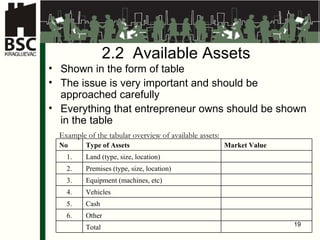
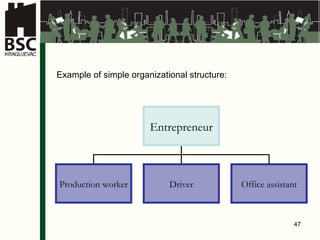
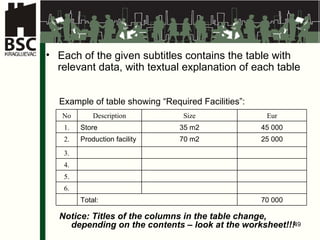
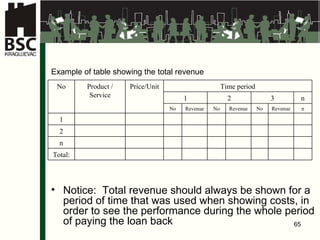
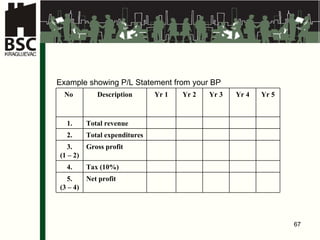
This document provides an agenda and overview for a business planning training module. The schedule includes introductions, presentations on business plan structure and idea generation, group worksheets and daily presentations. The trainer's background is also outlined. Key topics to be covered are choosing a business idea, defining a business plan, market analysis, organizing a new business, and financial analysis. Participants will work individually and in groups to develop elements of a business plan over multiple days.