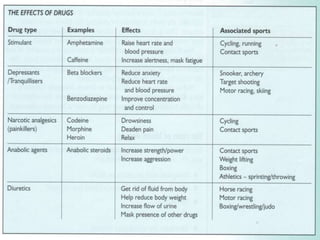
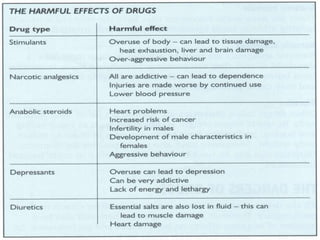
This document discusses performance enhancing drugs in sports. It defines drugs as substances that can produce physical or psychological effects when taken. It then discusses why athletes may be tempted to take performance enhancing drugs, noting the high stakes of competition and potential financial rewards. The document categorizes performance enhancing drugs into prohibited classes of substances like stimulants, narcotics, anabolic steroids, and diuretics. It also discusses prohibited methods like blood doping. Side effects of various drugs are explained.