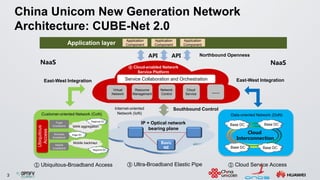
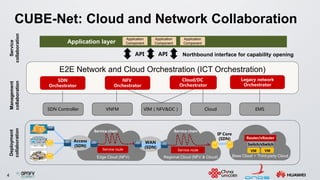
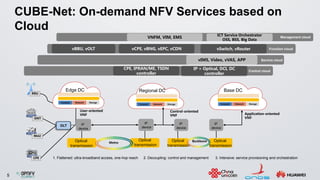
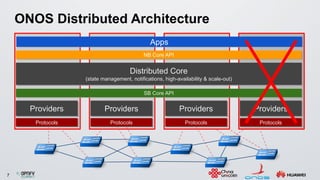
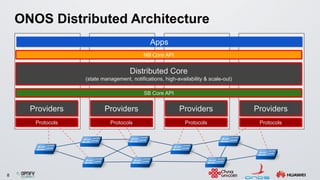
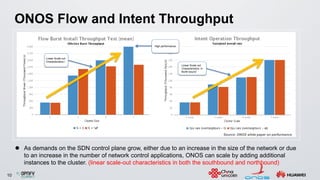
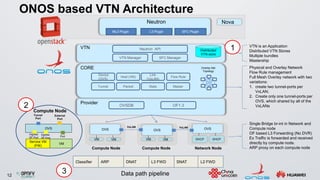
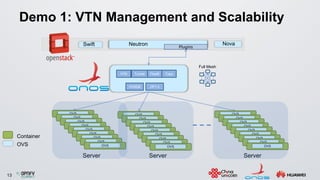
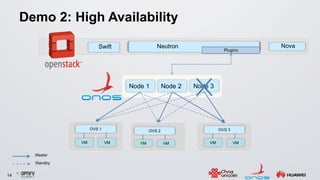
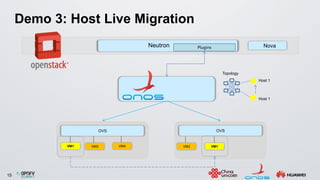
The document discusses an ONOS-based virtual tenant network (VTN) implementation. It provides an overview of the architecture, including that ONOS uses a distributed architecture to provide high availability, scalability, and performance. It also allows for linear scalability. The VTN architecture runs on top of ONOS and uses Neutron and OpenStack for management of virtual networks and tenants. It allows for VTN management and scalability, high availability, and live migration of VM hosts.