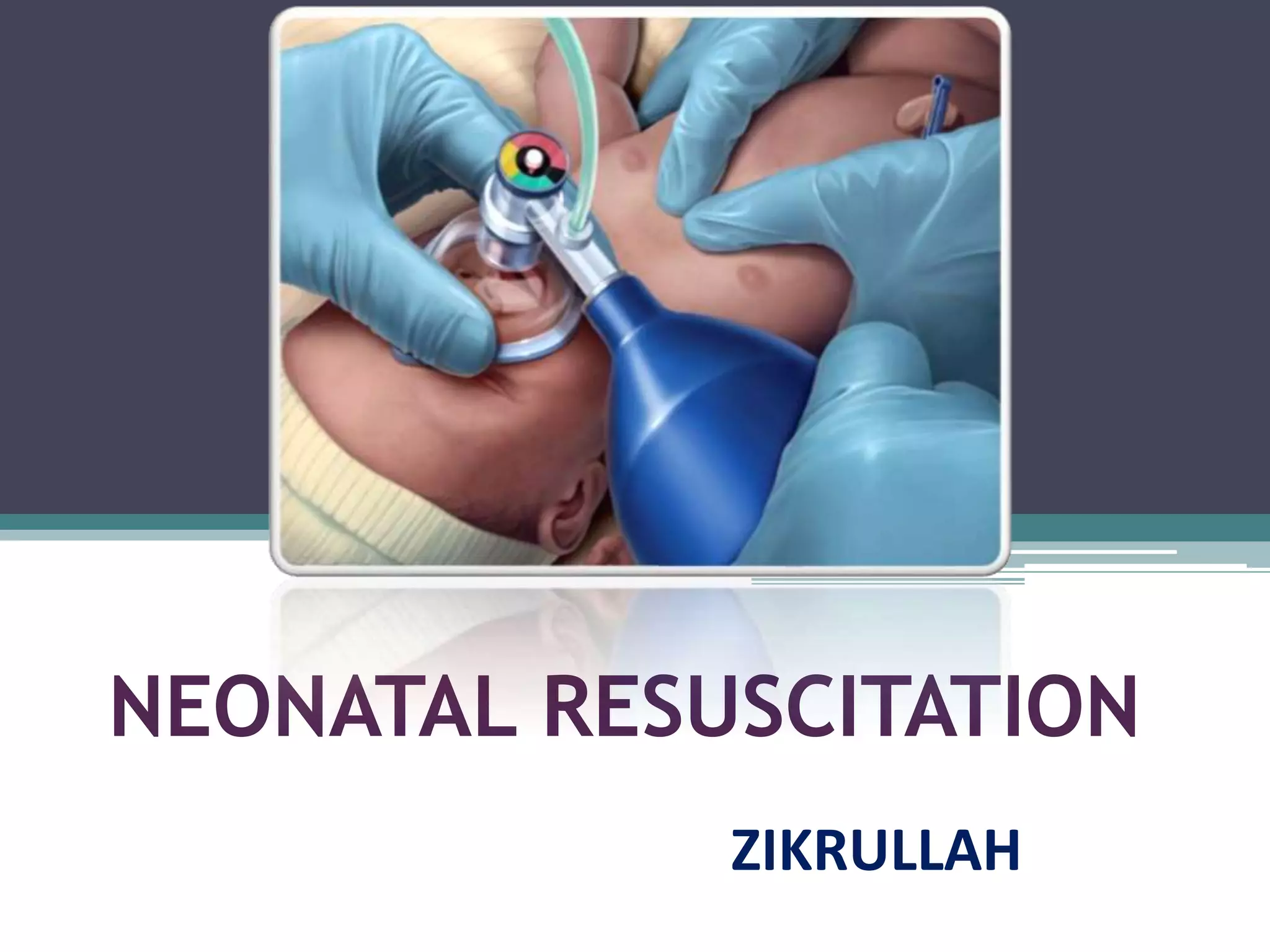
Neonatal resuscitation involves assessing newborns at birth and providing interventions to babies having difficulty transitioning from intrauterine to extrauterine life. About 10% of newborns require some assistance to begin breathing, while less than 1% require extensive resuscitation including ventilation, chest compressions, or medications. The Apgar score is used to evaluate neonatal well-being at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. Babies requiring resuscitation are initially stabilized, including warming, positioning, and clearing airways. Oxygen supplementation and positive pressure ventilation may then be provided if needed based on heart rate and respiration assessment.