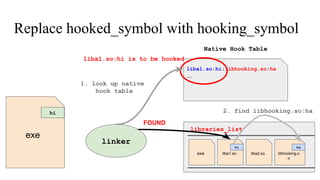
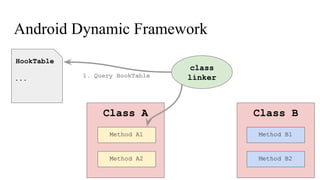
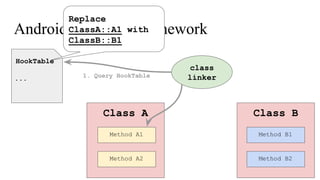
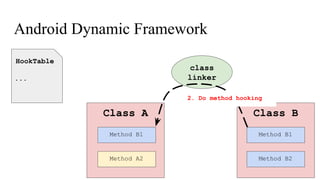
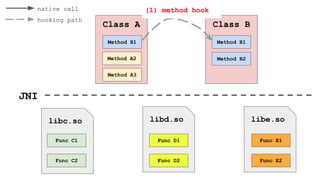
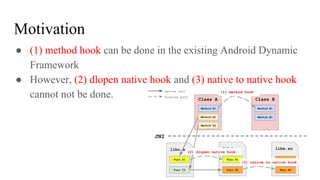
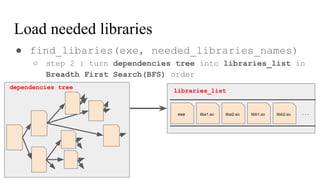
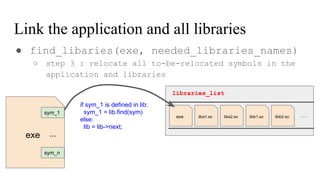
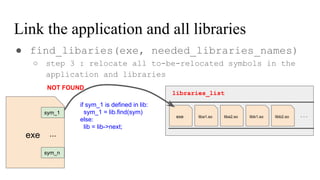
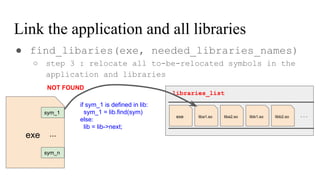
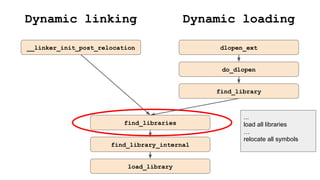
The document discusses the implementation of a native hook mechanism in the Android dynamic framework, specifically within the Bionic linker. This mechanism allows for dynamic replacement of Java methods and enhances the framework's capabilities, enabling both method hooking and native library loading without needing to modify APKs. The paper outlines the technical details of the linking and loading processes, applications, and potential future work in this area.




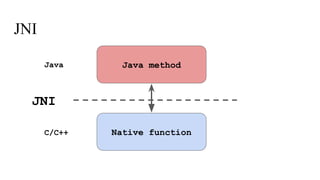
![Java calls native
class HelloWorld {
private native void print(); // print() is native function
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloWorld().print();
}
static {
System.loadLibrary("hello"); // This loads libhello.so
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nativehookmechanisminandroidbioniclinker-160804095317/85/Native-hook-mechanism-in-Android-Bionic-linker-6-320.jpg)









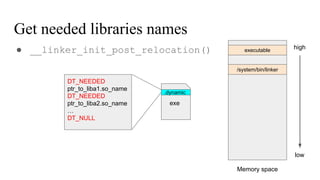
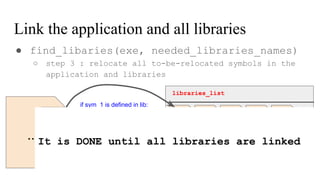
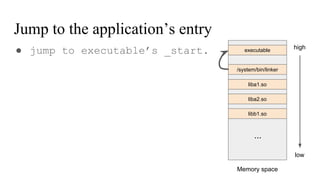
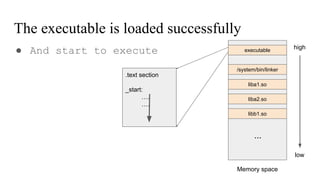
![Get needed libraries names
● __linker_init_post_relocation()
/system/bin/linker
high
low
Memory space
executable
exe
DT_NEEDED
ptr_to_liba1.so_name
DT_NEEDED
ptr_to_liba2.so_name
…
DT_NULL
.dynamic
char needed_libraries_names[] = {
“liba1.so”,
“liba2.so”
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nativehookmechanisminandroidbioniclinker-160804095317/85/Native-hook-mechanism-in-Android-Bionic-linker-31-320.jpg)



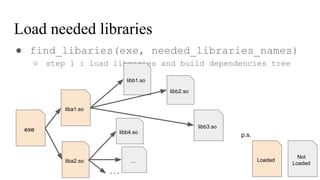
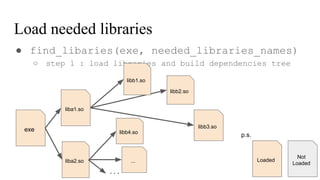
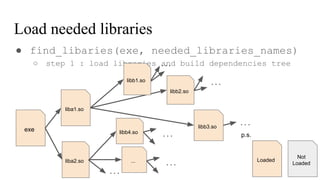

