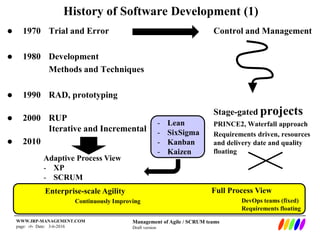
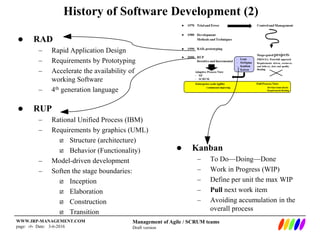
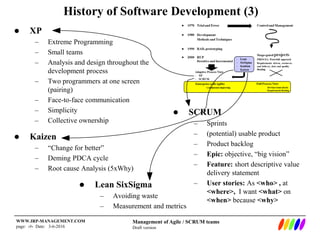
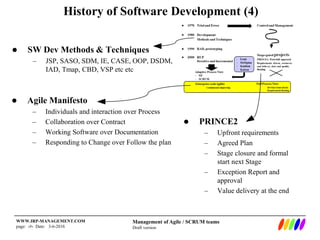
The document outlines the evolution of software development methodologies, highlighting techniques like Agile, Scrum, and Lean. It discusses the impact of trends such as globalization and digital economy on future business and IT roles, predicting a shift towards integrated enterprise-scale agility. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of collaboration and adaptability in modern software project management.