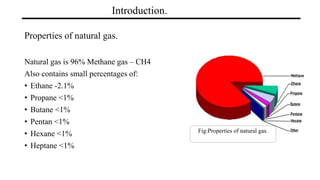
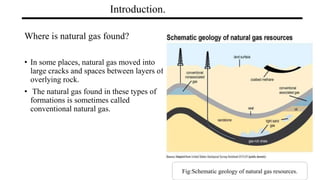
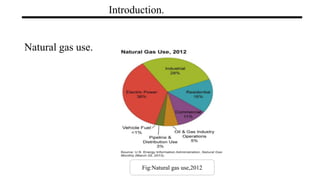
Natural Gas
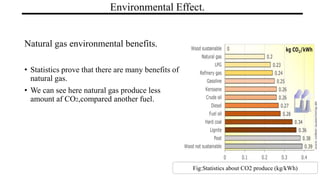
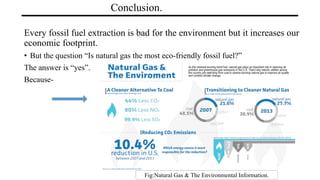
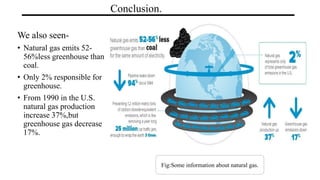
Natural gas is composed primarily of methane found in large underground deposits. It is used widely as an energy source. Historically, natural gas was first discovered being released from lakes and used in lighting in the early 1800s. It is extracted through drilling operations and transported through pipelines. Major applications include electricity generation, industrial processes like manufacturing and chemicals, residential heating and cooking, and commercial uses. While natural gas produces fewer emissions than coal or oil, drilling and transportation can impact the environment if not properly regulated. Overall, natural gas has significant economic benefits and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than other fossil fuels.