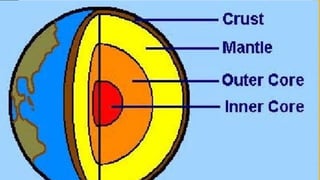
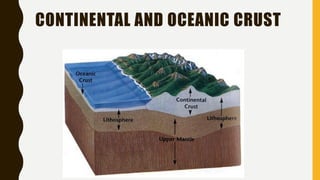
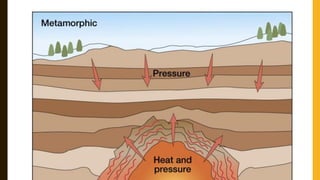
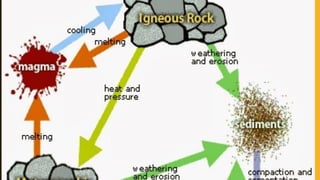
The document discusses the layers of the Earth. It states that the Earth has an outer crust made of lighter materials like silica and alumina. Below the crust is the mantle, which makes up 84% of the Earth's volume and is composed of molten rock. The innermost layer is the core, which is made of iron and nickel and is the hottest part of Earth.