Intelligence (AI), a technology that's not just enhancing our lives but revolutionizing entire industries.
Main news related to the CCS TSI 2023 (2023/1695)

An English 🇬🇧 translation of a presentation to the speech I gave about the main changes brought by CCS TSI 2023 at the biggest Czech conference on Communications and signalling systems on Railways, which was held in Clarion Hotel Olomouc from 7th to 9th November 2023 (konferenceszt.cz). Attended by around 500 participants and 200 on-line followers.
The original Czech 🇨🇿 version of the presentation can be found here: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/hlavni-novinky-souvisejici-s-ccs-tsi-2023-2023-1695/269688092 .
The videorecording (in Czech) from the presentation is available here: https://youtu.be/WzjJWm4IyPk?si=SImb06tuXGb30BEH .
Cosa hanno in comune un mattoncino Lego e la backdoor XZ?

ABSTRACT: A prima vista, un mattoncino Lego e la backdoor XZ potrebbero avere in comune il fatto di essere entrambi blocchi di costruzione, o dipendenze di progetti creativi e software. La realtà è che un mattoncino Lego e il caso della backdoor XZ hanno molto di più di tutto ciò in comune.
Partecipate alla presentazione per immergervi in una storia di interoperabilità, standard e formati aperti, per poi discutere del ruolo importante che i contributori hanno in una comunità open source sostenibile.
BIO: Sostenitrice del software libero e dei formati standard e aperti. È stata un membro attivo dei progetti Fedora e openSUSE e ha co-fondato l'Associazione LibreItalia dove è stata coinvolta in diversi eventi, migrazioni e formazione relativi a LibreOffice. In precedenza ha lavorato a migrazioni e corsi di formazione su LibreOffice per diverse amministrazioni pubbliche e privati. Da gennaio 2020 lavora in SUSE come Software Release Engineer per Uyuni e SUSE Manager e quando non segue la sua passione per i computer e per Geeko coltiva la sua curiosità per l'astronomia (da cui deriva il suo nickname deneb_alpha).
Generating privacy-protected synthetic data using Secludy and Milvus

During this demo, the founders of Secludy will demonstrate how their system utilizes Milvus to store and manipulate embeddings for generating privacy-protected synthetic data. Their approach not only maintains the confidentiality of the original data but also enhances the utility and scalability of LLMs under privacy constraints. Attendees, including machine learning engineers, data scientists, and data managers, will witness first-hand how Secludy's integration with Milvus empowers organizations to harness the power of LLMs securely and efficiently.
Building Production Ready Search Pipelines with Spark and Milvus

Spark is the widely used ETL tool for processing, indexing and ingesting data to serving stack for search. Milvus is the production-ready open-source vector database. In this talk we will show how to use Spark to process unstructured data to extract vector representations, and push the vectors to Milvus vector database for search serving.
Best 20 SEO Techniques To Improve Website Visibility In SERP

Boost your website's visibility with proven SEO techniques! Our latest blog dives into essential strategies to enhance your online presence, increase traffic, and rank higher on search engines. From keyword optimization to quality content creation, learn how to make your site stand out in the crowded digital landscape. Discover actionable tips and expert insights to elevate your SEO game.
Webinar: Designing a schema for a Data Warehouse

Are you new to data warehouses (DWH)? Do you need to check whether your data warehouse follows the best practices for a good design? In both cases, this webinar is for you.
A data warehouse is a central relational database that contains all measurements about a business or an organisation. This data comes from a variety of heterogeneous data sources, which includes databases of any type that back the applications used by the company, data files exported by some applications, or APIs provided by internal or external services.
But designing a data warehouse correctly is a hard task, which requires gathering information about the business processes that need to be analysed in the first place. These processes must be translated into so-called star schemas, which means, denormalised databases where each table represents a dimension or facts.
We will discuss these topics:
- How to gather information about a business;
- Understanding dictionaries and how to identify business entities;
- Dimensions and facts;
- Setting a table granularity;
- Types of facts;
- Types of dimensions;
- Snowflakes and how to avoid them;
- Expanding existing dimensions and facts.
Presentation of the OECD Artificial Intelligence Review of Germany

Consult the full report at https://www.oecd.org/digital/oecd-artificial-intelligence-review-of-germany-609808d6-en.htm
Your One-Stop Shop for Python Success: Top 10 US Python Development Providers

