Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times



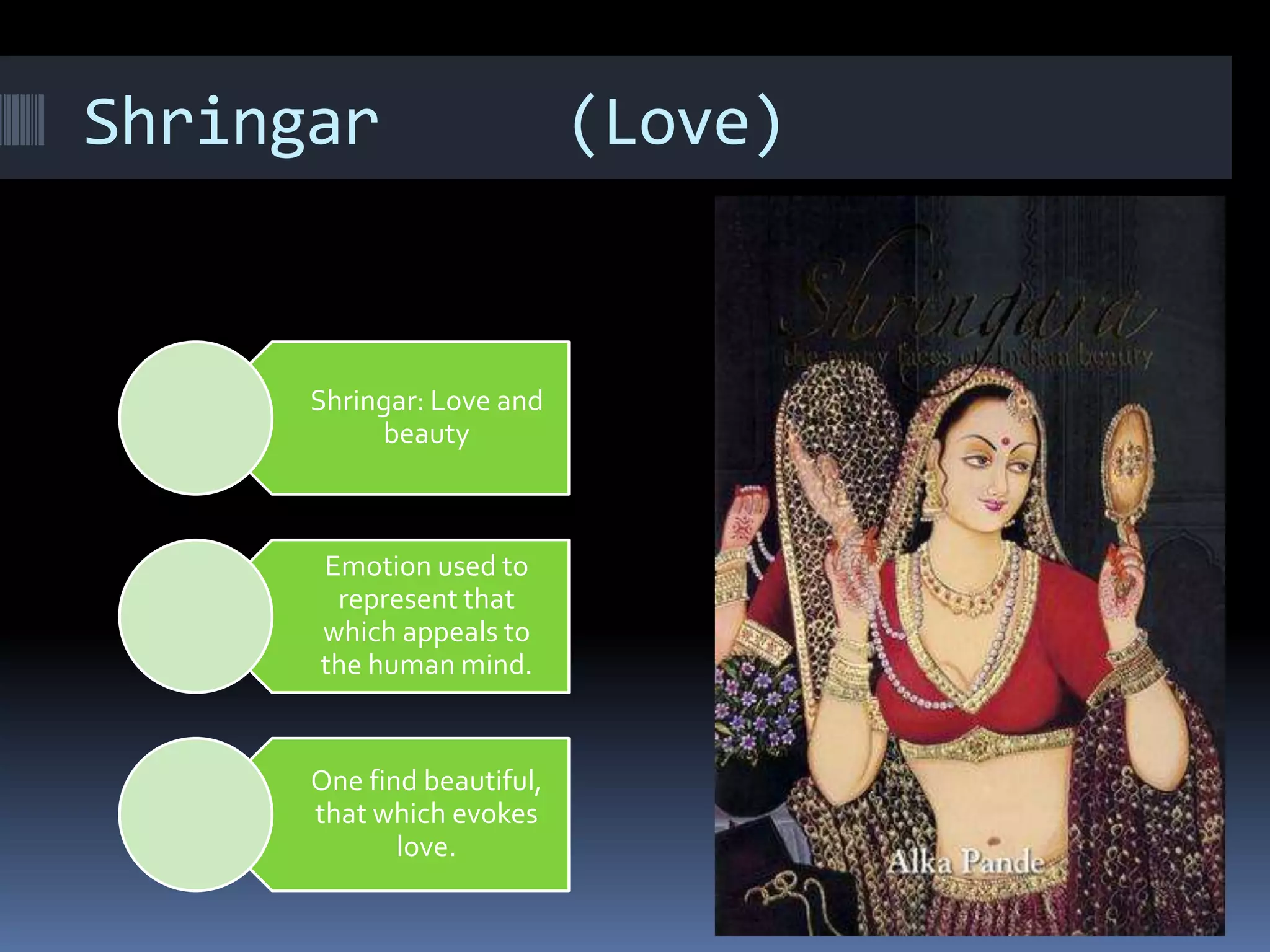

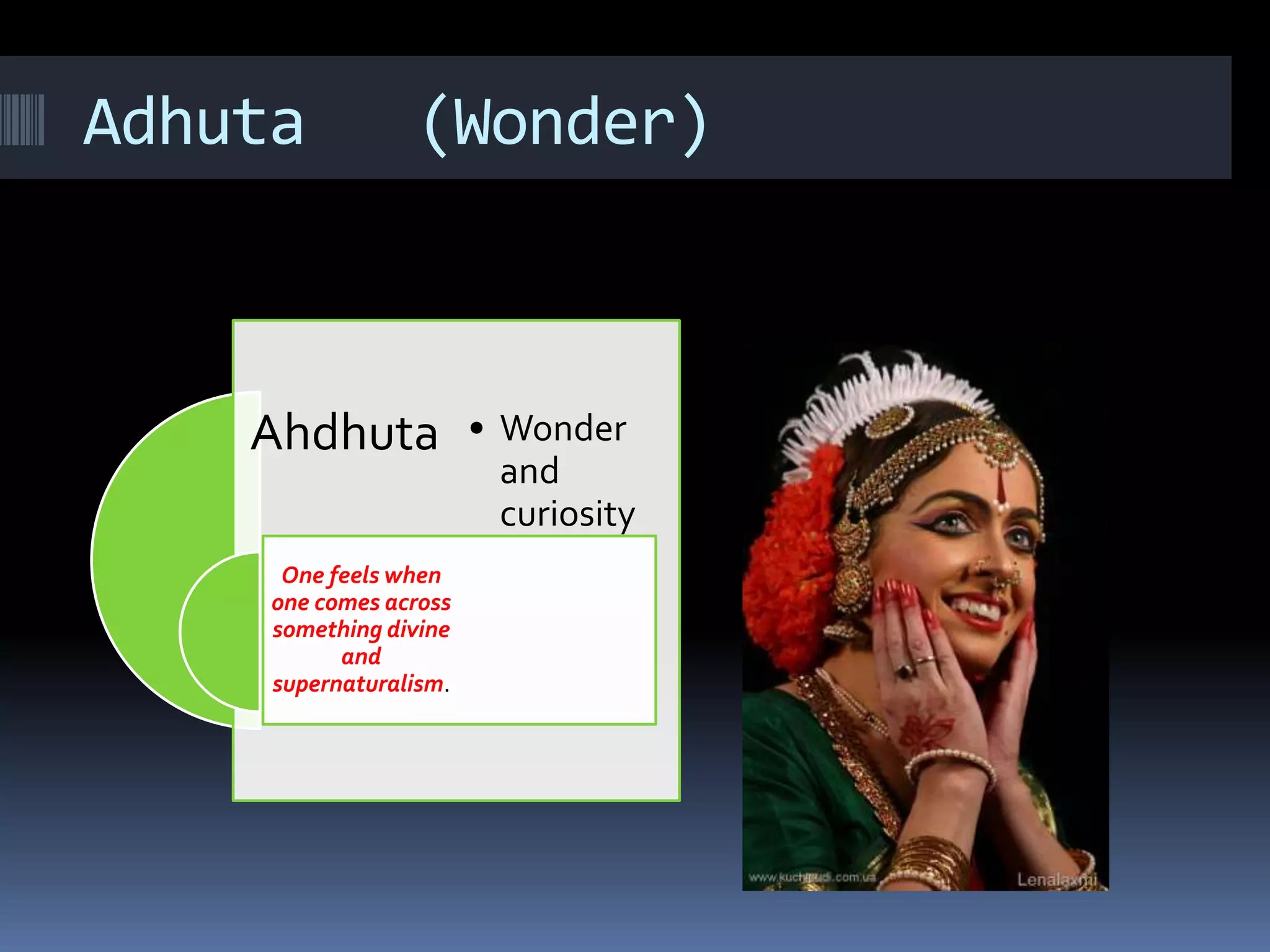

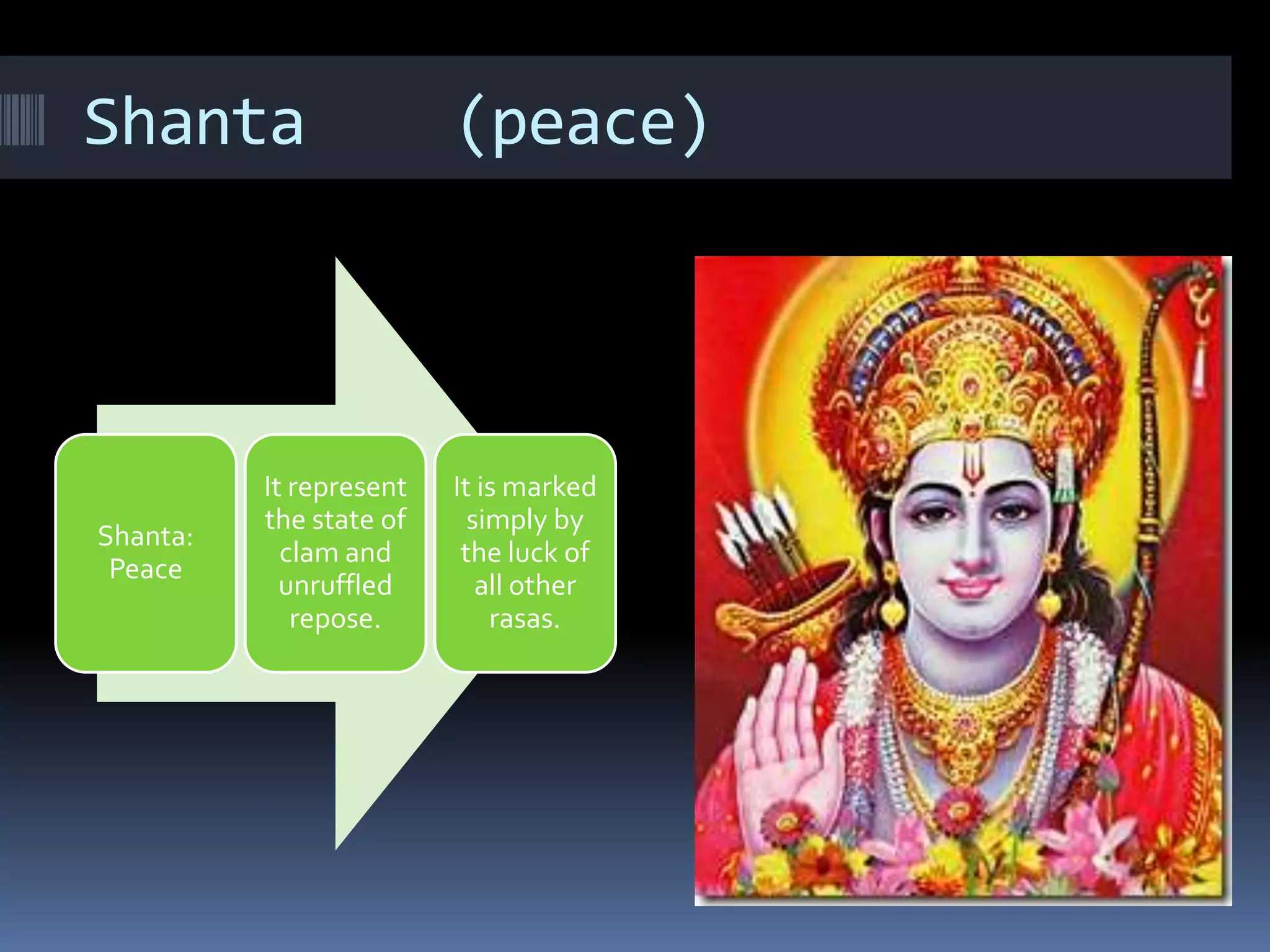


