Embed presentation
Downloaded 78 times

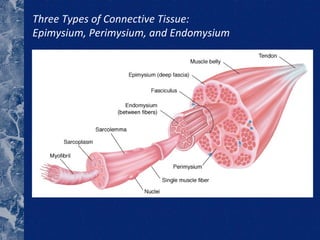
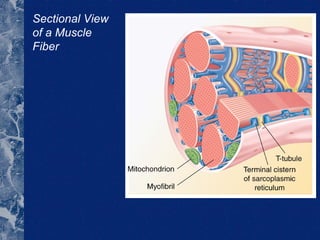
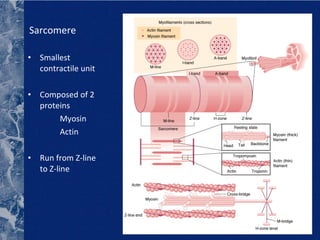
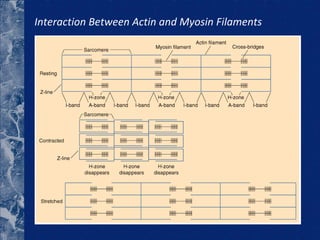


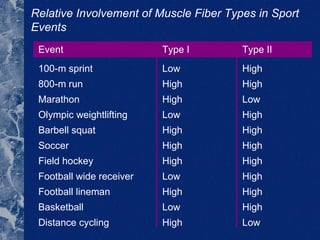

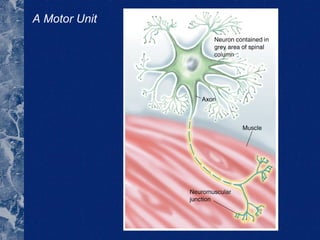
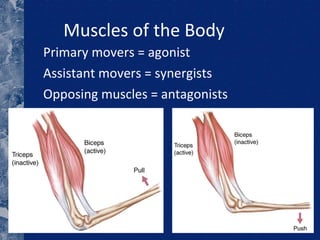

There are three types of connective tissue - epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium - that surround and interconnect muscle fibers. The sarcomere is the smallest contractile unit of a muscle, composed of the proteins actin and myosin. Muscle fibers come in two main types - type I (slow twitch) and type II (fast twitch) - and vary in length, number of nuclei, and ratio between individuals. The type of muscle fibers predominantly used depends on the sport or activity, such as type I fibers for marathon running and type II fibers for sprinting. Motor units are composed of a motor neuron and either type I or type II muscle fibers, and vary in size depending