Simplify your search for a reliable Python development partner! This list presents the top 10 trusted US providers offering comprehensive Python development services, ensuring your project's success from conception to completion.
Ocean lotus Threat actors project by John Sitima 2024 (1).pptx

Ocean Lotus cyber threat actors represent a sophisticated, persistent, and politically motivated group that poses a significant risk to organizations and individuals in the Southeast Asian region. Their continuous evolution and adaptability underscore the need for robust cybersecurity measures and international cooperation to identify and mitigate the threats posed by such advanced persistent threat groups.
Artificial Intelligence for XMLDevelopment

In the rapidly evolving landscape of technologies, XML continues to play a vital role in structuring, storing, and transporting data across diverse systems. The recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) present new methodologies for enhancing XML development workflows, introducing efficiency, automation, and intelligent capabilities. This presentation will outline the scope and perspective of utilizing AI in XML development. The potential benefits and the possible pitfalls will be highlighted, providing a balanced view of the subject.
We will explore the capabilities of AI in understanding XML markup languages and autonomously creating structured XML content. Additionally, we will examine the capacity of AI to enrich plain text with appropriate XML markup. Practical examples and methodological guidelines will be provided to elucidate how AI can be effectively prompted to interpret and generate accurate XML markup.
Further emphasis will be placed on the role of AI in developing XSLT, or schemas such as XSD and Schematron. We will address the techniques and strategies adopted to create prompts for generating code, explaining code, or refactoring the code, and the results achieved.
The discussion will extend to how AI can be used to transform XML content. In particular, the focus will be on the use of AI XPath extension functions in XSLT, Schematron, Schematron Quick Fixes, or for XML content refactoring.
The presentation aims to deliver a comprehensive overview of AI usage in XML development, providing attendees with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions. Whether you’re at the early stages of adopting AI or considering integrating it in advanced XML development, this presentation will cover all levels of expertise.
By highlighting the potential advantages and challenges of integrating AI with XML development tools and languages, the presentation seeks to inspire thoughtful conversation around the future of XML development. We’ll not only delve into the technical aspects of AI-powered XML development but also discuss practical implications and possible future directions.
5th LF Energy Power Grid Model Meet-up Slides

5th Power Grid Model Meet-up
It is with great pleasure that we extend to you an invitation to the 5th Power Grid Model Meet-up, scheduled for 6th June 2024. This event will adopt a hybrid format, allowing participants to join us either through an online Mircosoft Teams session or in person at TU/e located at Den Dolech 2, Eindhoven, Netherlands. The meet-up will be hosted by Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e), a research university specializing in engineering science & technology.
Power Grid Model
The global energy transition is placing new and unprecedented demands on Distribution System Operators (DSOs). Alongside upgrades to grid capacity, processes such as digitization, capacity optimization, and congestion management are becoming vital for delivering reliable services.
Power Grid Model is an open source project from Linux Foundation Energy and provides a calculation engine that is increasingly essential for DSOs. It offers a standards-based foundation enabling real-time power systems analysis, simulations of electrical power grids, and sophisticated what-if analysis. In addition, it enables in-depth studies and analysis of the electrical power grid’s behavior and performance. This comprehensive model incorporates essential factors such as power generation capacity, electrical losses, voltage levels, power flows, and system stability.
Power Grid Model is currently being applied in a wide variety of use cases, including grid planning, expansion, reliability, and congestion studies. It can also help in analyzing the impact of renewable energy integration, assessing the effects of disturbances or faults, and developing strategies for grid control and optimization.
What to expect
For the upcoming meetup we are organizing, we have an exciting lineup of activities planned:
-Insightful presentations covering two practical applications of the Power Grid Model.
-An update on the latest advancements in Power Grid -Model technology during the first and second quarters of 2024.
-An interactive brainstorming session to discuss and propose new feature requests.
-An opportunity to connect with fellow Power Grid Model enthusiasts and users.
Programming Foundation Models with DSPy - Meetup Slides

Prompting language models is hard, while programming language models is easy. In this talk, I will discuss the state-of-the-art framework DSPy for programming foundation models with its powerful optimizers and runtime constraint system.
Salesforce Integration for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions A...

