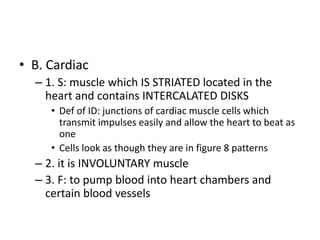
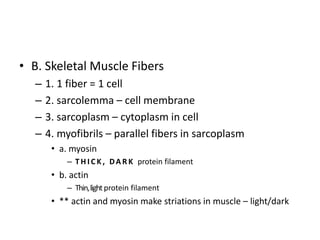
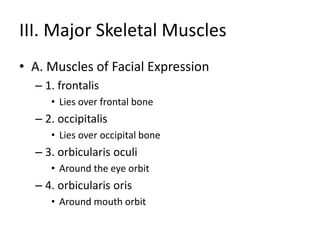
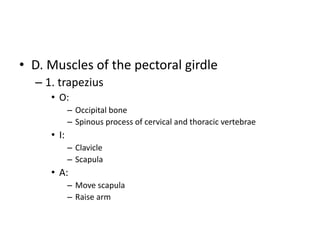
The muscular system contains three main types of muscle: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, attaching to bones to enable movement. It has a layered connective tissue covering and is composed of fibers containing myofibrils of actin and myosin. Contraction occurs when a motor neuron stimulates calcium release, causing myosin bridges to attach to actin and slide the filaments, shortening the muscle. Major skeletal muscles include those of the face, neck, shoulder, arm, abdomen, thigh, leg, foot and toes which work antagonistically or synergistically to enable movement.