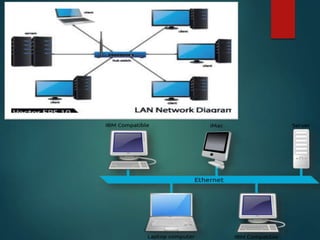
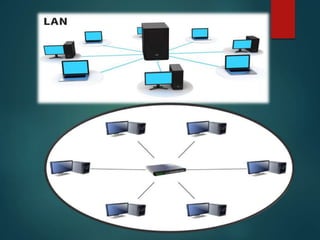
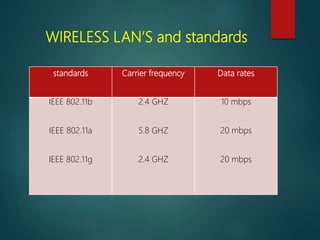
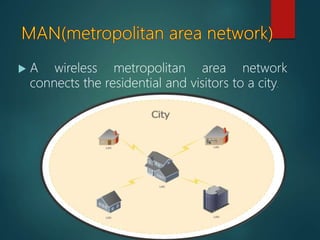
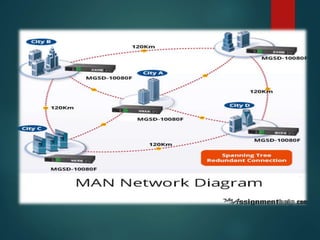
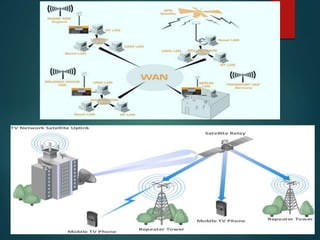
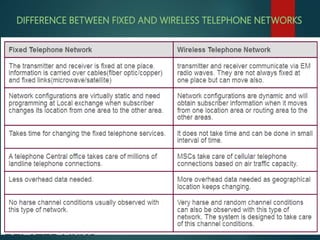
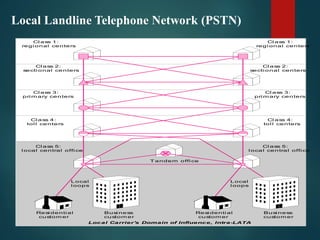
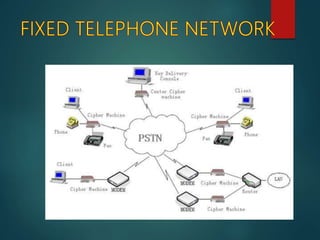
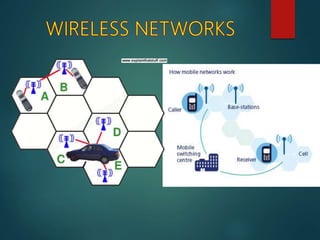
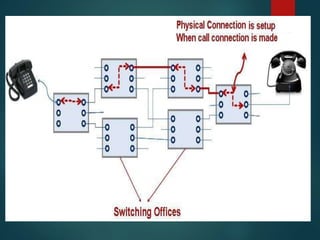
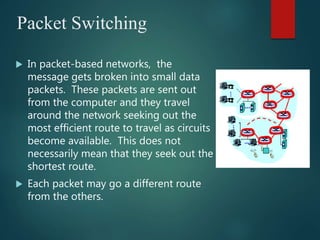
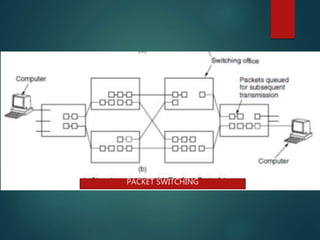
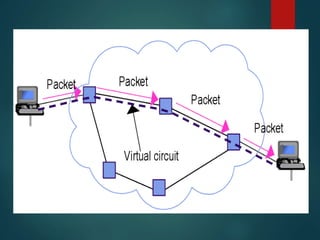
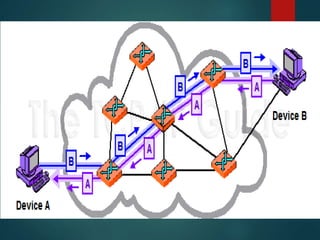
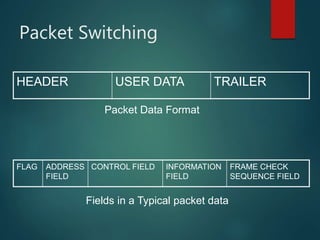
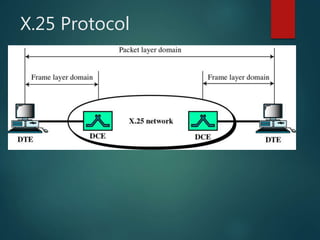
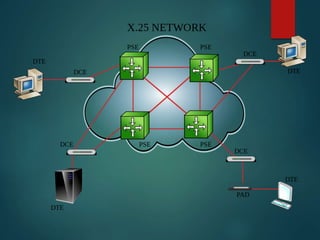
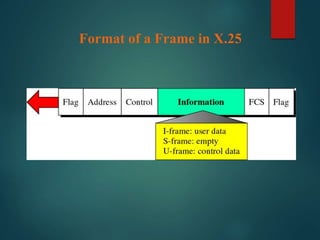
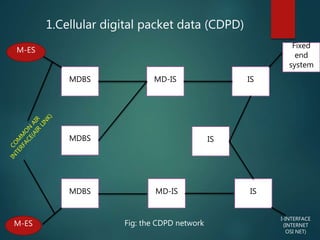
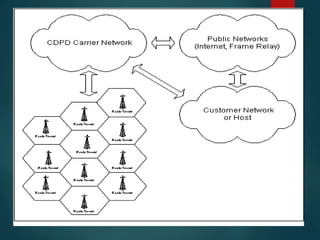
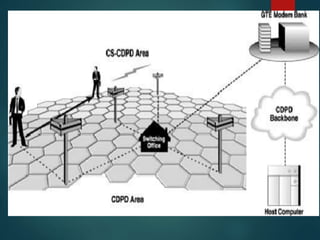