Sidekick Solutions uses Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions Apricot) and automation solutions to integrate data for business workflows.
We believe integration and automation are essential to user experience and the promise of efficient work through technology. Automation is the critical ingredient to realizing that full vision. We develop integration products and services for Bonterra Case Management software to support the deployment of automations for a variety of use cases.
This video focuses on integration of Salesforce with Bonterra Impact Management.
Interested in deploying an integration with Salesforce for Bonterra Impact Management? Contact us at sales@sidekicksolutionsllc.com to discuss next steps.
Introduction of Cybersecurity with OSS at Code Europe 2024

I develop the Ruby programming language, RubyGems, and Bundler, which are package managers for Ruby. Today, I will introduce how to enhance the security of your application using open-source software (OSS) examples from Ruby and RubyGems.
The first topic is CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures). I have published CVEs many times. But what exactly is a CVE? I'll provide a basic understanding of CVEs and explain how to detect and handle vulnerabilities in OSS.
Next, let's discuss package managers. Package managers play a critical role in the OSS ecosystem. I'll explain how to manage library dependencies in your application.
I'll share insights into how the Ruby and RubyGems core team works to keep our ecosystem safe. By the end of this talk, you'll have a better understanding of how to safeguard your code.
National Security Agency - NSA mobile device best practices

Threats to mobile devices are more prevalent and increasing in scope and complexity. Users of mobile devices desire to take full advantage of the features
available on those devices, but many of the features provide convenience and capability but sacrifice security. This best practices guide outlines steps the users can take to better protect personal devices and information.
Monitoring and Managing Anomaly Detection on OpenShift.pdf

Monitoring and Managing Anomaly Detection on OpenShift
Overview
Dive into the world of anomaly detection on edge devices with our comprehensive hands-on tutorial. This SlideShare presentation will guide you through the entire process, from data collection and model training to edge deployment and real-time monitoring. Perfect for those looking to implement robust anomaly detection systems on resource-constrained IoT/edge devices.
Key Topics Covered
1. Introduction to Anomaly Detection
- Understand the fundamentals of anomaly detection and its importance in identifying unusual behavior or failures in systems.
2. Understanding Edge (IoT)
- Learn about edge computing and IoT, and how they enable real-time data processing and decision-making at the source.
3. What is ArgoCD?
- Discover ArgoCD, a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes, and its role in deploying applications on edge devices.
4. Deployment Using ArgoCD for Edge Devices
- Step-by-step guide on deploying anomaly detection models on edge devices using ArgoCD.
5. Introduction to Apache Kafka and S3
- Explore Apache Kafka for real-time data streaming and Amazon S3 for scalable storage solutions.
6. Viewing Kafka Messages in the Data Lake
- Learn how to view and analyze Kafka messages stored in a data lake for better insights.
7. What is Prometheus?
- Get to know Prometheus, an open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit, and its application in monitoring edge devices.
8. Monitoring Application Metrics with Prometheus
- Detailed instructions on setting up Prometheus to monitor the performance and health of your anomaly detection system.
9. What is Camel K?
- Introduction to Camel K, a lightweight integration framework built on Apache Camel, designed for Kubernetes.
10. Configuring Camel K Integrations for Data Pipelines
- Learn how to configure Camel K for seamless data pipeline integrations in your anomaly detection workflow.
11. What is a Jupyter Notebook?
- Overview of Jupyter Notebooks, an open-source web application for creating and sharing documents with live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text.
12. Jupyter Notebooks with Code Examples
- Hands-on examples and code snippets in Jupyter Notebooks to help you implement and test anomaly detection models.
Recently uploaded (20)
AI 101: An Introduction to the Basics and Impact of Artificial Intelligence

AI 101: An Introduction to the Basics and Impact of Artificial Intelligence
Cosa hanno in comune un mattoncino Lego e la backdoor XZ?

Cosa hanno in comune un mattoncino Lego e la backdoor XZ?
Generating privacy-protected synthetic data using Secludy and Milvus

Generating privacy-protected synthetic data using Secludy and Milvus
Building Production Ready Search Pipelines with Spark and Milvus

Building Production Ready Search Pipelines with Spark and Milvus
Best 20 SEO Techniques To Improve Website Visibility In SERP

Best 20 SEO Techniques To Improve Website Visibility In SERP
Presentation of the OECD Artificial Intelligence Review of Germany

Presentation of the OECD Artificial Intelligence Review of Germany
Your One-Stop Shop for Python Success: Top 10 US Python Development Providers

Your One-Stop Shop for Python Success: Top 10 US Python Development Providers
Ocean lotus Threat actors project by John Sitima 2024 (1).pptx

Ocean lotus Threat actors project by John Sitima 2024 (1).pptx
Programming Foundation Models with DSPy - Meetup Slides

Programming Foundation Models with DSPy - Meetup Slides
Salesforce Integration for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions A...

