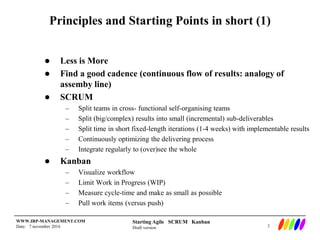
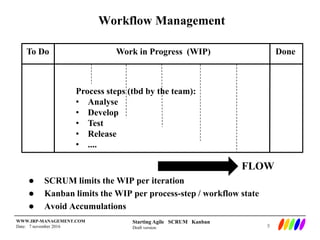
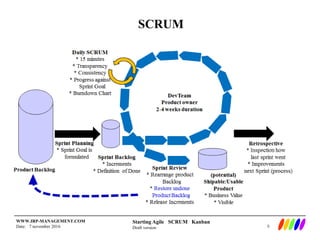
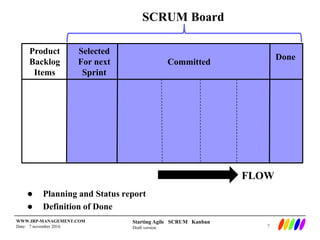
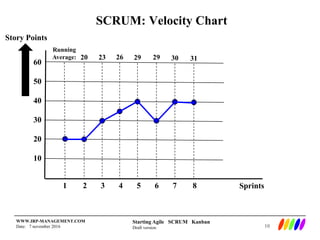
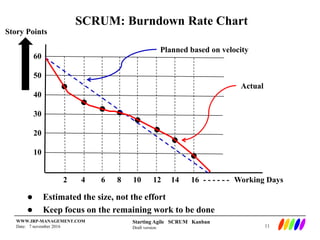
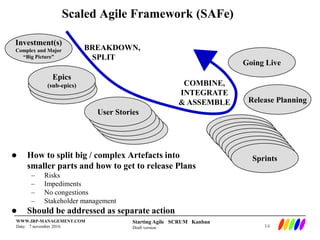
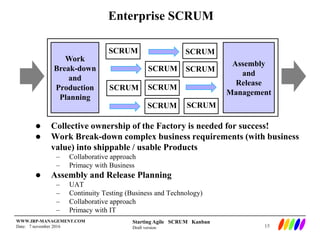
The document outlines the preparation and foundational principles for implementing Agile methodologies, specifically Scrum and Kanban, including team roles, workflow management, and requirements management. It emphasizes the importance of cross-functional teams, iterative development, and workflow visualization to optimize processes and deliver value. Additionally, it discusses metrics like velocity and burndown rates to track progress and ensure effective planning.