Embed presentation



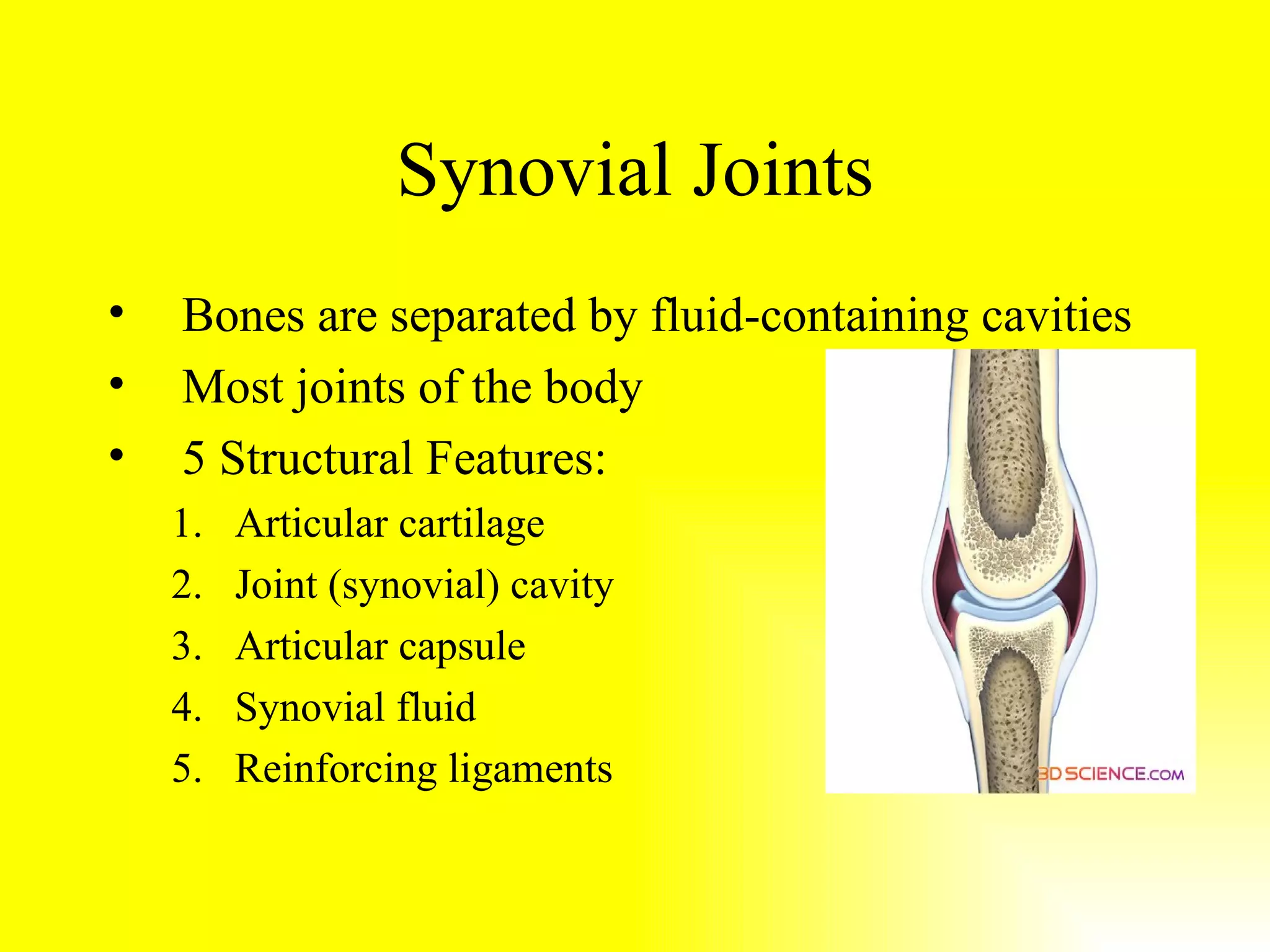












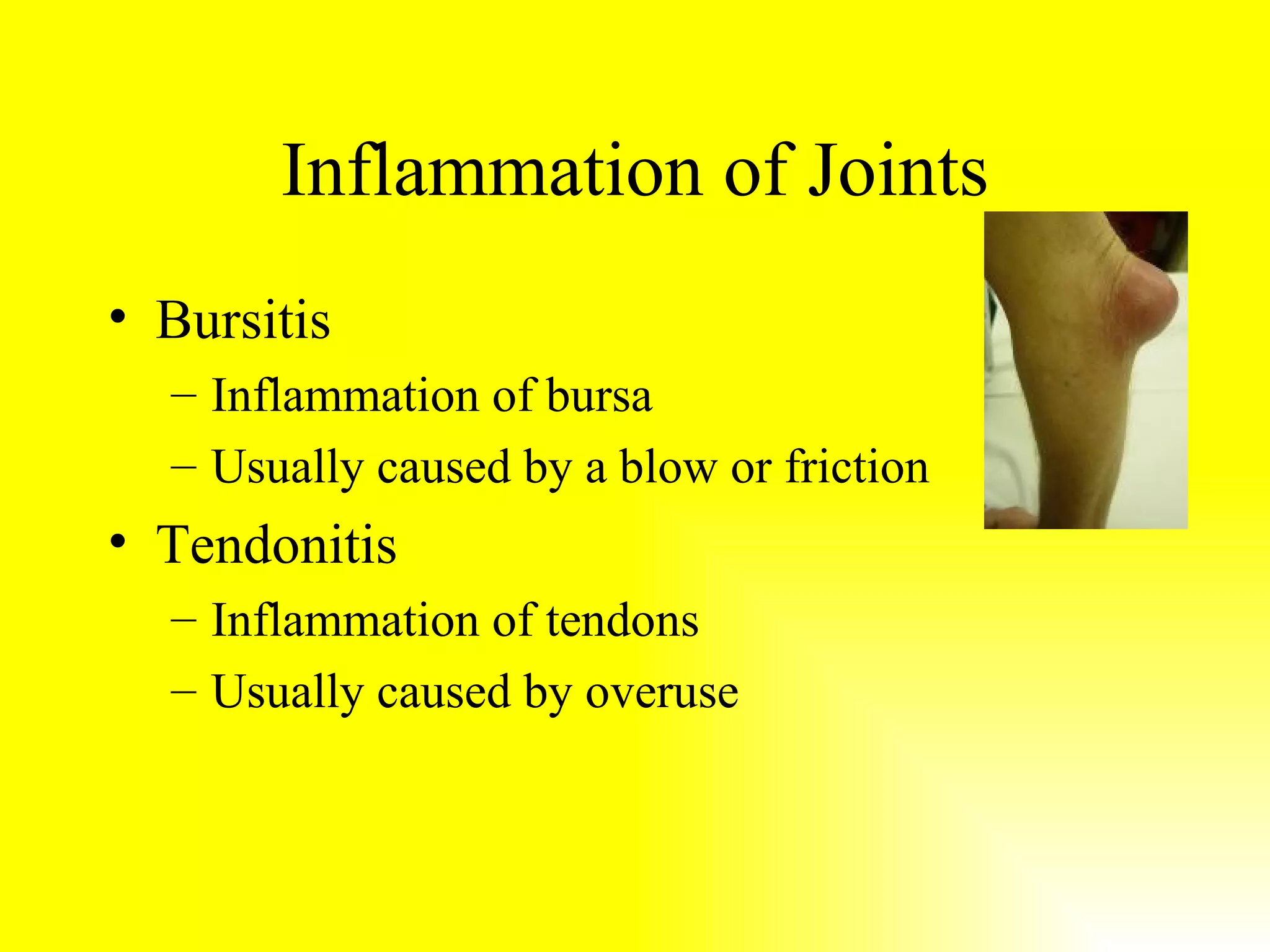



Joints connect bones and allow movement. They are classified structurally as fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial, and functionally as immovable, slight movement, or free movement. Synovial joints have articular cartilage, a joint cavity, a joint capsule, synovial fluid, and ligaments. They allow gliding and angular movements like flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction. Common synovial joints are plane, hinge, pivot, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints. Common joint injuries are sprains and subluxations, while common joint issues are bursitis, tendonitis, and the degenerative diseases osteoarthritis and rheumatoid



















