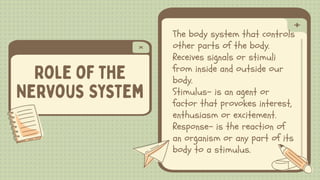
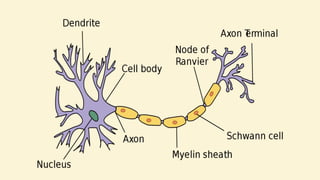
1) The document discusses the nervous system, which controls other parts of the body and receives signals from inside and outside the body. It describes the main parts of the nervous system including neurons, the central nervous system, and the peripheral nervous system.
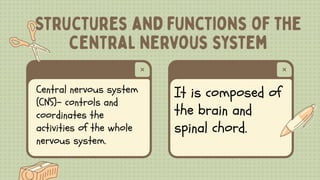
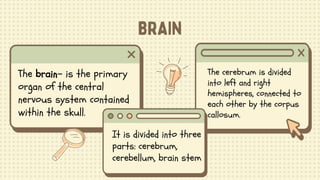
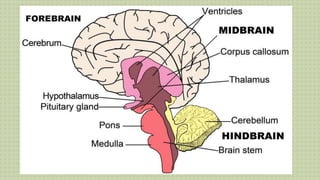
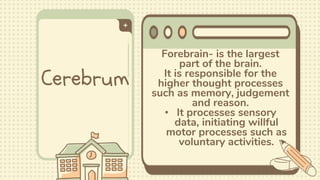
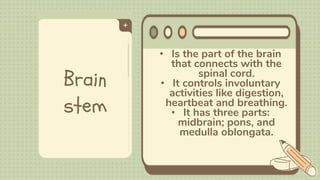
2) The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The cerebrum controls higher thought processes while the cerebellum controls muscle coordination.
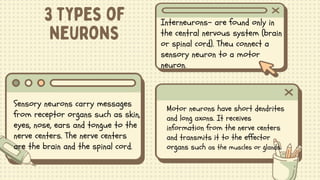
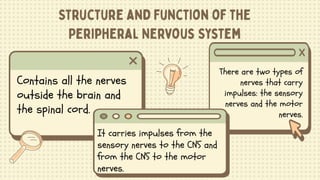
3) The peripheral nervous system includes all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, carrying signals between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. It is made up of sensory nerves which receive stimuli and motor