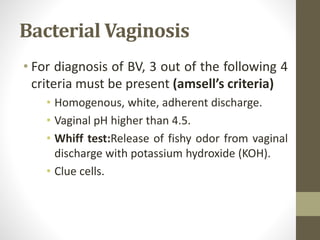
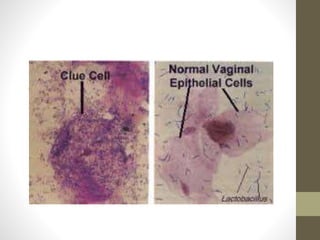
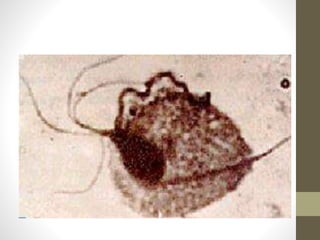
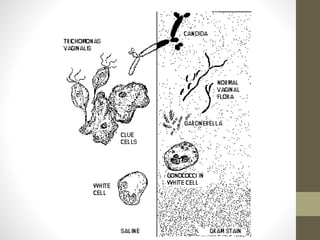
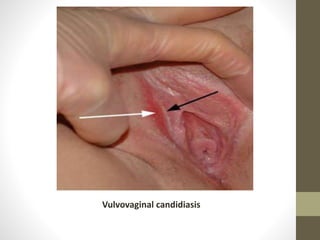
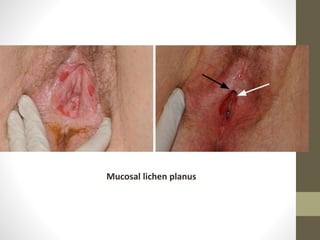
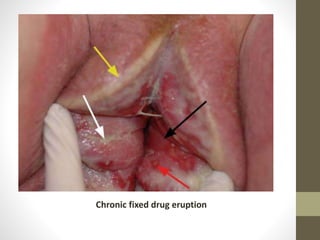
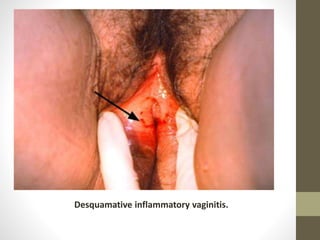
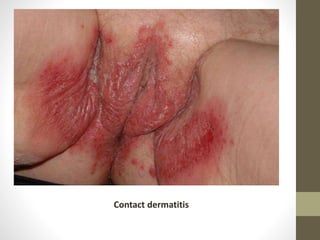
The document discusses various types of vaginitis, including bacterial vaginosis, vaginal candidiasis, and trichomoniasis, detailing their causes, symptoms, and treatments. It highlights the prevalence of these infections and provides diagnostic criteria and recommended therapies for each condition. Persistent vaginitis is defined as recurring symptoms, with various common and uncommon causes identified.