Salesforce Integration for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions A...
Introduction of Cybersecurity with OSS at Code Europe 2024

Introduction of Cybersecurity with OSS at Code Europe 2024
National Security Agency - NSA mobile device best practices

National Security Agency - NSA mobile device best practices
Monitoring and Managing Anomaly Detection on OpenShift.pdf

Monitoring and Managing Anomaly Detection on OpenShift.pdf
Networking
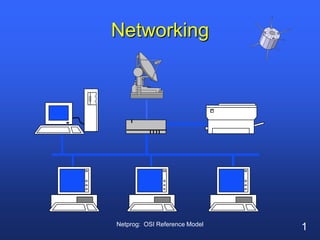
- 1. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Networking
- 2. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Network “ ... communication system for connecting end-systems” End-systems a.k.a. “hosts” PCs, workstations dedicated computers network components
- 3. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Multiaccess vs. Point-to-point Multiaccess means shared medium. many end-systems share the same physical communication resources (wire, frequency, ...) There must be some arbitration mechanism. Point-to-point only 2 systems involved no doubt about where data came from !
- 4. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Multiaccess Point-to-point
- 5. Netprog: OSI Reference Model LAN - Local Area Network connects computers that are physically close together ( < 1 mile). high speed multi-access Technologies: Ethernet 10 Mbps, 100Mbps Token Ring 16 Mbps FDDI 100 Mbps
- 6. Netprog: OSI Reference Model WAN - Wide Area Network connects computers that are physically far apart. “long-haul network”. typically slower than a LAN. typically less reliable than a LAN. point-to-point Technologies: telephone lines Satellite communications
- 7. Netprog: OSI Reference Model MAN - Metropolitan Area Network Larger than a LAN and smaller than a WAN - example: campus-wide network - multi-access network Technologies: coaxial cable microwave
- 8. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Internetwork Connection of 2 or more distinct (possibly dissimilar) networks. Requires some kind of network device to facilitate the connection. Net A Net B
- 9. Netprog: OSI Reference Model OSI Reference Model Layered model: 7. Application 6. Presentation 5. Session 4. Transport 3. Network 2. Data Link 1. Physical
- 10. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Responsibility: transmission of raw bits over a communication channel. Issues: mechanical and electrical interfaces time per bit distances The Physical Layer
- 11. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Data Link Layer - Data Link Control Responsibility: provide an error-free communication link Issues: framing (dividing data into chunks) header & trailer bits addressing 10110110101 01100010011 10110000001
- 12. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Data Link Layer - The MAC sublayer Medium Access Control - needed by mutiaccess networks. MAC provides DLC with “virtual wires” on multiaccess networks.
- 13. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Network Layer Responsibilities: path selection between end-systems (routing). subnet flow control. fragmentation & reassembly translation between different network types. Issues: packet headers virtual circuits
- 14. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Transport Layer Responsibilities: provides virtual end-to-end links between peer processes. end-to-end flow control Issues: headers error detection reliable communication
- 15. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Session Layer Responsibilities: establishes, manages, and terminates sessions between applications. service location lookup Many protocol suites do not include a session layer.
- 16. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Presentation Layer Responsibilities: data encryption data compression data conversion Many protocol suites do not include a Presentation Layer.
- 17. Netprog: OSI Reference Model The Application Layer Responsibilities: anything not provided by any of the other layers Issues: application level protocols appropriate selection of “type of service”
- 18. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Layering & Headers Each layer needs to add some control information to the data in order to do it’s job. This information is typically prepended to the data before being given to the lower layer. Once the lower layers deliver the the data and control information - the peer layer uses the control information.
- 19. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Headers DATA Process Process Transport Transport DATA H Network Network DATA H H Data Link Data Link DATA H H H
- 20. Netprog: OSI Reference Model What are the headers? Physical: no header - just a bunch of bits. Data Link: address of the receiving endpoints address of the sending endpoint length of the data checksum.
- 22. header checksum
- 25. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Connecting Networks Repeater: physical layer Bridge: data link layer Router: network layer Gateway: network layer and above.
- 26. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Repeater Copies bits from one network to another Does not look at any bits Allows the extension of a network beyond physical length limitations REPEATER
- 27. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Bridge Copies frames from one network to another Can operate selectively - does not copy all frames (must look at data-link headers). Extends the network beyond physical length limitations. BRIDGE
- 28. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Router Copies packets from one network to another. Makes decisions about what route a packet should take (looks at network headers). ROUTER
