The nervous system is made up of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (nerves). The central nervous system acts as the body's control center and coordinates activities. Impulses travel through neurons to reach the brain. The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Together they allow the body to rapidly respond to stimuli.
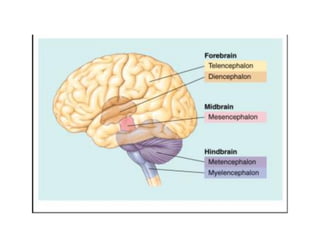
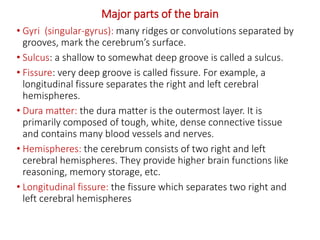
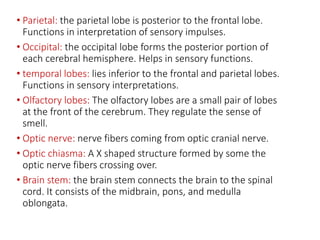
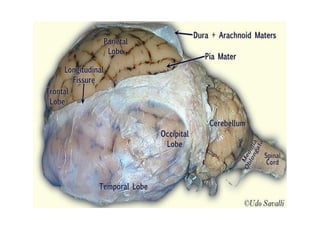
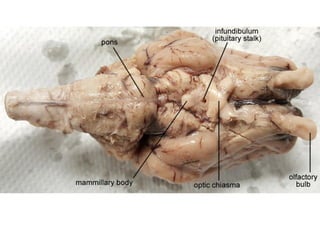
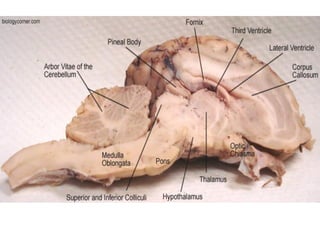
The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain includes the cerebrum and controls higher functions. The midbrain connects the forebrain to the hindbrain. The hindbrain assists in regulating automatic functions and sensory information relay. Within the brain, structures such as the cerebellum,