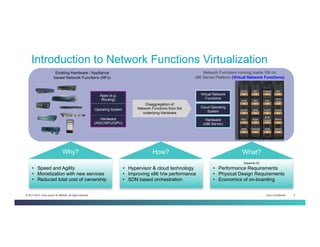
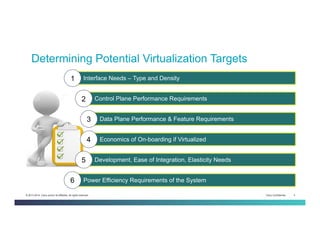
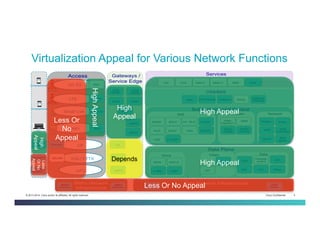
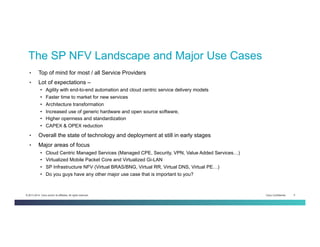
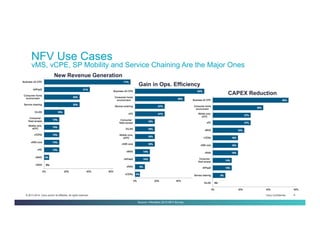
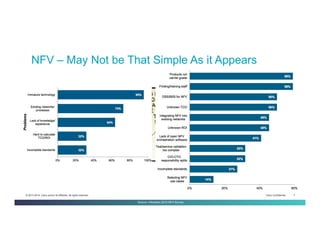
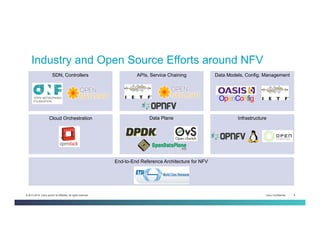
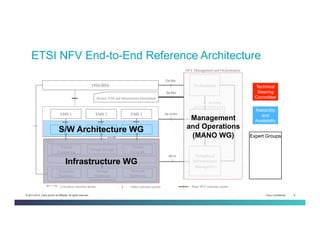
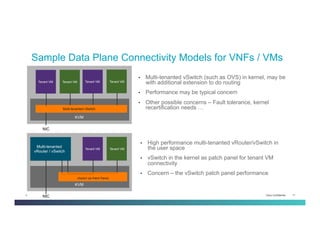
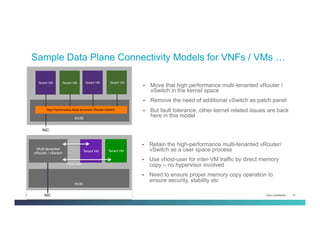
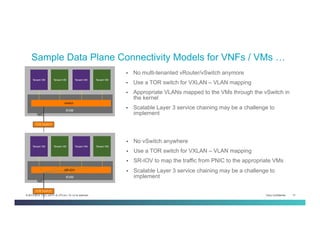
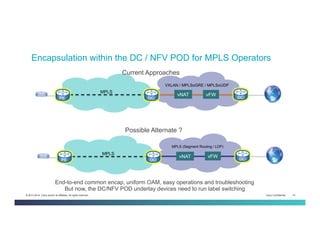
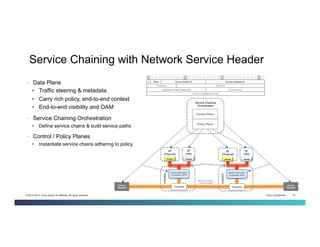
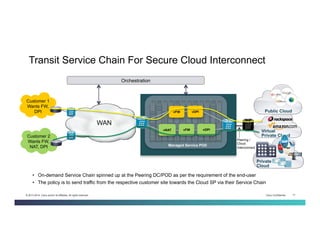
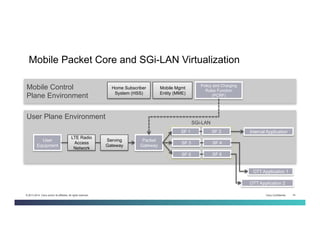
The document discusses Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and its significance in disaggregating network functions from hardware to improve agility and reduce costs through virtualization on x86 platforms. It highlights the major use cases, potential targets for virtualization, and the required skillsets for implementing NFV, such as cloud orchestration and service function chaining. The document also outlines NFV reference architecture, terminology, and challenges related to performance, integration, and new operational paradigms.