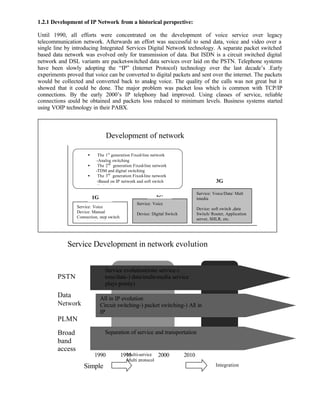
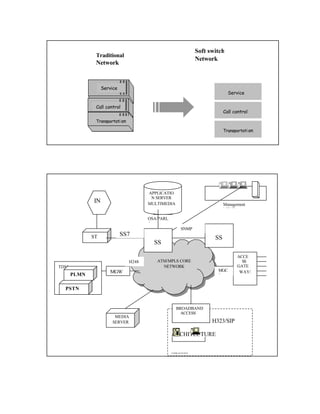
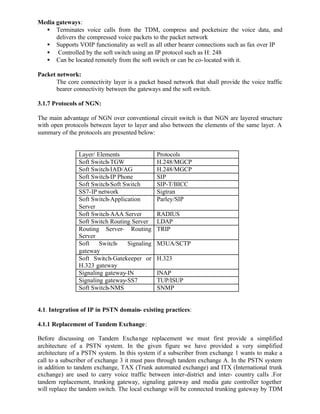
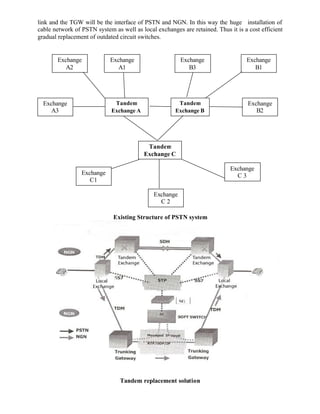
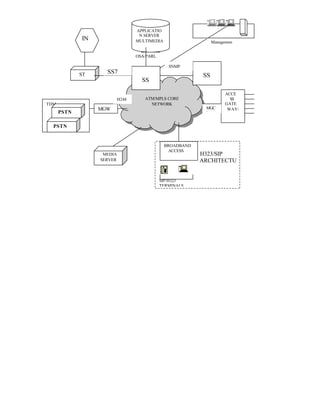
This document provides a summary of integrating IP telephony into the public switched telephone network (PSTN) environment. It discusses the evolution of PSTN from analog to digital networks and the emergence of time division switching. It then outlines the architecture of a soft switch solution for integration, including edge, core, control, and application layers. Finally, it discusses existing practices for integration, such as replacing tandem exchanges, and considers the specific context of integrating IP networks in Bangladesh.