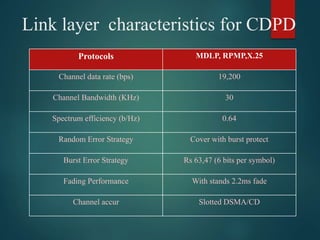
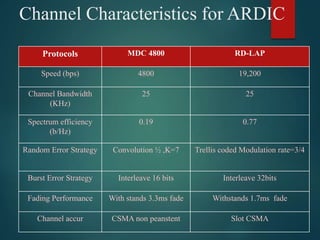
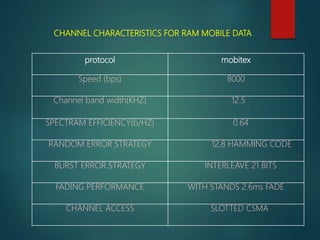
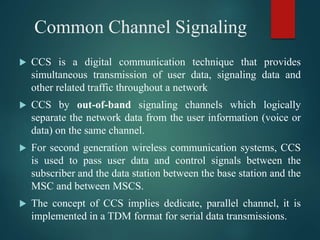
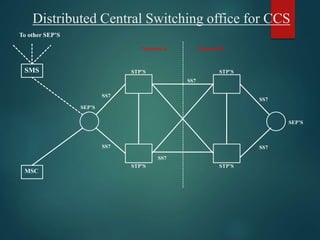
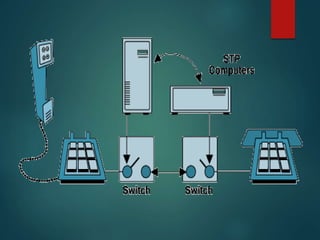
The document discusses different types of wireless networks and their characteristics. It summarizes wireless networks as being classified based on their coverage area, from personal area networks (PANs) covering a single room up to wide area networks (WANs) spanning countries. It then provides details on various wireless data network standards and technologies, including local area networks (LANs), Bluetooth, wireless metropolitan area networks, and wide area networks. It also discusses early wireless data services like cellular digital packet data (CDPD), ARDIS, and RAM mobile data that used packet switching for mobile data connectivity.