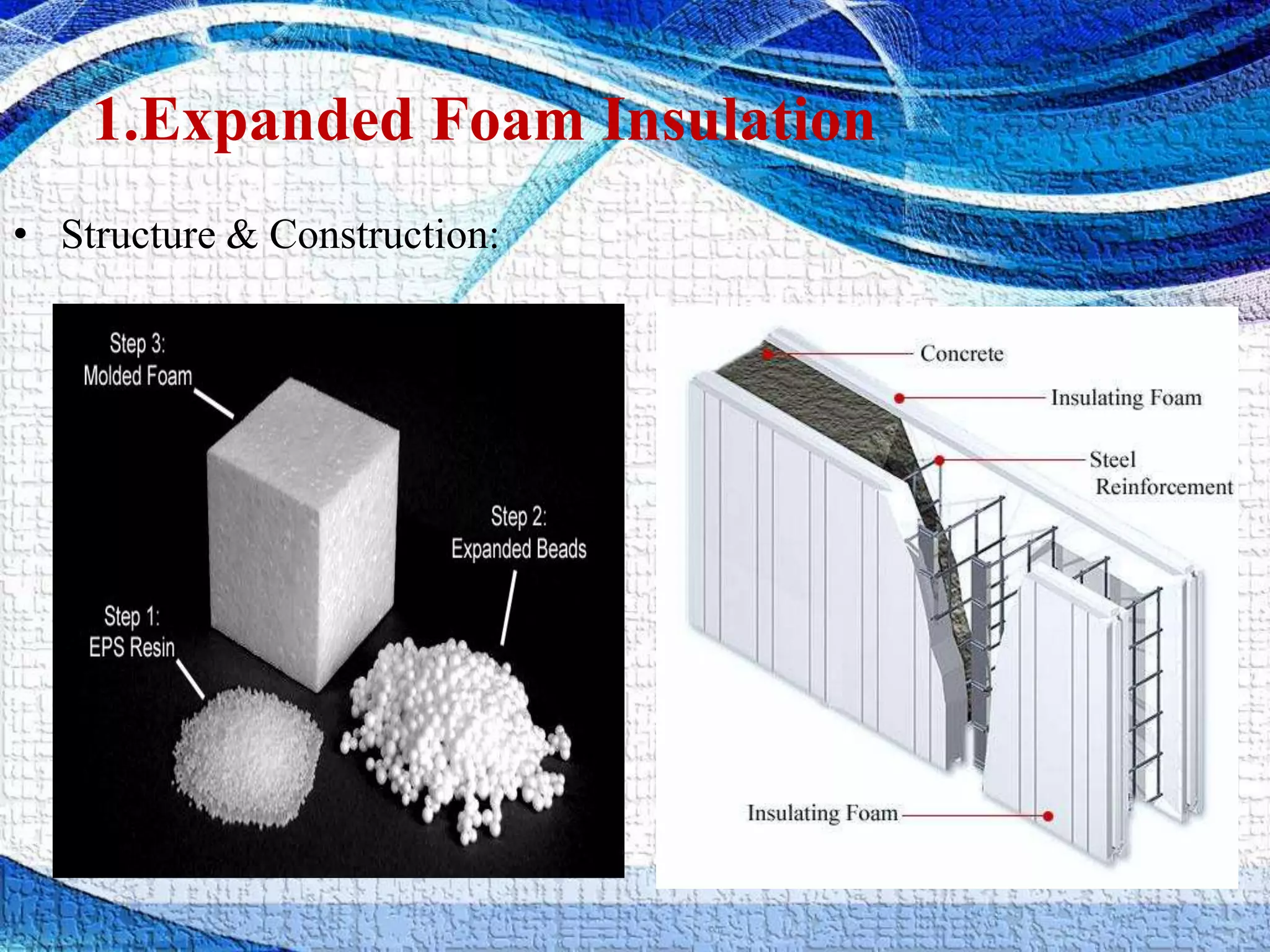
Cryogenic insulations are needed to minimize heat transfer into storage tanks and transfer lines for cryogenic liquids. There are several types of insulation classified based on cost, weight, ease of application, and thermal conductivity. Expanded foams, gas-filled powders, and fiber materials provide insulation through a cellular or porous structure that reduces conduction and convection. Vacuum, evacuated, and opacified powder insulations further reduce conduction and radiation by removing gases. Multilayer insulation uses alternating conductive and non-conductive layers under vacuum to maximize reflection of radiation for optimal heat transfer prevention. The type used depends on the insulation needs and limitations of the specific cryogenic system.