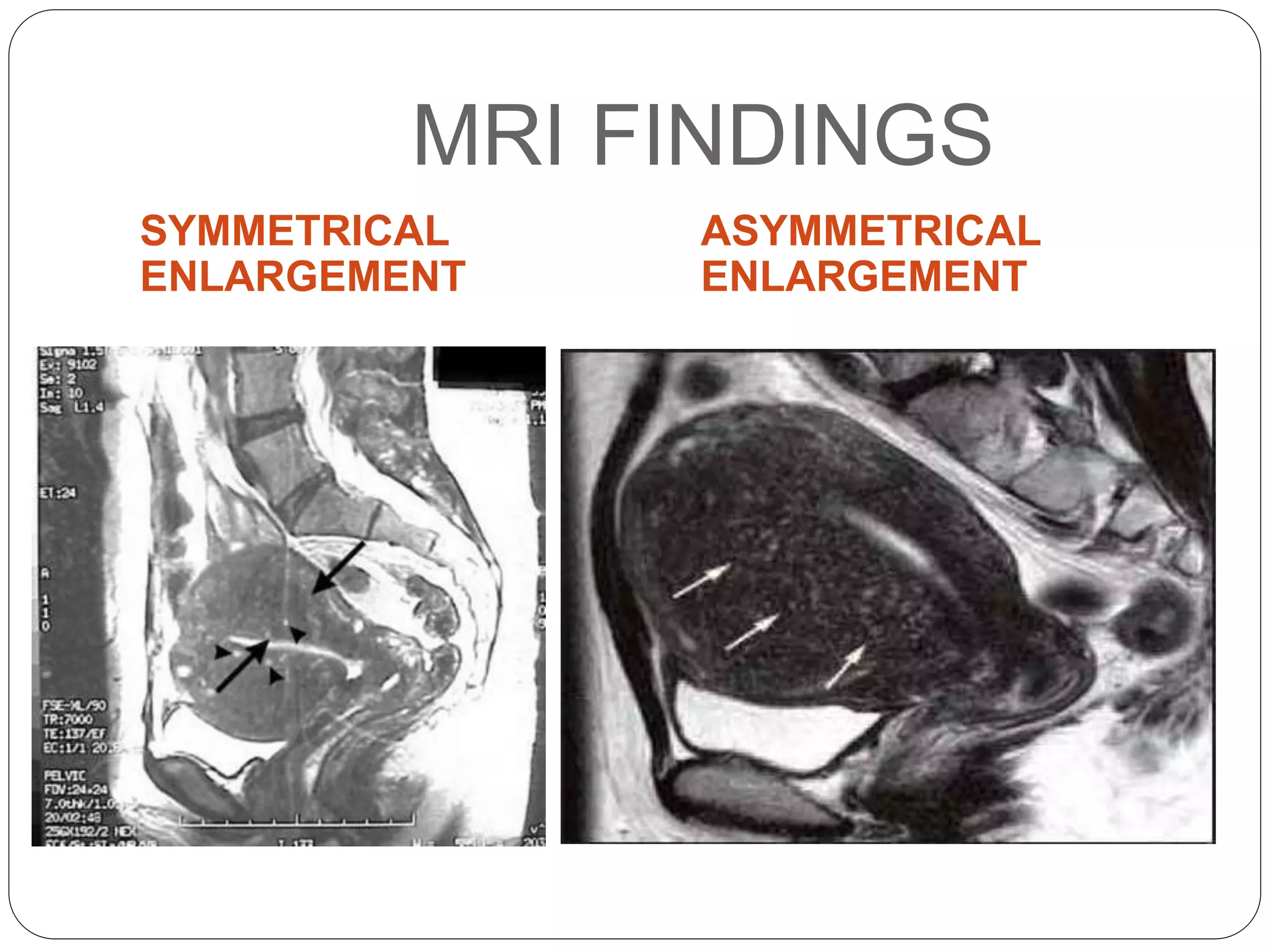
Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial islands within the uterine wall, typically affecting women over 40, though younger women can also be affected. Clinical features include menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea, and pelvic discomfort, with MRI being the preferred diagnostic tool due to its superior accuracy. Management options vary based on age and patient interest, ranging from hysterectomy to medical treatments like NSAIDs and hormonal therapies.