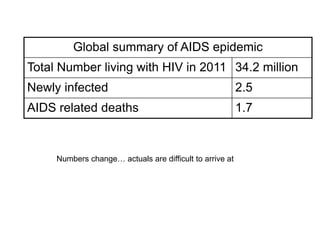
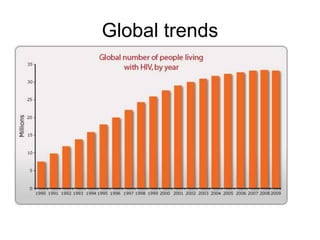
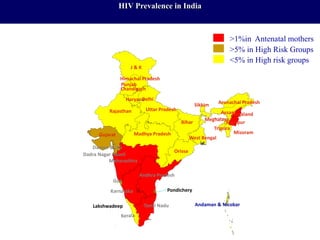
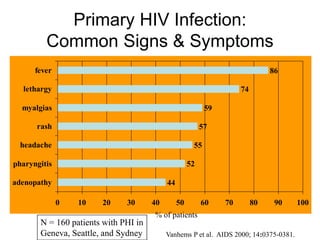
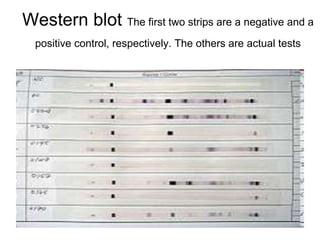
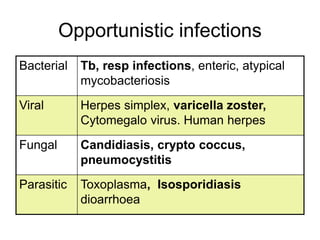
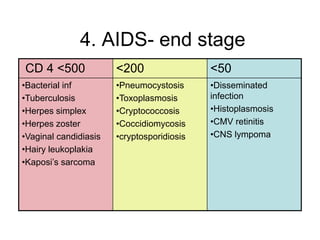
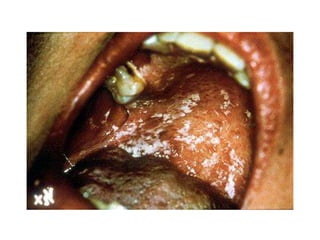
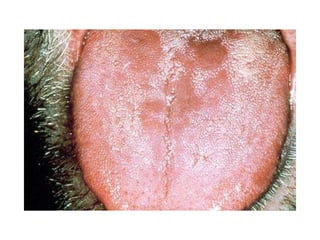
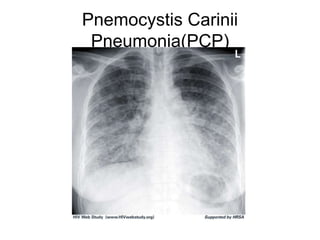
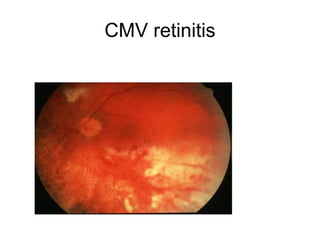
This document provides an overview of HIV/AIDS. It discusses how HIV is a retrovirus that infects and destroys CD4 cells, leading to AIDS if untreated. HIV is transmitted via bodily fluids and causes a spectrum of infections and illnesses as it progresses. Diagnosis involves antibody tests or viral load tests. Treatment involves antiretroviral drugs to suppress HIV and prevent opportunistic infections. Prevention strategies include education, safer sex practices, needle exchange programs, and universal precautions. Globally, an estimated 34 million people live with HIV/AIDS.