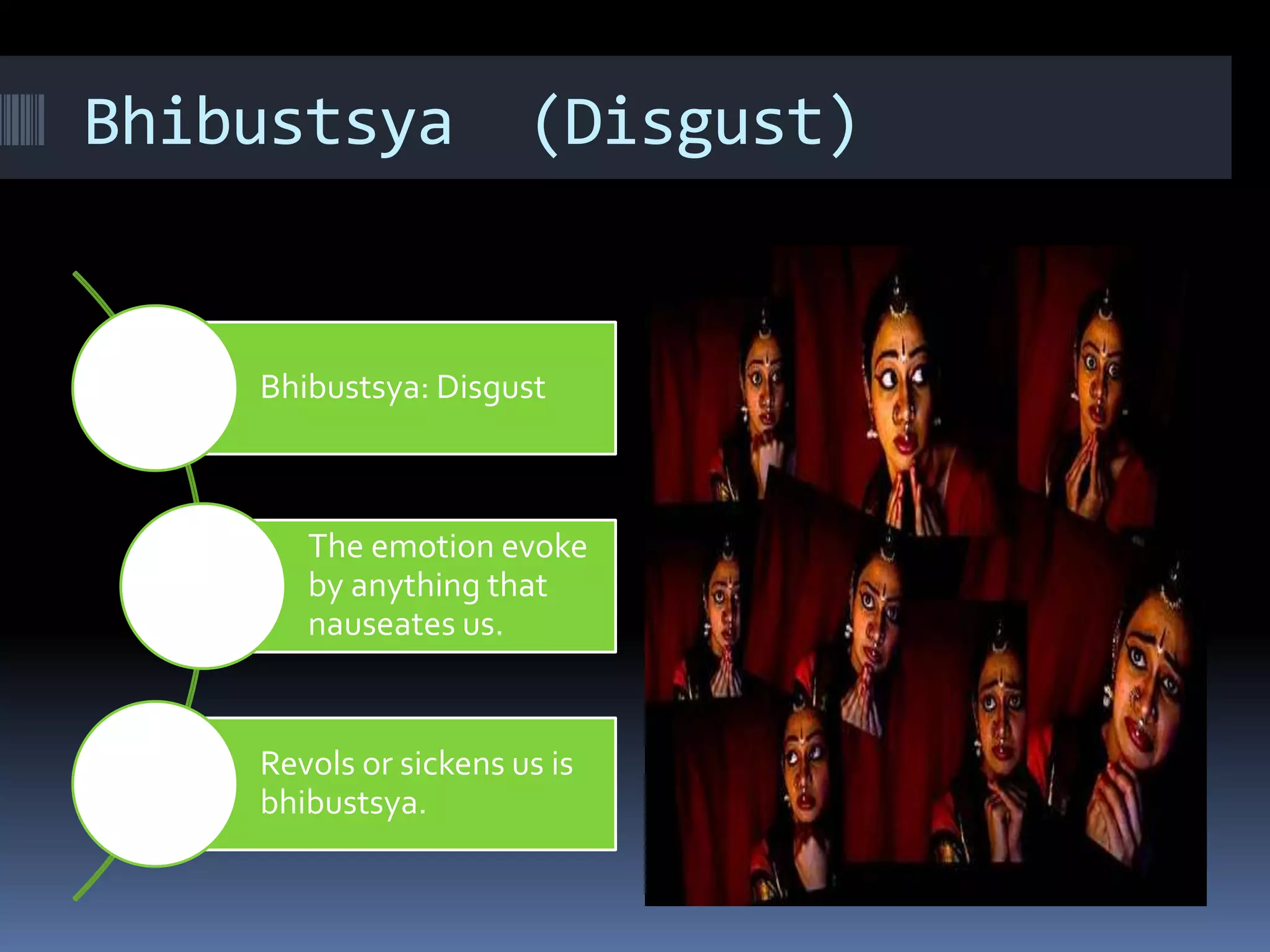



This document is a student paper on the topic of Rasa theory submitted to a professor. It introduces Rasa theory as originating from the Natyashastra text describing 9 basic human emotions or rasas. These are then defined as: love (Shringar), laughter (Hasya), wonder (Adhuta), heroic (Veera), peace (Shanta), grief (Karuna), horror (Bhayank), disgust (Bhibastsya), and bravery (Shorya). Each rasa is then briefly described in terms of the emotion it represents.













