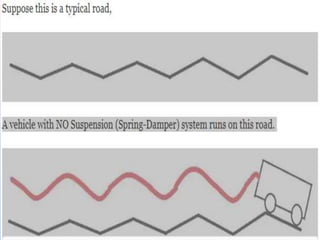
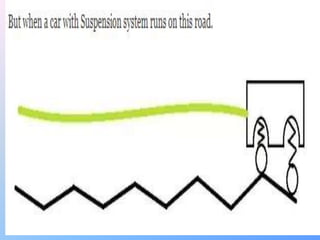
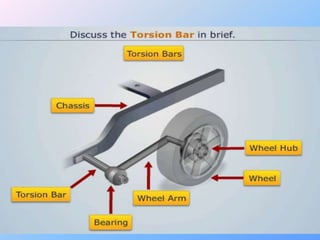
The document discusses suspension systems and types of springs. It defines suspension as the system connecting a vehicle to its wheels that allows motion over irregular road surfaces. The main parts of a suspension system are identified as wheels, springs/dampers, shock absorbers, linkages, and bushings. Suspension functions to absorb shocks and maintain stability during pitching and rolling. The types of springs discussed are coil springs, leaf springs, air springs, and torsion bars. Coil springs store more energy per unit volume than leaf springs and are used in independent suspensions. Leaf springs provide lateral axle location but are heavy and prone to weakening over time.