- 29. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Gateway Operates as a router Data conversions above the network layer. Conversions: encapsulation - use an intermediate network translation - connect different application protocols encrpyption - could be done by a gateway
- 30. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Encapsulation Example Gateway Gateway Provides service connectivity even though intermediate network does not support protocols.
- 31. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Translation Gateway Translate from green protocol to brown protocol
- 32. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Encryption gateway Secure Network Secure Network Encryption/Decryption Gateways ? GW GW ? ? InsecureNetwork
- 33. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Hardware vs. Software Repeaters are typically hardware devices. Bridges can be implemented in hardware or software. Routers & Gateways are typically implemented in software so that they can be extended to handle new protocols. Many workstations can operate as routers or gateways.
- 34. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Byte Ordering Different computer architectures use different byte ordering to represent multibyte values. 16 bit integer: Low Byte High Byte Address A High Byte Low Byte Address A+1
- 35. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Byte Ordering Big-Endian IBM 370 Motorola 68000 Sun Little-Endian IBM 80x86 DEC VAX DEC PDP-11 Low Byte High Byte High Byte Low Byte Addr A Addr A+1 Addr A Addr A+1
- 36. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Byte Order and Networking Suppose a Big Endian machine sends a 16 bit integer with the value 2: A Little Endian machine will think it got the number 512: 0000000000000010 0000001000000000
- 37. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Network Byte Order Conversion of application-level data is left up to the presentation layer. But hold on !!! How do lower level layers communicate if they all represent values differently ? (data length fields in headers) A fixed byte order is used (called network byte order) for all control data.
- 38. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Multiplexing “.. to combine many into one”. Many processes sharing a single network interface. A single process could use multiple protocols. More on this when we look at TCP/IP.
- 39. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Modes of Service connection-oriented vs. connectionless sequencing error-control flow-control byte stream vs. message based full-duplex vs. half-duplex.
- 40. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Connection-Oriented vs. Connectionless Service A connection-oriented service includes the establishment of a logical connection between 2 processes. establish logical connection transfer data terminate connection. Connectionless services involve sending of independent messages.
- 41. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Sequencing Sequencing provides support for an order to communications. A service that includes sequencing requires that messages (or bytes) are received in the same order they are sent.
- 42. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Error Control Some services require error detection (it is important to know when a transmission error has occured). Checksums provide a simple error detection mechanism. Error control sometimes involves notification and retransmission.
- 43. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Flow Control Flow control prevents the sending process from overwhelming the receiving process. Flow control can be handled a variety of ways - this is one of the major research issues in the development of the next generation of networks (ATM).
- 44. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Byte Stream vs. Message Byte stream implies an ordered sequence of bytes with no message boundaries. Message oriented services provide communication service to chunks of data called datagrams.
- 45. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Full- vs. Half-Duplex Full-Duplex services support the transfer of data in both directions. Half-Duplex services support the transfer of data in a single direction.
- 46. Netprog: OSI Reference Model End-to-End vs. Hop-toHop Many service modes/features such as flow control and error control can be done either: between endpoints of the communication. -or- between every 2 nodes on the path between the endpoints.
- 47. Netprog: OSI Reference Model End-to-End Process A Process B
- 48. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Hop-by-Hop Process A Process B
- 49. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Buffering Buffering can provide more efficient communications. Buffering is most useful for byte stream services. Process A Process B Send Buffer Recv. Buffer
- 50. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Addresses Each communication endpoint must have an address. Consider 2 processes communicating over an internet: the network must be specified the host (end-system) must be specified the process must be specified.
- 51. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Addresses at Layers Physical Layer: no address necessary Data Link Layer - address must be able to select any host on the network. Network Layer - address must be able to provide information to enable routing. Transport Layer - address must identify the destination process.
- 52. Netprog: OSI Reference Model Broadcasts Many networks support the notion of sending a message from one host to all other hosts on the network. A special address called the “broadcast address” is often used. Some popular network services are based on broadcasting (YP/NIS, rup, rusers)