Embed presentation
Downloaded 99 times





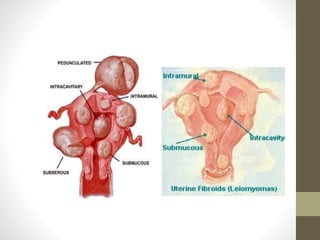
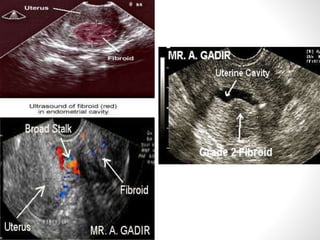
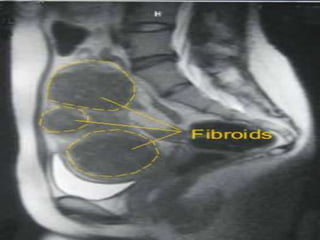







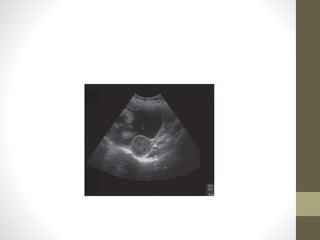


Fibroids (leiomyomas) are benign smooth muscle cell tumors of the uterus that are commonly found in women. They vary in location within the uterus and can cause symptoms like bleeding, infertility, pain, and abdominal enlargement. Fibroids are typically diagnosed through ultrasound, hysteroscopy, or other imaging tests. Treatment options depend on a woman's age, parity, number of fibroids, and symptoms, and may include medication, myomectomy, hysterectomy, or uterine artery embolization. Fibroids can complicate pregnancy by increasing risks of abortion, preterm labor, pain, and cesarean section.


















