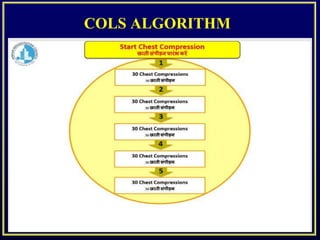
The document discusses cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and basic life support (BLS). It notes that cardiac arrest and respiratory arrest are common causes of death. CPR combines rescue breathing and chest compressions to provide oxygen to the lungs and circulate oxygen-rich blood until heartbeat and breathing can be restored. BLS can be performed by trained laypeople through techniques like hands-only CPR to help cardiac arrest victims until more advanced medical support arrives. The document emphasizes the importance of immediate intervention to improve survival rates for cardiac arrest and other emergencies.