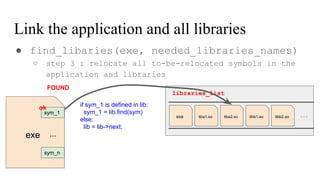
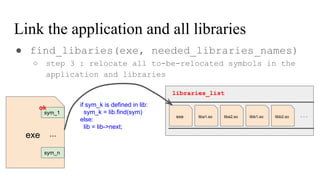

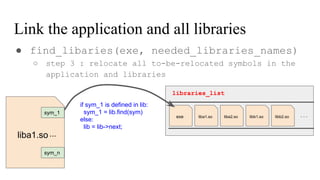
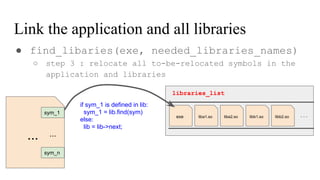



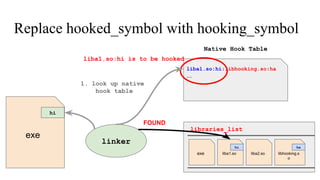
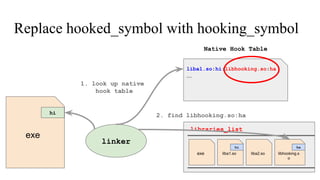
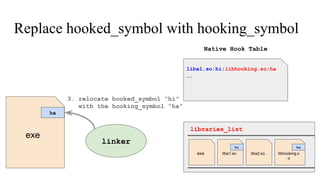


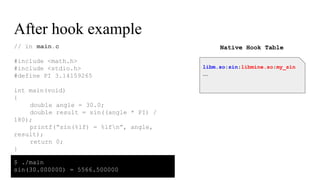
![// in libmine.so
#include “native_hook.h”
double my_sin(double x)
{
char hooked_lib[] = "/system/lib/libm.so";
char hooked_symbol[] = "sin";
double (*hooked_sin)(double) = find_lib_symbol(hooked_lib, hooked_symbol);
/*
before hook : you can do something before calling hooked_func
*/
double result = hooked_sin(x);
/*
after hook : you can do something after calling hooked_func
*/
result += 5566;
return result;
}
After hook example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nativehookmechanisminandroidbioniclinker-160804095317/85/Native-hook-mechanism-in-Android-Bionic-linker-68-320.jpg)
![double my_sin(double x)
{
char hooked_lib[] = "/system/lib/libm.so";
char hooked_symbol[] = "sin";
static void* cache_ptr = NULL;
double (*hooked_sin)(double) = NULL;
if (cache_ptr) {
hooked_sin = cache_ptr;
} else {
hooked_sin = find_lib_symbol(hooked_lib, hooked_symbol);
}
if (hooked_sin) {
cache_ptr = (void*)hooked_sin;
}
double result = hooked_sin(x);
result += 5566;
return result;
}
Before/After hook with cache](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nativehookmechanisminandroidbioniclinker-160804095317/85/Native-hook-mechanism-in-Android-Bionic-linker-70-320.jpg)
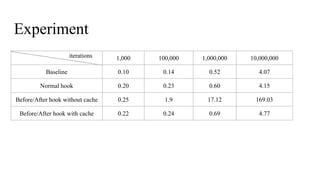
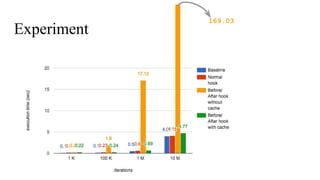

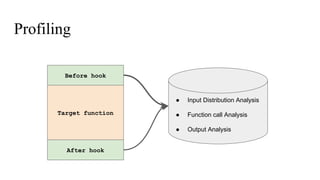

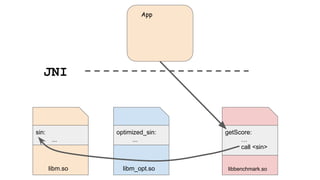








![void* find_lib_symbol(char* lib_name, char* symbol)
{
// Using dl_iterate_phdr() to get the symbol’s address
// in the loaded library whose name is lib_name.
static void* unordered_map<std::string, void*> cache = nullptr;
std::string lib_symbol = std::string(lib_name) + symbol;
if (cache) {
unordered_map<std::string, void*>::iterator it = cache.find(lib_symbol);
if (it != cache.end()) {
return it->second;
}
}
…
// find ptr_to_symbol
if (ptr_to_symbol) {
cache[lib_symbol] = ptr_to_symbol;
}
return ptr_to_symbol;
}
Before/After hook with cache in find_lib_symbol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nativehookmechanisminandroidbioniclinker-160804095317/85/Native-hook-mechanism-in-Android-Bionic-linker-89-320.jpg)