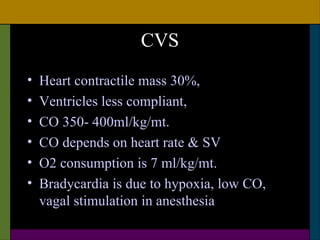
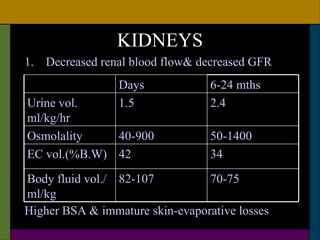
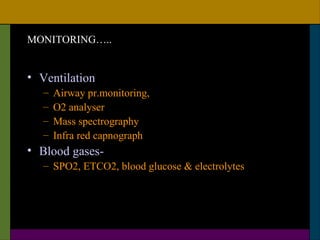
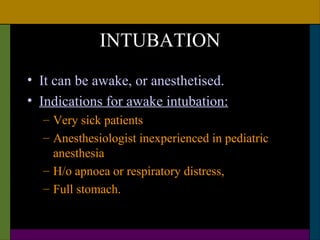
This document discusses neonatal surgical emergencies and anesthetic management considerations. It covers the physiological differences of the neonatal system including the cardiovascular, respiratory, renal and thermal regulation systems. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining normothermia, oxygenation, hydration and glucose levels. The document provides guidance on optimization, monitoring, induction, intubation, maintenance and recovery for neonatal anesthesia. Special attention is needed in the postoperative period to prevent complications like apnea, laryngospasm and cardiac arrest.