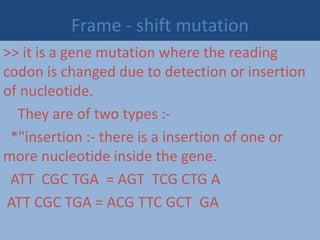
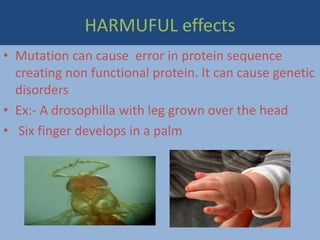
Mutations are heritable changes in genetic material that can be caused spontaneously during DNA replication or induced by environmental factors like radiation. There are different types of mutations including chromosomal, gene, and frameshift mutations. Frameshift mutations occur due to the insertion or deletion of nucleotides, changing the reading frame. Mutations can have beneficial effects by creating genetic variation and driving evolution, but they can also have harmful effects by causing genetic disorders or nonfunctional proteins.