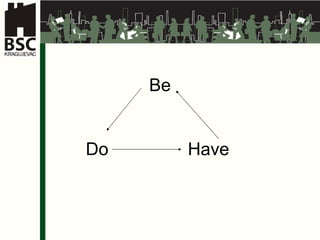
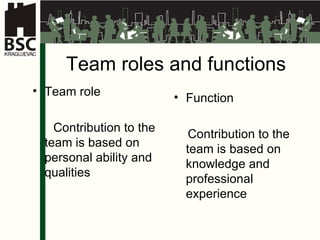
This document provides an overview of various management skills including entrepreneurship, leadership, motivation, conflict management, presentation skills, and team building. It discusses how managers can develop these skills and addresses challenges such as demotivators, goal setting, and strategy development. Case studies are presented on production planning and tourism strategy to demonstrate teamwork applications.