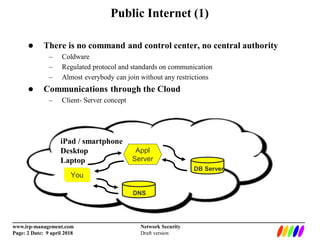
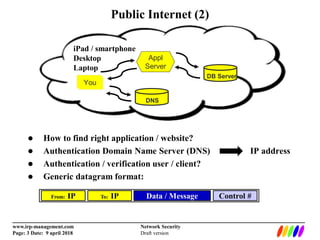
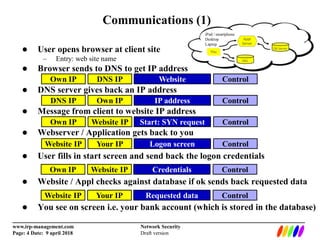
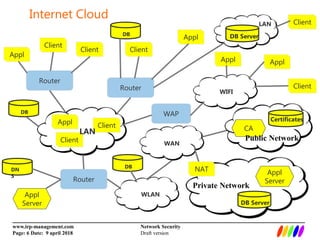
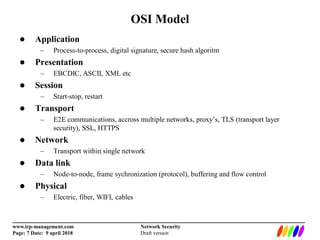
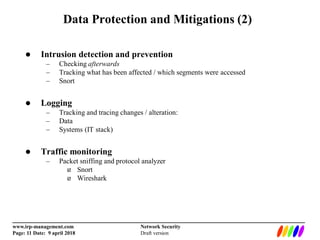
The document outlines the fundamentals of network security, including the lack of central authority on the public internet and communication protocols involving clients and servers. It discusses various threats such as DDoS attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and spoofing, along with mitigation strategies including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection. Additionally, it covers data protection methods like proxy servers, certificate authorities, and traffic monitoring for enhanced security.