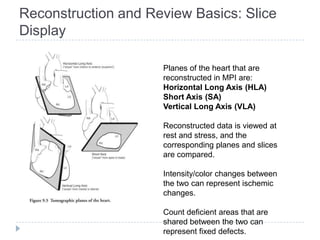
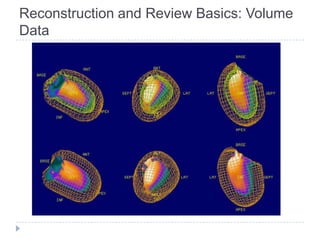
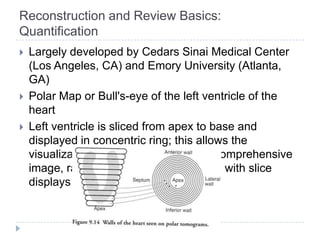
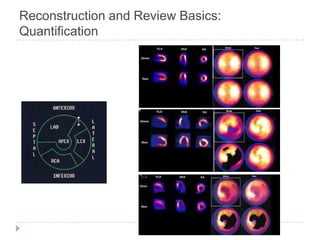
This document discusses myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI), a nuclear imaging technique used to detect coronary artery disease. It describes the indications for MPI, including detecting CAD, assessing stenosis, evaluating prognosis, and assessing medical therapy. Risk factors for CAD like smoking, obesity, and high cholesterol are outlined. The document details how CAD causes reduced blood flow and describes associated symptoms. Treatment options for CAD include drugs, angioplasty, stents, and bypass surgery. Imaging protocols and reconstruction techniques for MPI are also summarized.