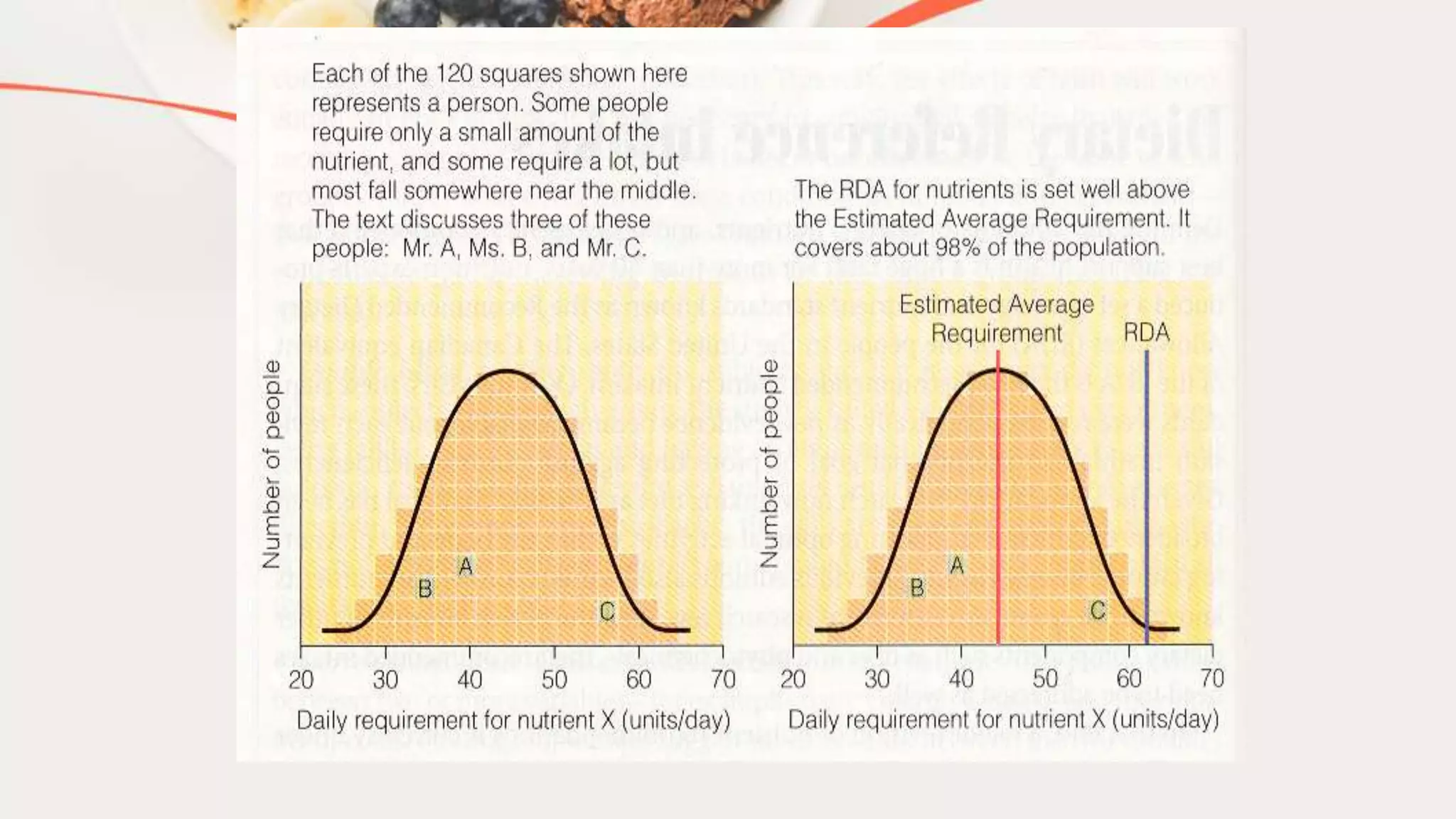
This document discusses Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs), which are nutrient-based reference values used to assess dietary needs. DRIs include the Estimated Average Requirement, Recommended Dietary Allowance, Adequate Intake, Tolerable Upper Intake Level, and Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges. The Recommended Dietary Allowance is set at the EAR plus two standard deviations to cover 98% of the population's needs. Examples of vitamin C and calcium DRIs are provided to illustrate how the values are determined based on scientific studies and potential for toxicity.